To improve the complete remission (CR) rate of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients and alleviate the severe side effects of double induction chemotherapy, we combined a standard regimen with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) priming chemotherapy to compose a new double induction regimen for AML patients who failed to achieve CR after the first course.
Patients and methodsNinety-seven patients with AML who did not achieve CR after the first course of standard chemotherapy were enrolled. Among them, 45 patients received G-CSF priming combined with low-dose chemotherapy during days 20–22 of the first course of chemotherapy, serving as priming group, 52 patients were administered standard chemotherapy again, serving as control group.
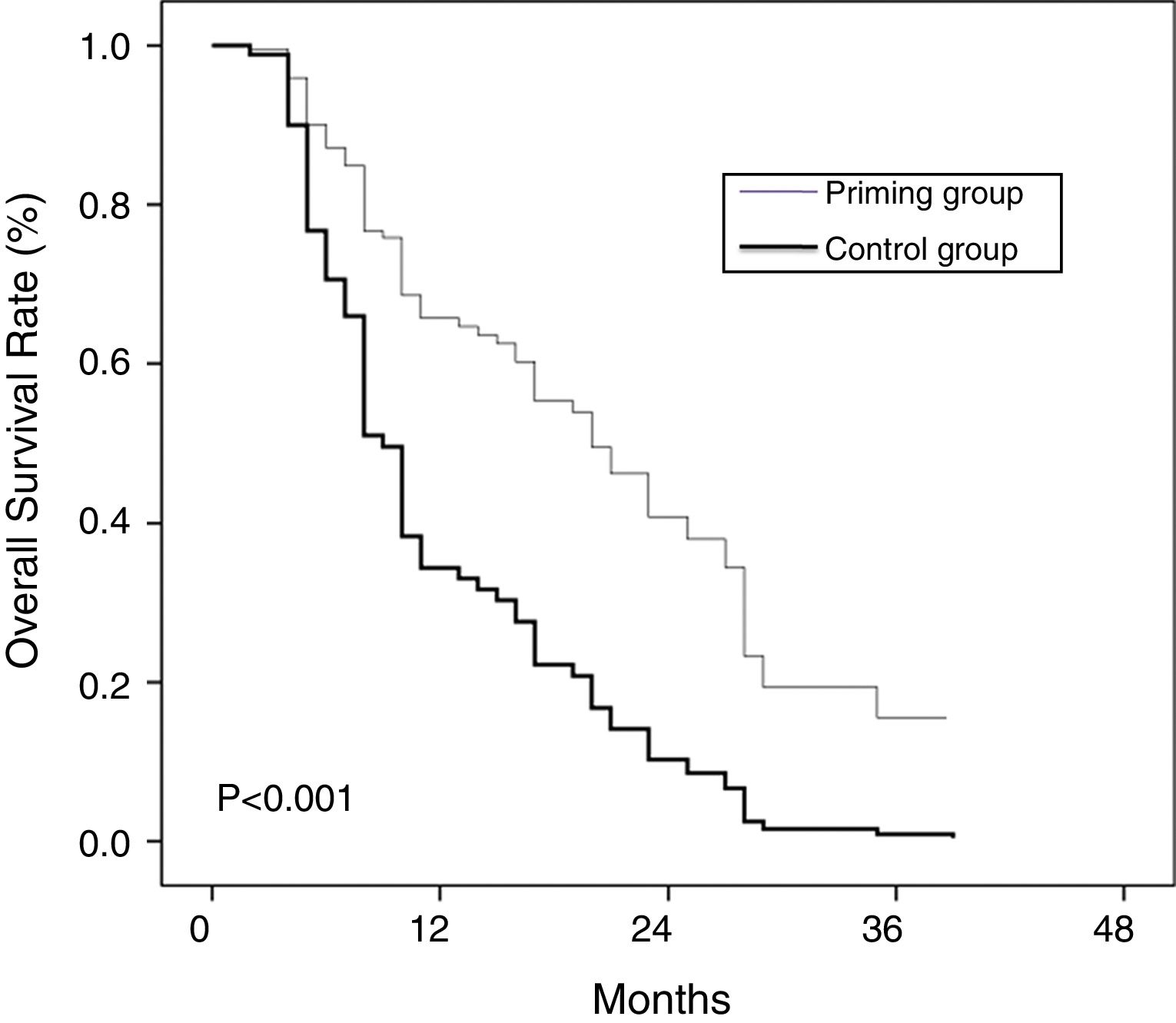
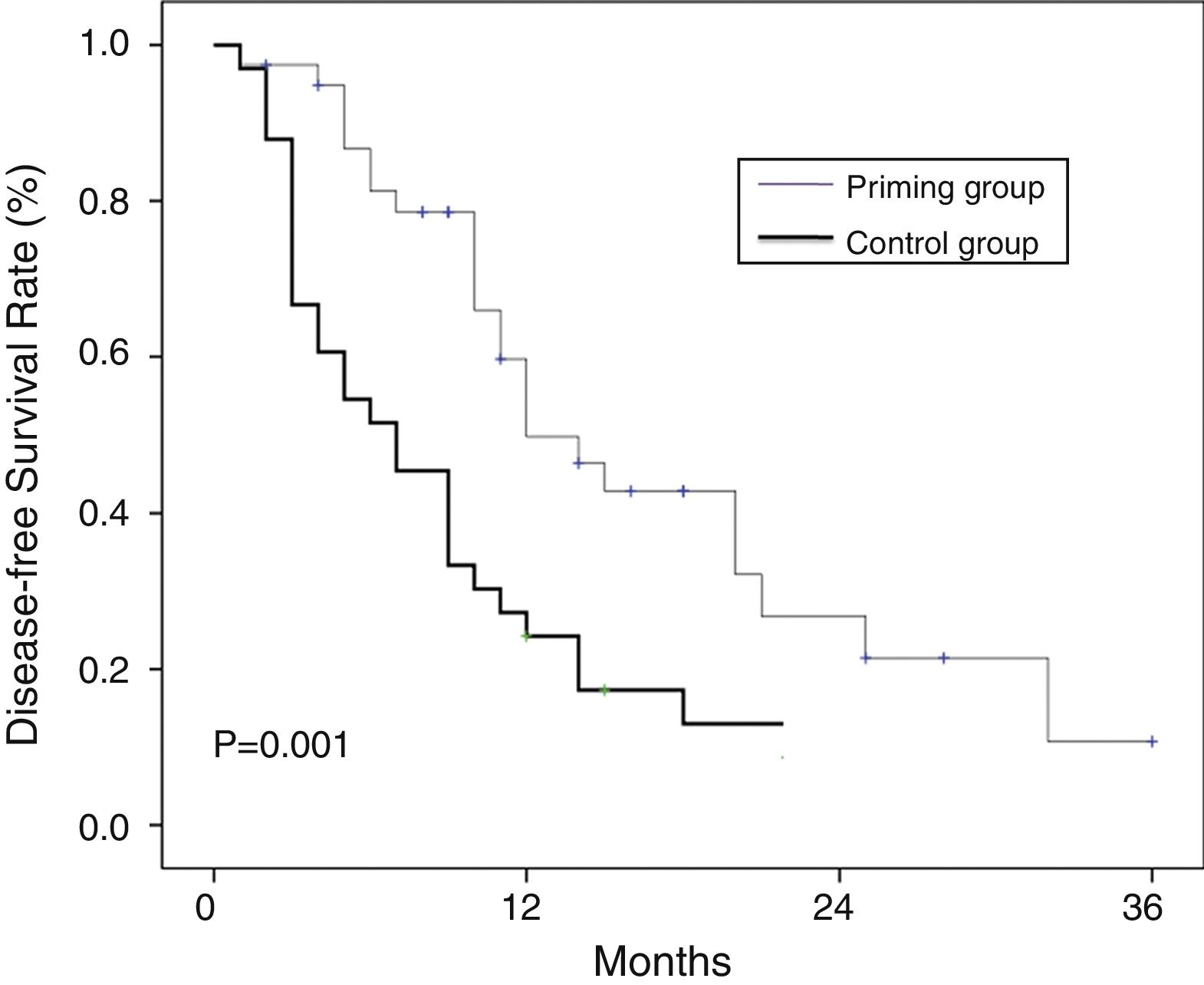
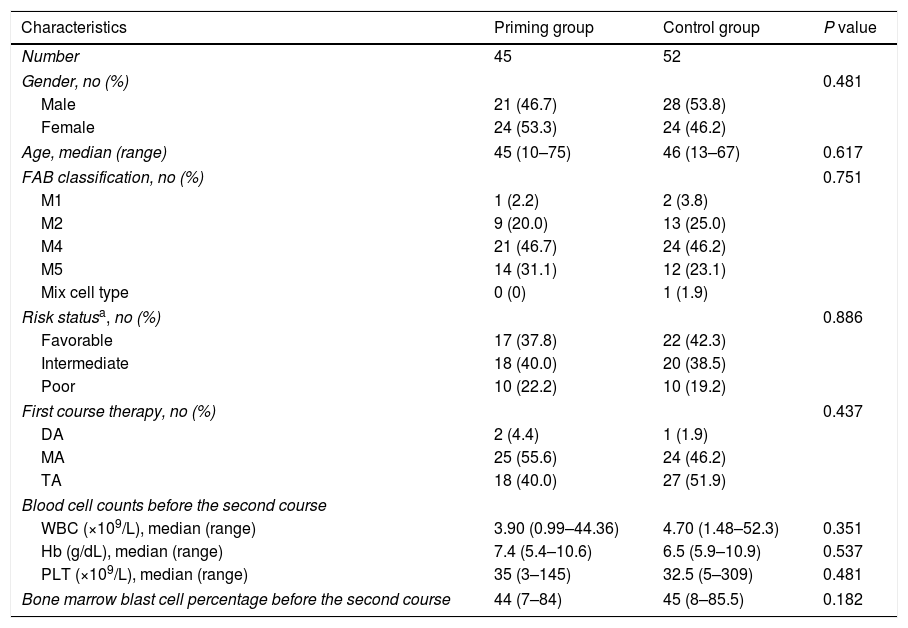
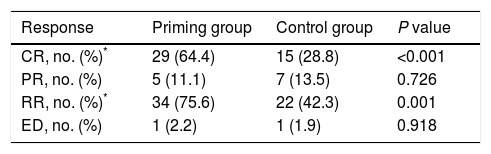
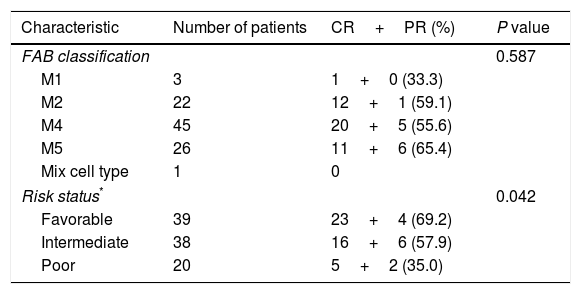
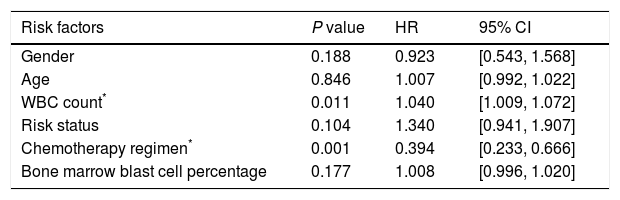
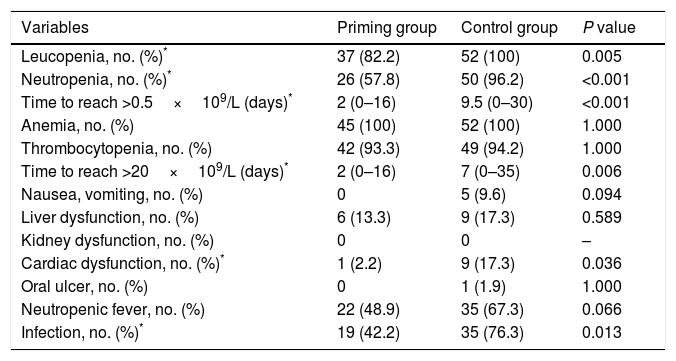
