The use of cyclosporine A (CsA) is associated with different adverse effects including hypertension and nephrotoxicity. The present study aimed to compare the inhibitory effects of l-arginine & l-citrulline on CsA-induced blood pressure and biochemical changes in the serum of rats.
MethodsThirty-six rats were divided into 6 groups received daily: (1) 1ml distilled water, (2) 200mg/kg l-citrulline IP, (3) 25mg/kg CsA SC, (4) CsA+l-citrulline with the same dose of the former groups, (5) 200mg/kg l-arginine IP and (6) l-arginie+CsA with the same doses of group 4 for 7 days.
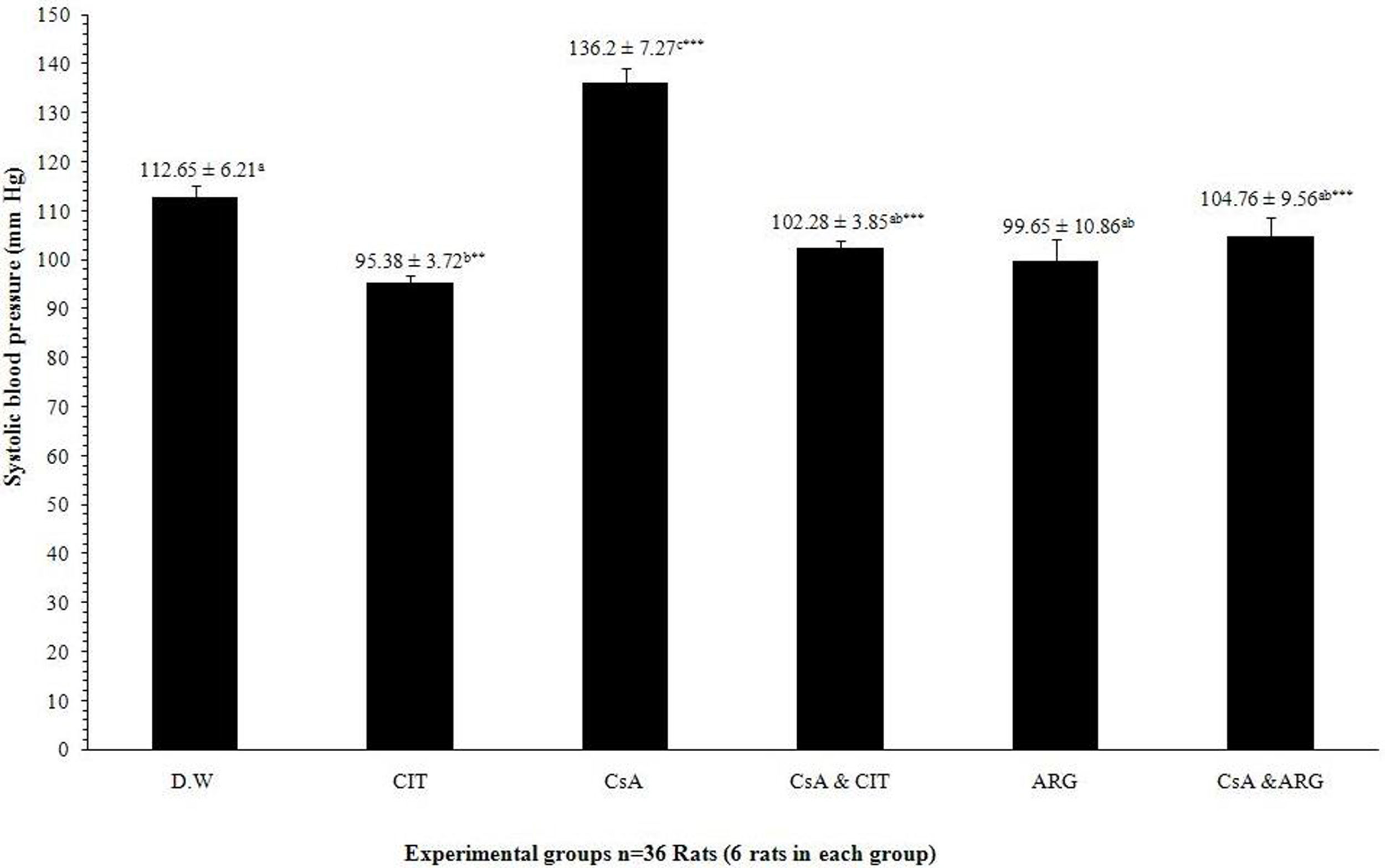
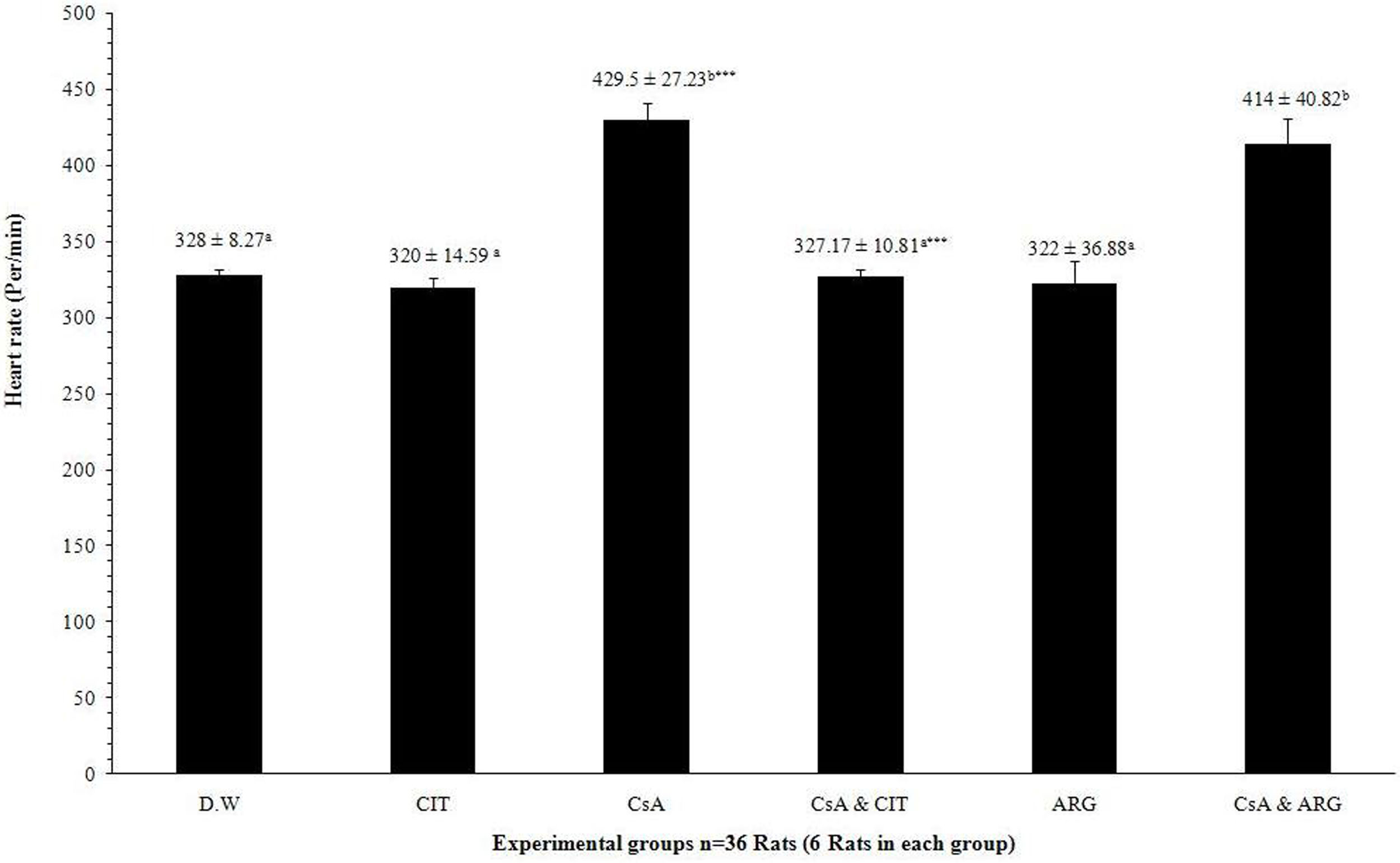
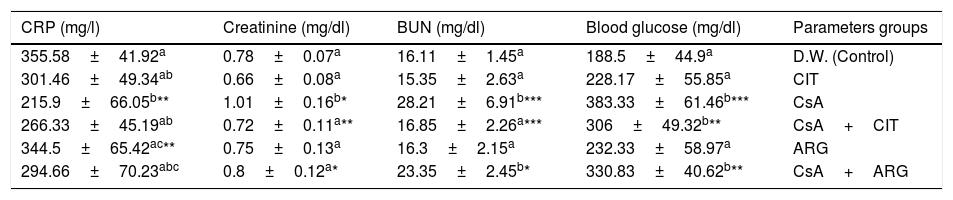
ResultsThe changes in the blood pressure, heart rate, creatinine, BUN, glucose and C-reactive protein (CRP) of the serum were determined in the treated animals. Significant (p<0.001) increase was shown in the blood pressure and heart rate of CsA treated rats compared to the control group. There were also a significant (p<0.05) increase in the creatinine, BUN and glucose, but a decrease in the CRP value in the CsA-treated group. However, l-citrulline