Journal Information
Vol. 48. Issue 1.
Pages 19-26 (January 2006)
Vol. 48. Issue 1.
Pages 19-26 (January 2006)
Calcificaciones intracraneales. Imagen por RM
Intracranial calcifications on MRI
Visits
24006
This item has received
Article information
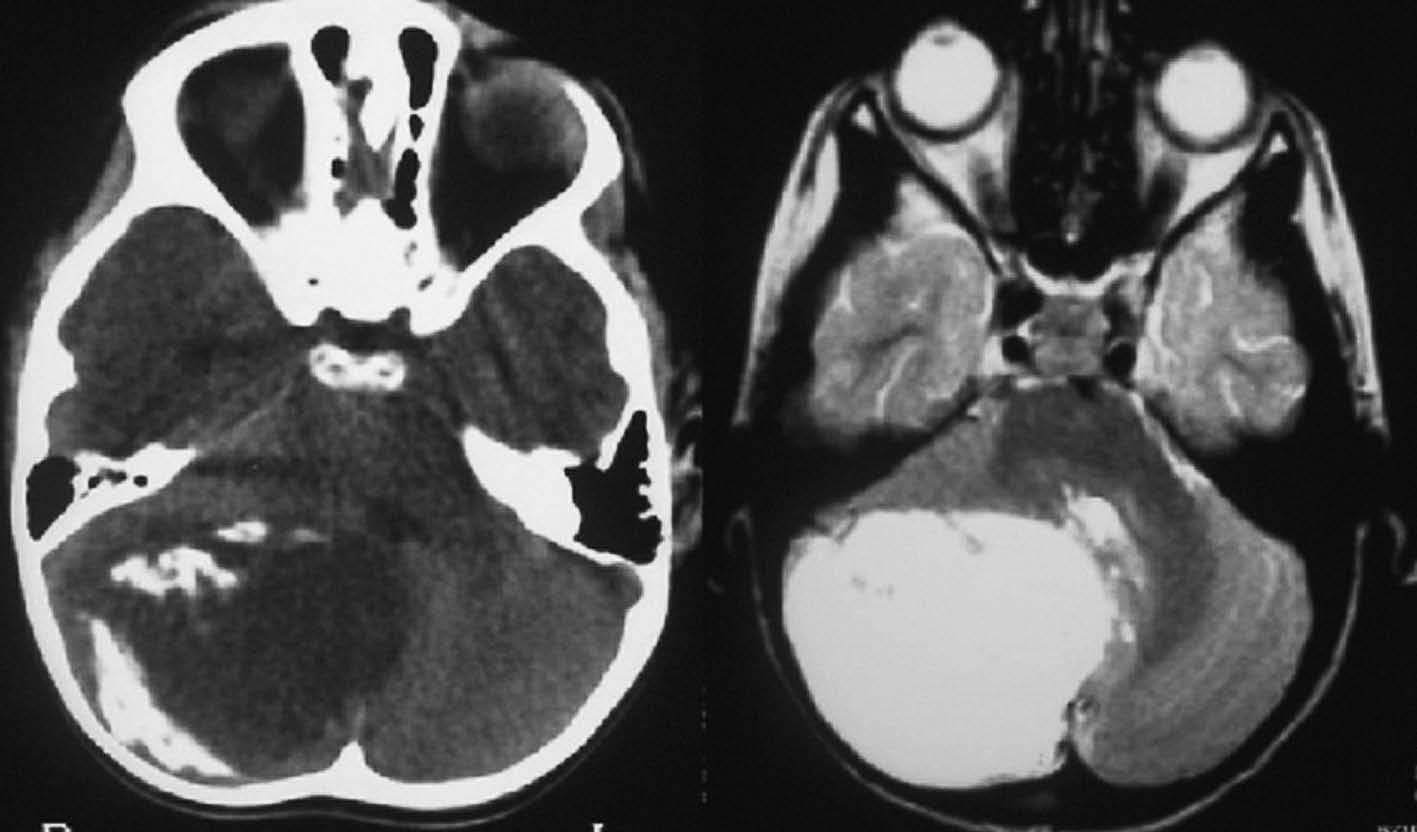
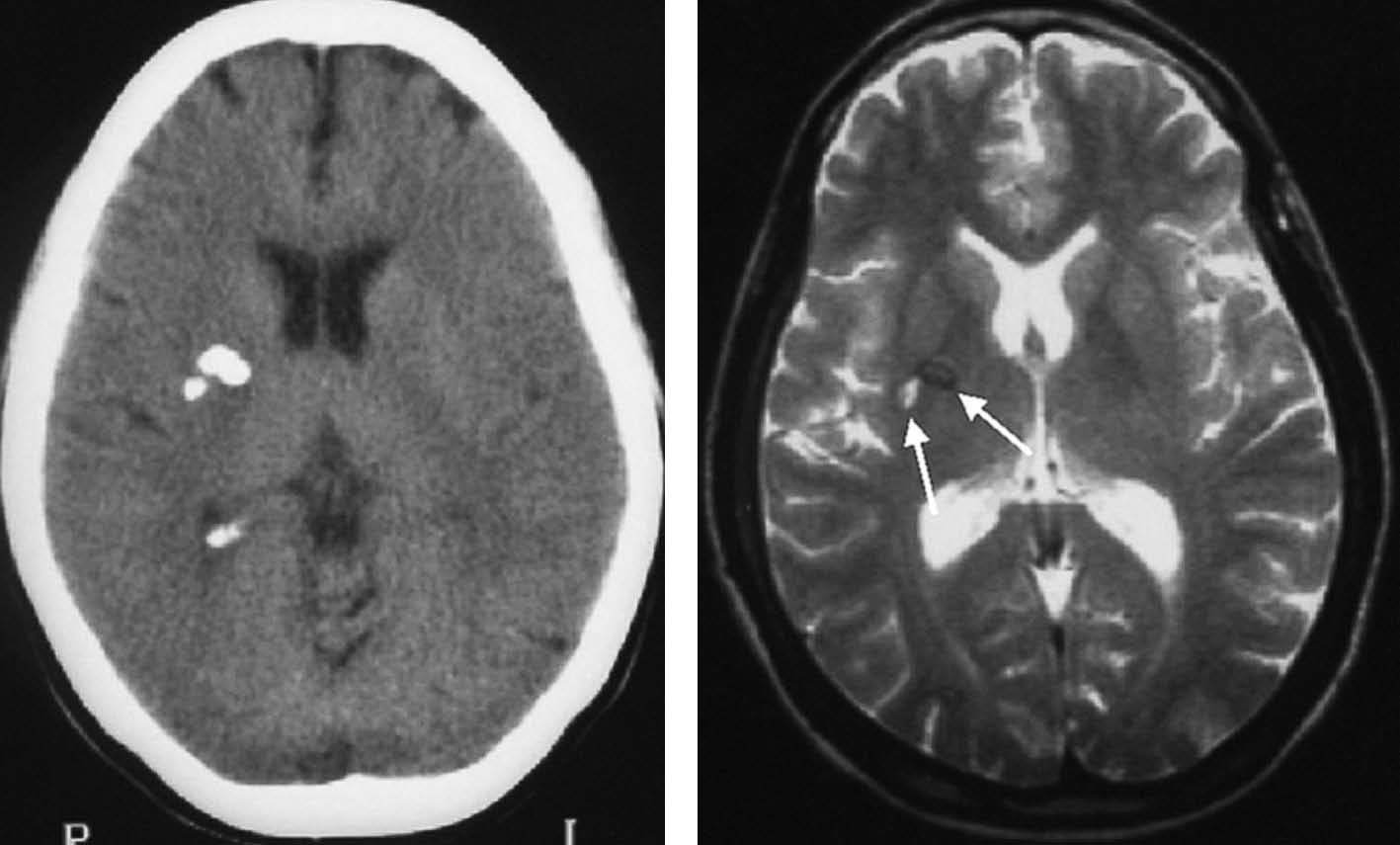
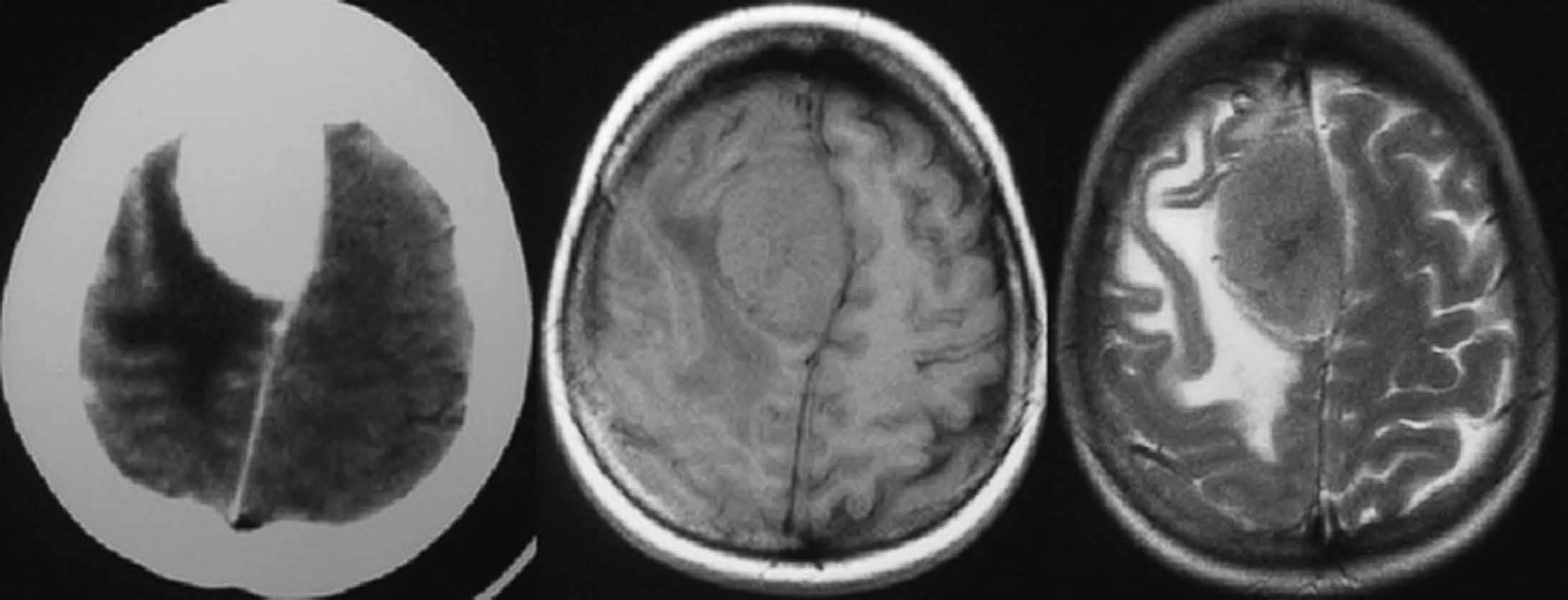
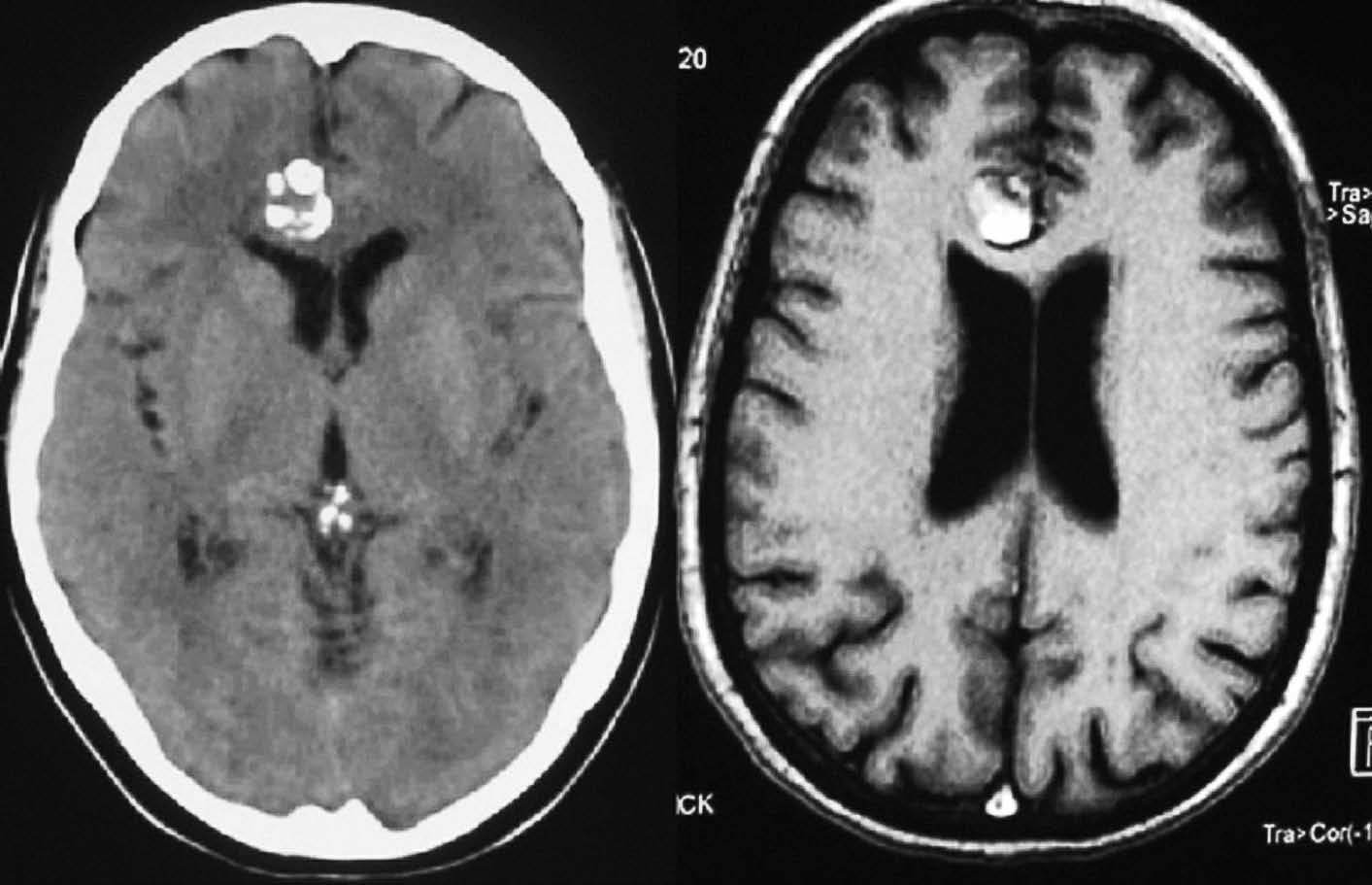
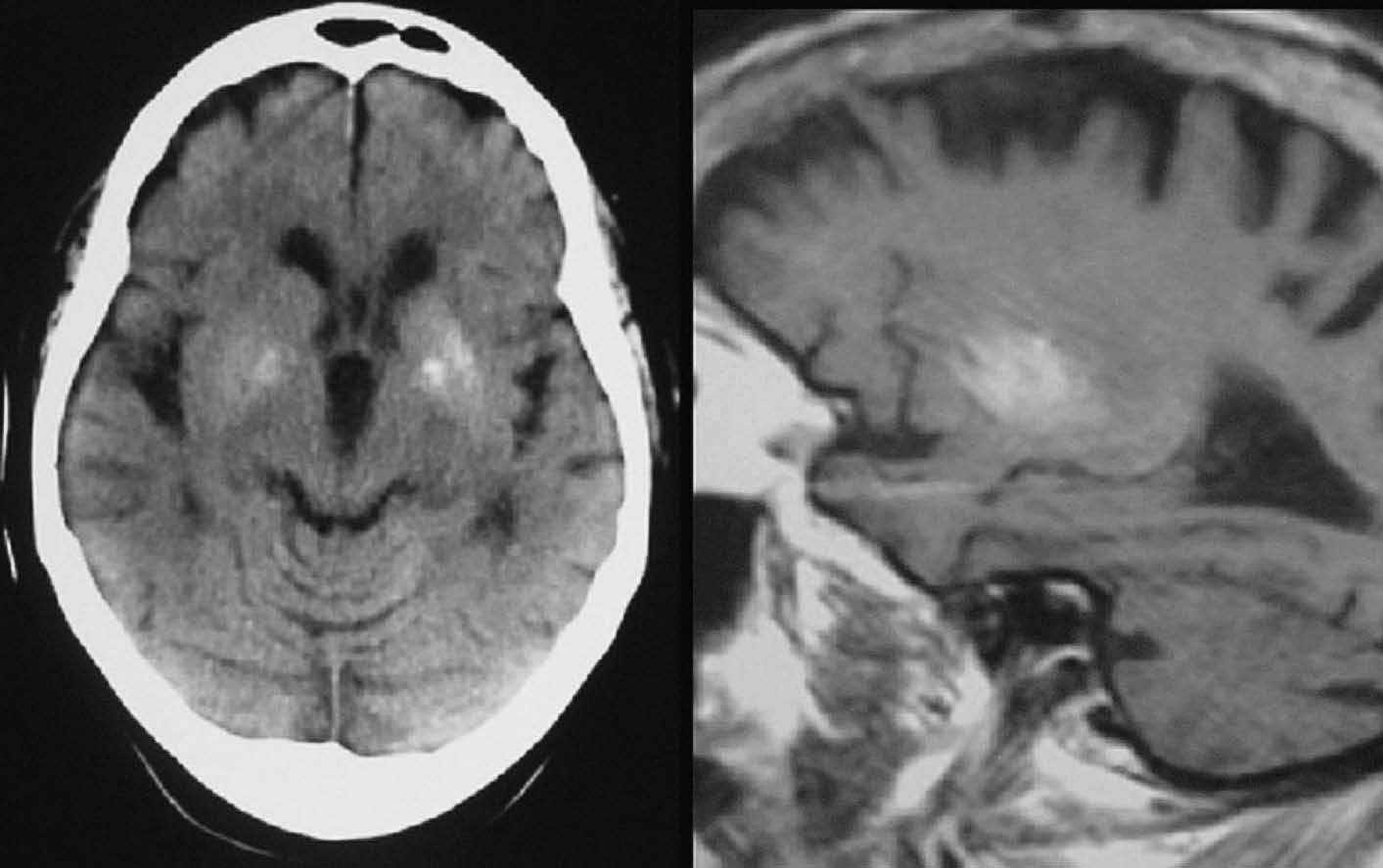