ResultsBetween the two groups there were no differences in the French–American–British (FAB) classification, risk status, the first course of chemotherapy, blood cell count or blasts percentage of bone marrow before the second course. But the CR rate was significantly higher and the adverse effect was much lower in the priming group than the control group. Cox multivariate regression analysis showed that WBC level before the second course and the selection of the second chemotherapy regimen were two independent factors for long survival of patients.
DiscussionThese results elucidate that standard chemotherapy followed by G-CSF priming new double induction chemotherapy is an effective method for AML patients to improve CR rate and reduce adverse effects.
Para mejorar la tasa de respuesta completa (RC) en los pacientes con diagnóstico reciente de leucemia mieloide aguda (LMA), y aliviar los efectos secundarios graves de la quimioterapia de doble inducción, combinamos un régimen estándar de quimioterapia de cebado de factor estimulante de colonias de granulocitos (G-CSF) para componer un nuevo régimen de doble inducción para los pacientes de LMA que no pudieron lograr la RC tras la administración del primer curso.
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyó a 95 pacientes de LMA que no lograron la RC tras el primer curso de quimioterapia estándar. Entre ellos, a 45 pacientes se les administró cebado de G-CSF junto con baja dosis de quimioterapia durante los días 20 a 22 del primer curso, formando el grupo de cebado, y a 52 pacientes se les administró quimioterapia estándar de nuevo, y constituyeron el grupo control.
ResultadosNo se produjeron diferencias entre los 2 grupos conforme a la clasificación French-American-British (FAB), estatus del riesgo, primer curso de quimioterapia, recuento de hematocritos o porcentaje de blastos de la médula ósea con anterioridad al inicio del segundo curso. Pero la tasa de RC fue significativamente superior, y los efectos adversos fueron inferiores, en el grupo de cebado con respecto al grupo control. El análisis de regresión multivariante de Cox reflejó que el nivel leucocitario antes del segundo curso, y la selección del segundo régimen de quimioterapia fueron 2 factores independientes de la supervivencia larga de los pacientes.
DiscusiónEstos resultados esclarecen que la quimioterapia estándar seguida de quimioterapia de inducción doble de cebado de G-CSF constituye un método efectivo para mejorar la tasa de RC y reducir los efectos adversos en los pacientes de LMA.