significantly (p<0.001) inhibited the changes in the blood pressure and heart rate in CsA-treated as well as it was able to reduce blood pressure in non-treated group significantly (p<0.01). l-citrulline also inhibited the increased levels of BUN and creatinine induced by CsA, while, l-arginine was able to prevent the increased blood pressure and creatinine occurs after administration of CsA.
ConclusionsThese findings suggest that the l-citrulline is more efficient than l-arginine against the adverse effects induced by cyclosporine.
El uso de ciclosporina A (CsA) está asociado a diferentes efectos adversos que incluyen hipertensión y nefrotoxicidad. El objetivo del presente estudio es comparar los efectos inhibitorios de L-arginina y L-citrulina en la presión arterial inducida por CsA, y los cambios bioquímicos a nivel sérico en ratas.
MétodosSe dividieron 36 ratas en 6 grupos, que recibieron diariamente: 1) 1ml de agua destilada, 2) 200mg/kg de L-citrulina IP, 3) 25mg/kg de CsA SC, 4) la misma dosificación que los grupos anteriores de CsA+L-citrulina, 5) 200mg/kg de L-arginina IP y 6) la misma dosificación que el grupo 4 durante 7 días de L-arginina+CsA.
ResultadosSe determinaron los cambios de presión arterial, frecuencia cardiaca, creatinina, BUN, glucosa y proteína C reactiva (PCR) a nivel sérico, en los animales tratados. Se observó un incremento significativo (p<0,001) de presión arterial y frecuencia cardiaca en las ratas tratadas con CsA en comparación con el grupo control. También se produjo un incremento significativo (p<0,05) de los niveles de creatinina, BUN y glucosa, y una reducción del valor de PCR en el grupo tratado con CsA. Sin embargo, L-citrulina inhibió significativamente (p<0,001) los cambios de presión arterial y frecuencia cardiaca en las ratas tratadas con CsA, y también pudo reducir la presión arterial de manera considerable en el grupo no tratado (p<0,01). L-citrulina inhibió también los niveles incrementados de BUN y creatinina inducidos por CsA, y L-arginina fue capaz de impedir la incidencia del incremento de presión arterial y creatinina tras la administración de CsA.
ConclusionesEstos hallazgos sugieren que L-citrulina es más efectiva que L-arginina frente a los efectos adversos inducidos por ciclosporina.