ED and PE are the most common male sexual dysfunctions, although they remain underdiagnosed and undertreated.
AimTo ascertain how a group of Spanish urologists currently address ED and PE.
MethodsDescriptive study based on a self-designed questionnaire about the clinical practice in ED and PE upon diagnosis, treatment and monitoring, patient–physician relationship and the role of the patient's partner.
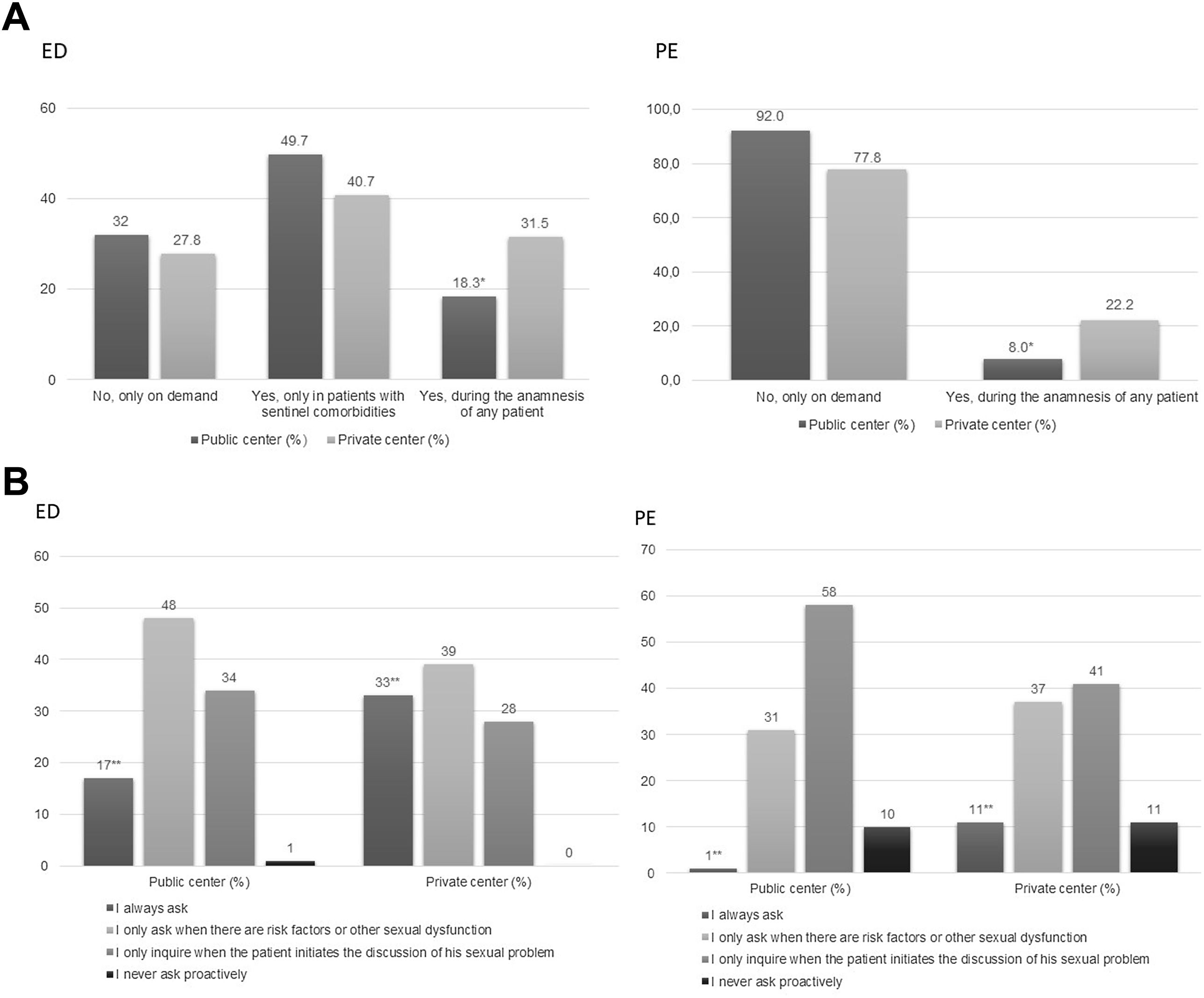
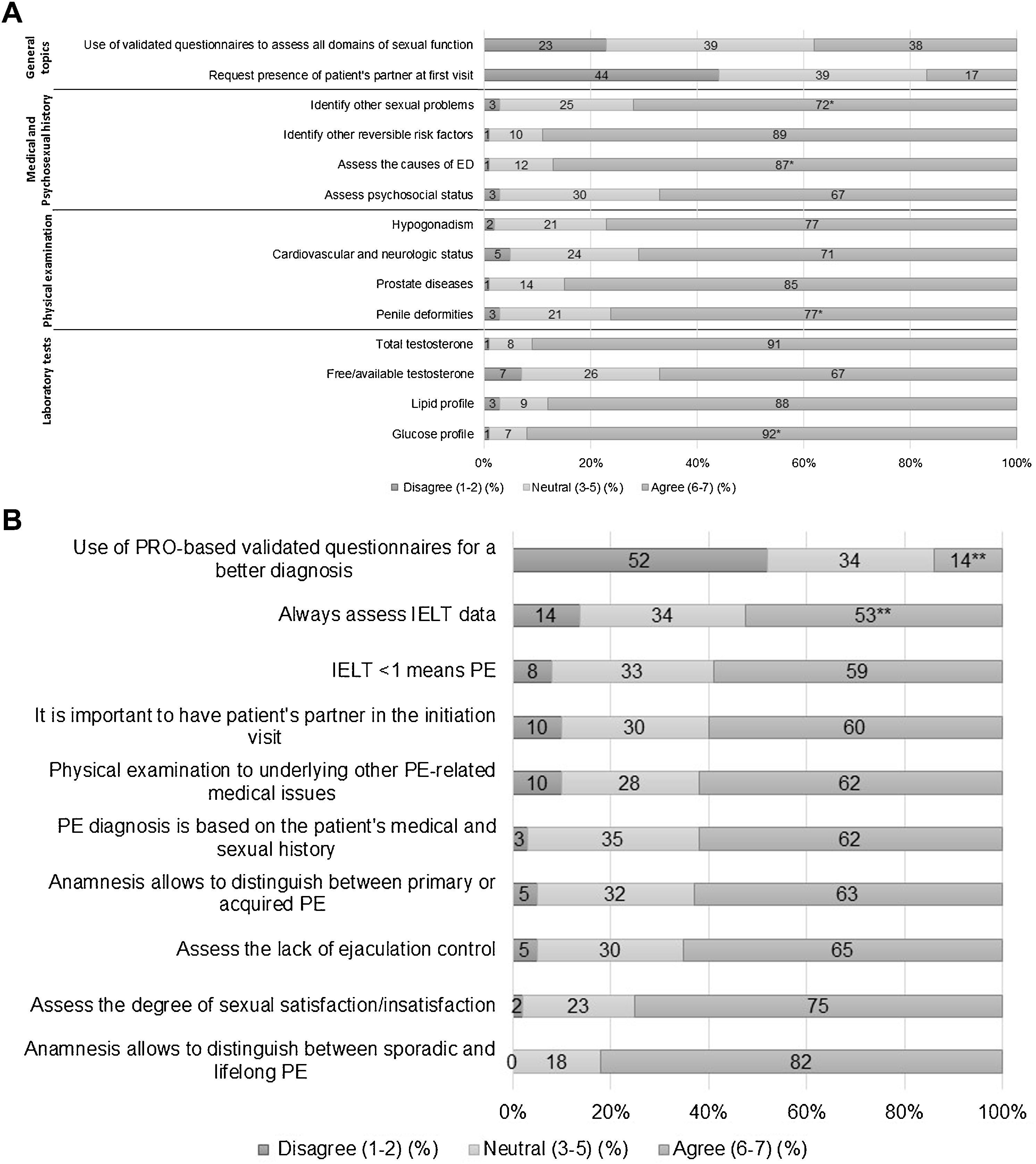
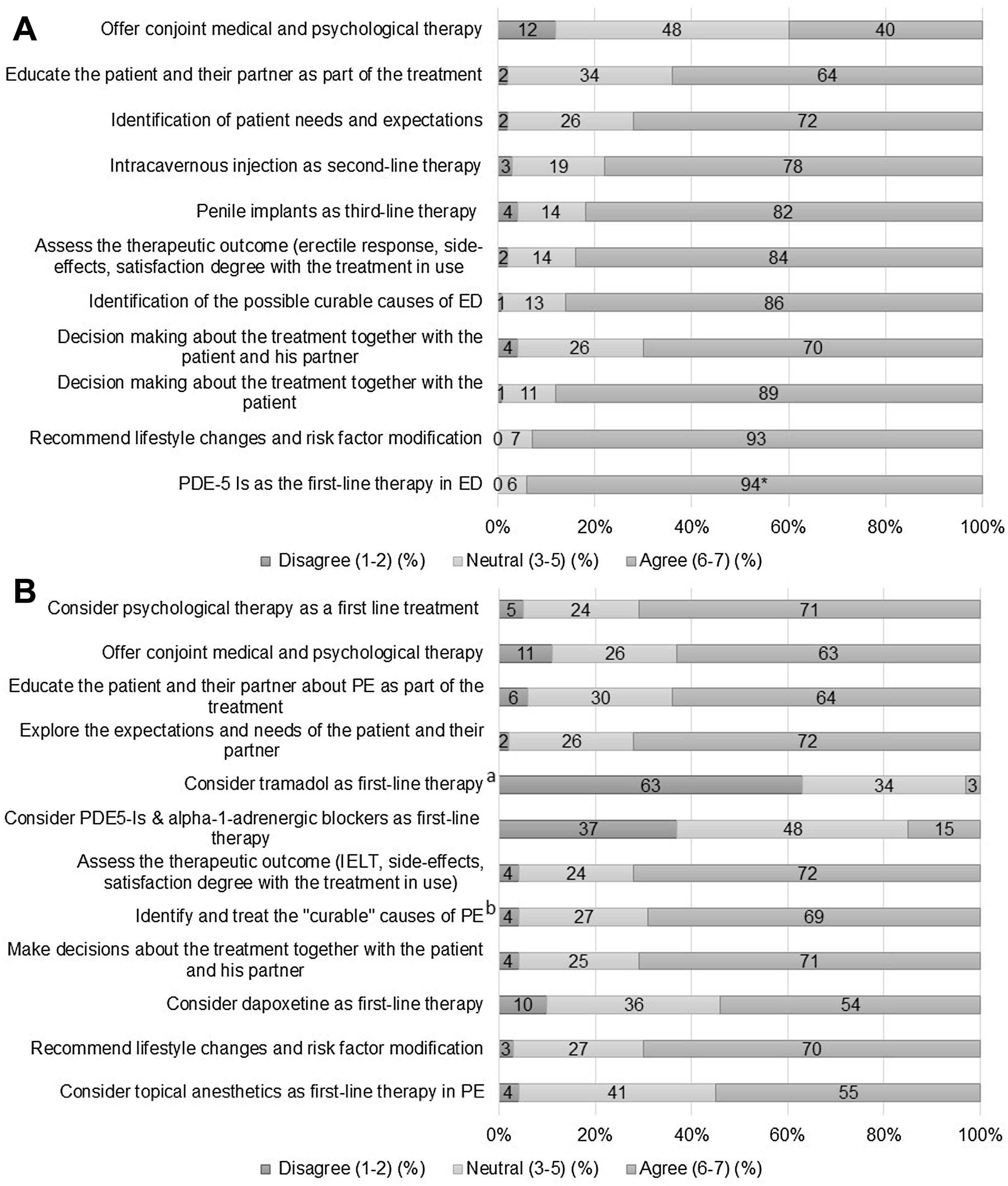
ResultsThe survey was completed by 188 experienced urologists. Most patients went to the urologist's office without a previous diagnosis (92% of the urologists found <10 PE-diagnosed patients in public settings). The diagnosis of ED and/or PE was mainly carried out by the current urologist and not by another professional, particularly in private centres as opposed to public centres (78.8% vs 57.0% for ED; 82.0% vs 62.6% for PE). Most urologists believed that these disorders are underdiagnosed and deemed them as general health issues. 38% of urologists acknowledged using validated questionnaires to diagnose ED. PE was considered a subjective problem rather than a true disease and the use of PRO-based diagnosis of PE was not