This study was performed to evaluate the effect of ethanolic extract of Turkish propolis (EEP) on testicular ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) damage in rats in terms of biochemistry and histopathology, for the first time.
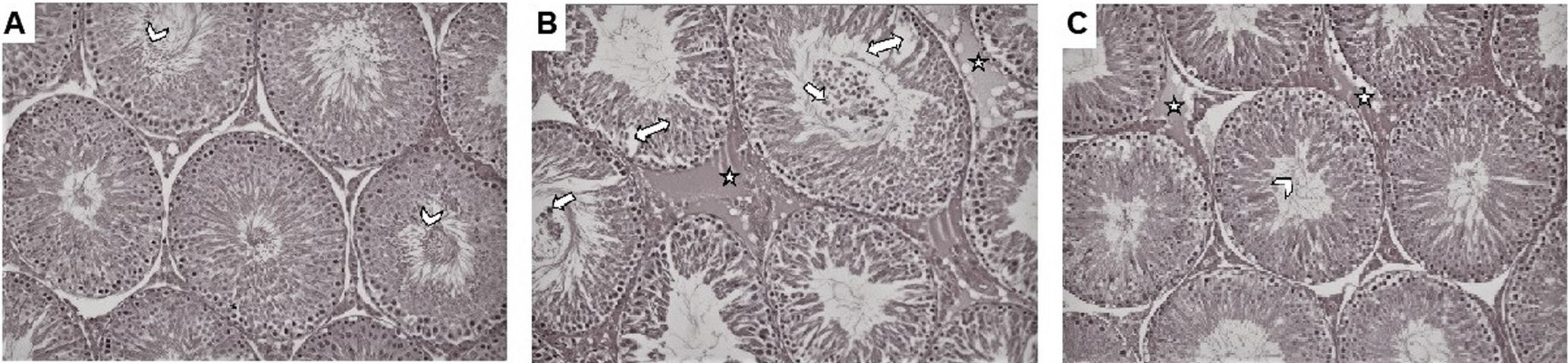
MethodsA total of 18 male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups with six rats in each group: control, torsion/detorsion (T/D), and T/D+EEP (100mg/kg). Testicular torsion was performed by 720° rotating the left testicle in a clockwise direction. The duration of ischemia was 4h and orchiectomy was performed after 2h of detorsion. EEP was applied only once 30min before detorsion. Tissue malondialdehyde (MDA), total oxidant status (TOS) and total antioxidant status (TAS) levels were determined using colorimetric methods. Oxidative stress index (OSI) was calculated by proportioning tissue TOS and TAS values to each other. Tissue glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) levels were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. Johnsen's testicle scoring system was used for histological evaluation.
ResultsIn the T/D group, it was determined that statistically significant decreasing in TAS, GSH, GPx levels and Johnsen score, and increasing in TOS, OSI and MDA levels (p<0.05) compared with control group. EEP administration statistically significantly restored this I/R damage (p<0.05).
ConclusionThis is the first study to show that propolis prevent I/R-induced testicular damage through its antioxidant activity. More comprehensive studies are needed to see the underlying mechanisms.
Este estudio se realizó para evaluar por primera vez el efecto del extracto etanólico de propóleo turco (EEP) sobre el daño por isquemia/reperfusión (I/R) testicular en ratas en términos de bioquímica e histopatología.
MétodosUn total de 18 ratas macho Sprague-Dawley se dividieron en 3 grupos con 6 ratas en cada grupo: control, torsión/detorsión (T/D) y T/D+EEP (100mg/kg). La torsión testicular se realizó con una rotación de 720° del testículo izquierdo en el sentido de las agujas del reloj. La duración de la isquemia fue de 4h y la orquiectomía se realizó a las 2h de la detorsión. EEP se aplicó solo una vez 30min antes de la detorsión. Los niveles de malondialdehído tisular (MDA), estado oxidante total (TOS) y estado antioxidante total (TAS) se determinaron mediante métodos colorimétricos. El índice de estrés oxidativo (OSI) se calculó proporcionando los valores de TOS y TAS del tejido entre sí. Los niveles de glutatión tisular (GSH) y glutatión peroxidasa (GPx) se determinaron utilizando kits de ensayo inmunoabsorbente ligado a enzimas (ELISA). Se utilizó el sistema de puntuación de testículos de Johnsen para la evaluación histológica.
ResultadosEn el grupo T/D, se determina una disminución estadísticamente significativa en los niveles de TAS, GSH, GPx y puntuación de Johnsen y un aumento en los niveles de TOS, OSI y MDA (p<0,05) en comparación con el grupo control. La administración de EEP restauró de forma estadísticamente significativa este daño I/R (p<0,05).
ConclusiónEste es el primer estudio que demuestra que el propóleo previene el daño testicular inducido por I/R a través de su actividad antioxidante. Se necesitan estudios más completos para ver los mecanismos subyacentes.