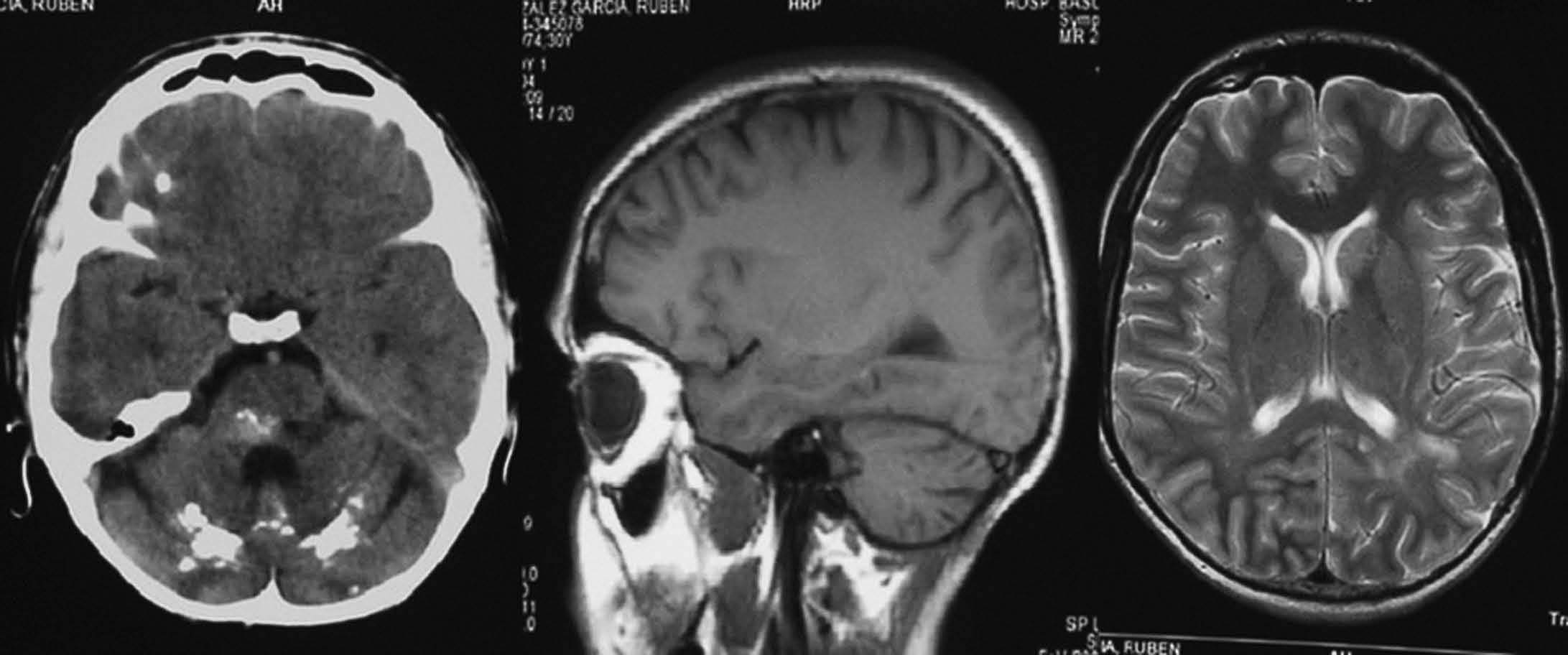
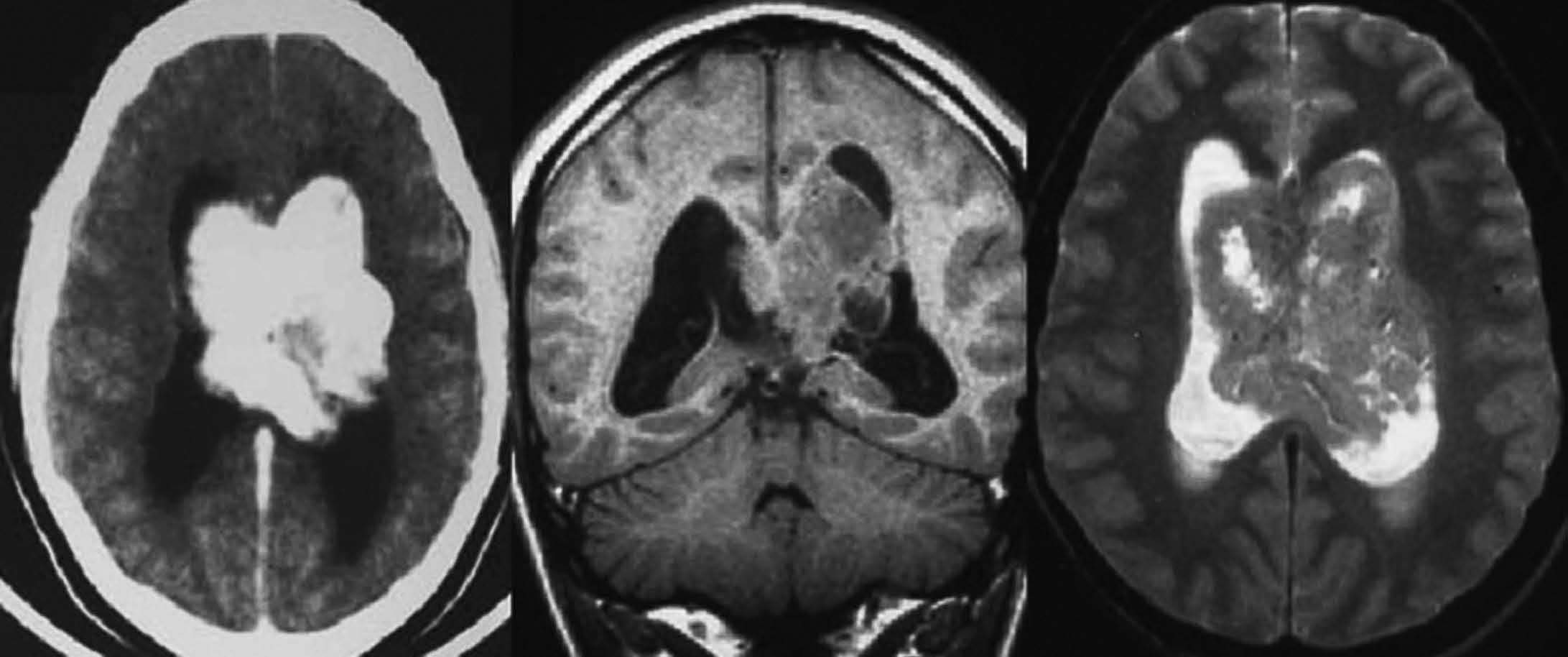
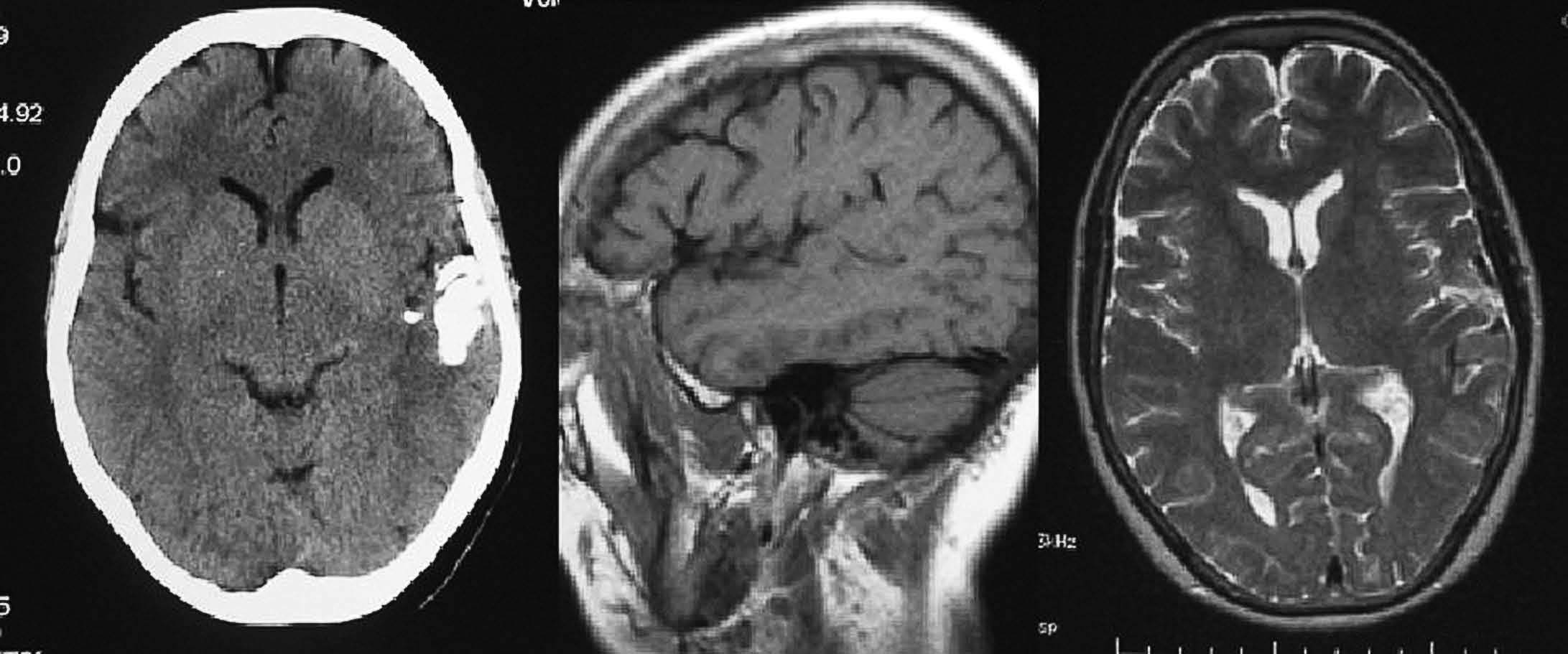
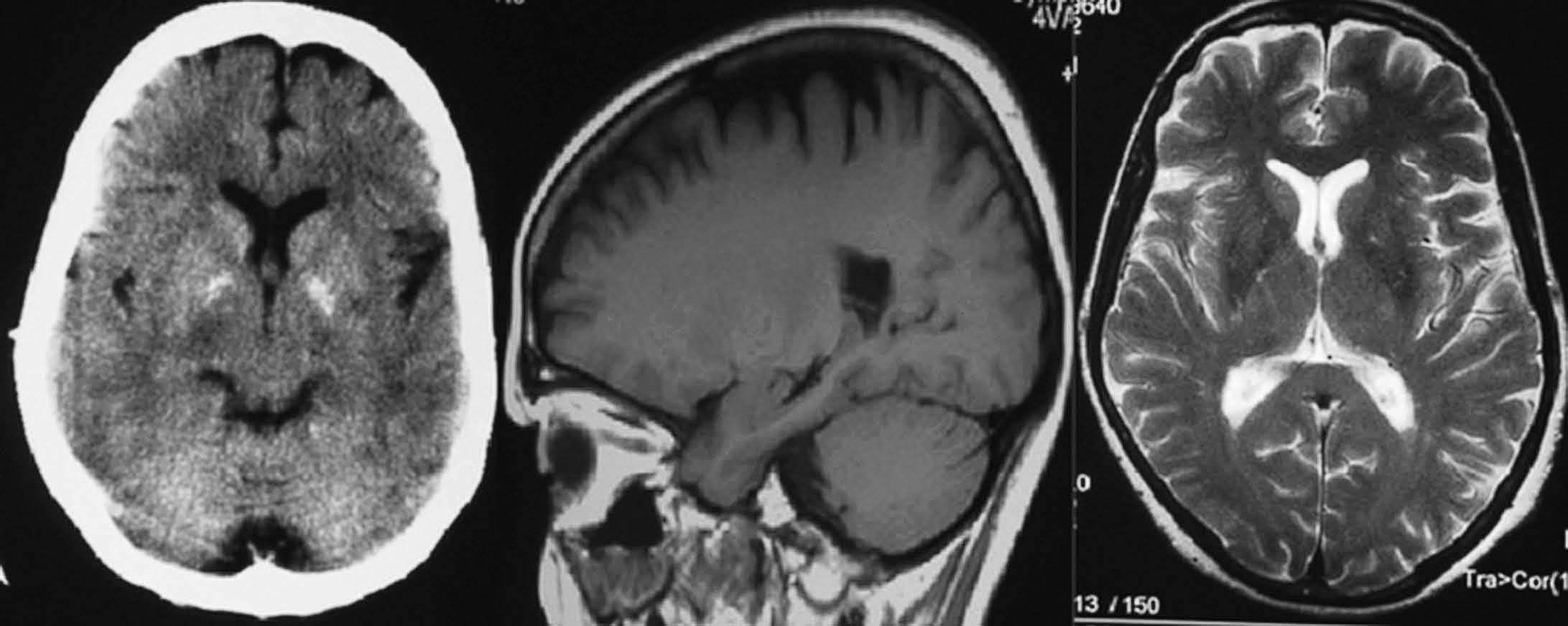
Objetivo. El objetivo del estudio fue demostrar la variabilidad en la apariencia de las calcificaciones intracraneales y su inespecificidad en estudios de resonancia magnética (RM) demostradas previamente por tomografía computarizada (TC). Material