generally accepted (14%). Treatment options of both disorders were chosen as expected. Referral to the andrologist is usually scheduled in moderate-to-severe PE or severe ED. The cohort seemed to be mostly neutral (50%–75% for ED and 40%–55% for PE) regarding patient reluctancy to talk about their sexual problem. Patients’ partners play an important role in helping men seeking treatment.
ConclusionUrologists should show more proactivity during anamnesis and routine visits to improve management of ED and PD.
A pesar de que, la DE y la EP son las disfunciones sexuales masculinas más frecuentes, siguen estando infradiagnosticadas e infratratadas.
ObjetivoConocer cómo es el abordaje actual de la DE y la EP, a partir de un grupo de urólogos españoles.
MétodoEstudio descriptivo, mediante un cuestionario predefinido, con relación a la práctica clínica de la DE y la EP, incluyendo su diagnóstico, su tratamiento y su seguimiento, la relación médico-paciente y el papel de la pareja.
ResultadosCiento ochenta y ocho urólogos expertos dieron respuesta al cuestionario predefinido. La mayoría de los pacientes acudieron a la consulta del urólogo sin un diagnóstico previo (el 92% de los urólogos hallaron <10 pacientes diagnosticados de PE en el ámbito público). El diagnóstico de la DE y/o la EP fue realizado mayoritariamente por el urólogo, y no por otro profesional, especialmente en el ámbito privado frente al público (78,8 frente al 57,0% para la DE; 82,0 frente al 62,6% para la EP). La gran mayoría de los urólogos señalaron que ambas disfunciones estaban siendo infradiagnosticadas y, por tanto, las consideraron como un problema de salud general. El 38% de los urólogos indicó utilizar cuestionarios validados para el diagnóstico de la DE. La EP se percibió como un problema subjetivo más que como una verdadera enfermedad, y el uso de PRO en el diagnóstico de la EP no fue generalmente aceptado (14%). La elección de las opciones de tratamiento de ambas disfunciones aconteció según lo esperado. Se consideró la derivación a andrología en los casos de la EP moderada-grave o en los casos de la DE grave. En cuanto a la reticencia de los pacientes a hablar de su problema sexual, la respuesta fue mayoritariamente neutra (50-75% para la DE y 40-55% para la EP). Las parejas de los pacientes desempeñan un papel importante en el momento que estos buscan opciones de tratamiento.
ConclusiónLos urólogos deben mostrar mayor proactividad, durante la anamnesis y las visitas de rutina, para mejorar el manejo de la DE y la EP.