y método. Presentamos un estudio de 21 pacientes con lesiones intracraneales calcificadas de diferente etiología objetivadas en TC y analizamos las características de señal en RM en el seno de dichas lesiones en secuencias potenciadas en T1 y T2, tomando como referencia la corteza cerebral. Resultados. La señal de las lesiones calcificadas intracraneales fue variable. Sin embargo, la apariencia más frecuente de las calcificaciones intracraneales en estudios de RM en secuencias potenciadas en T1 fue la de áreas isointensas con la corteza cerebral. En las secuencias potencias en T2 la presentación más común de las calcificaciones fue la de focos de hipointensidad. Conclusiones. Las calcificaciones intracraneales presentan características de señal variables en las imágenes de RM, siendo su aspecto inespecífico, lo que dificulta la caracterización de lesiones intracraneales. La RM no permite excluir o demostrar con seguridad la presencia de calcificaciones. La TC es la técnica de elección para el estudio de lesiones calcificadas, por tanto, el disponer de una TC craneal en el estudio de lesiones intracraneales permite su identificación y la caracterización de dichas lesiones.
Palabras clave:
resonancia magnética, calcificación, intracraneal
Objective. The aim of this study is to show that the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings for intracranial calcifications previously demonstrated at computed tomography (CT) are variable and unspecific. Material and method. We present a study of 21 patients with calcified intracranial lesions of different etiologies detected at CT. We analyze the MRI signal characteristics in these lesions in T1- and T2-weighted sequences, taking the cerebral cortex as a reference. Results. The MRI signal of the calcified intracranial lesion was variable. Nevertheless, the most frequent appearance on T1-weighted sequences was areas isointense with the cerebral cortex. The most frequent appearance on T2-weighted sequences was foci of hypointensity. Conclusions. Intracranial calcifications show variable MRI signal characteristics and have an unspecific appearance, making them difficult to characterize. MRI cannot reliably rule out or determine the presence of calcifications. CT study of intracranial lesions enables calcified lesions to be identified and characterized; therefore, CT is the technique of choice for the study of calcified lesions.
Keywords:
magnetic resonance, calcification, intracranial
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Radiología
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail