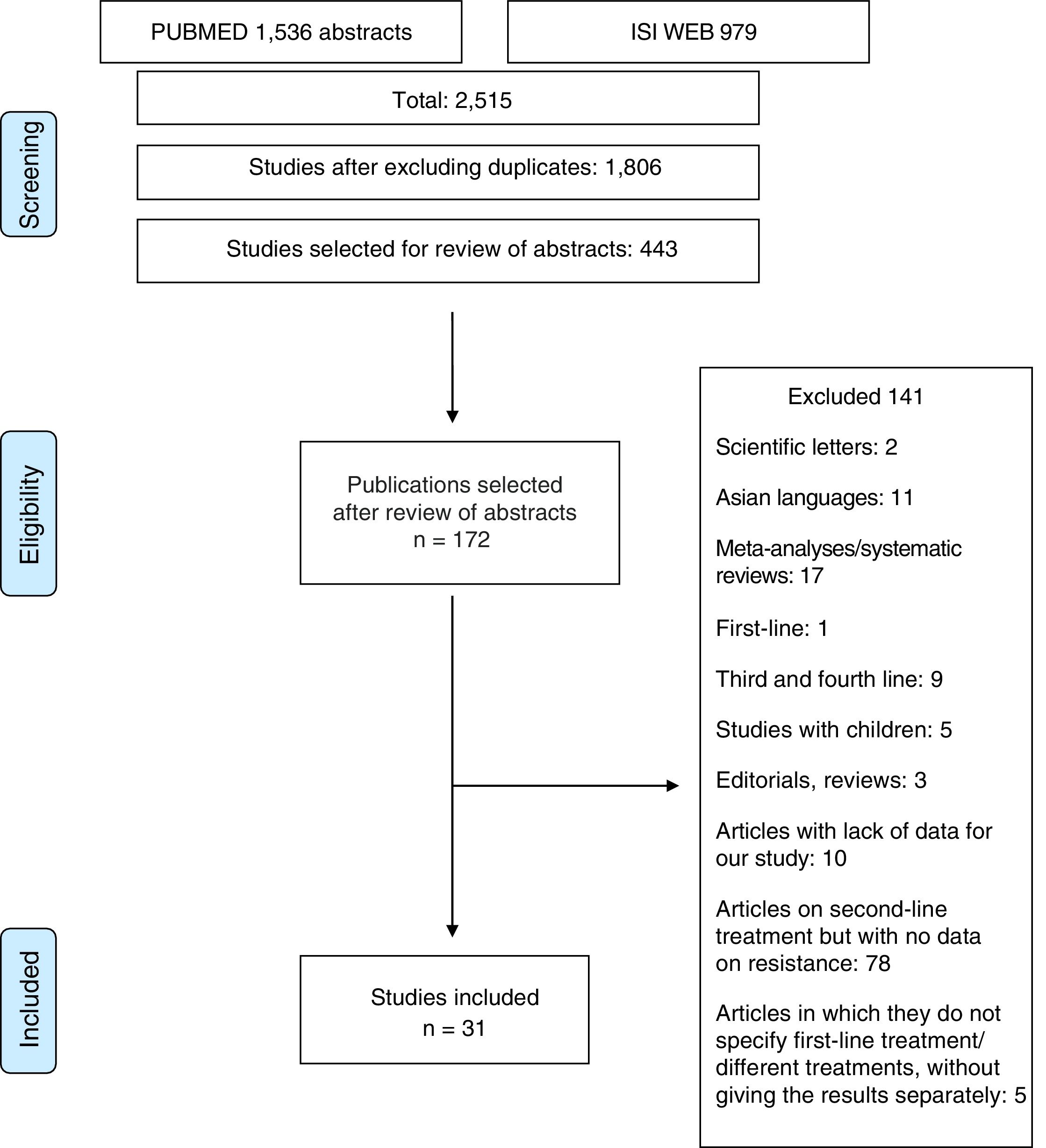
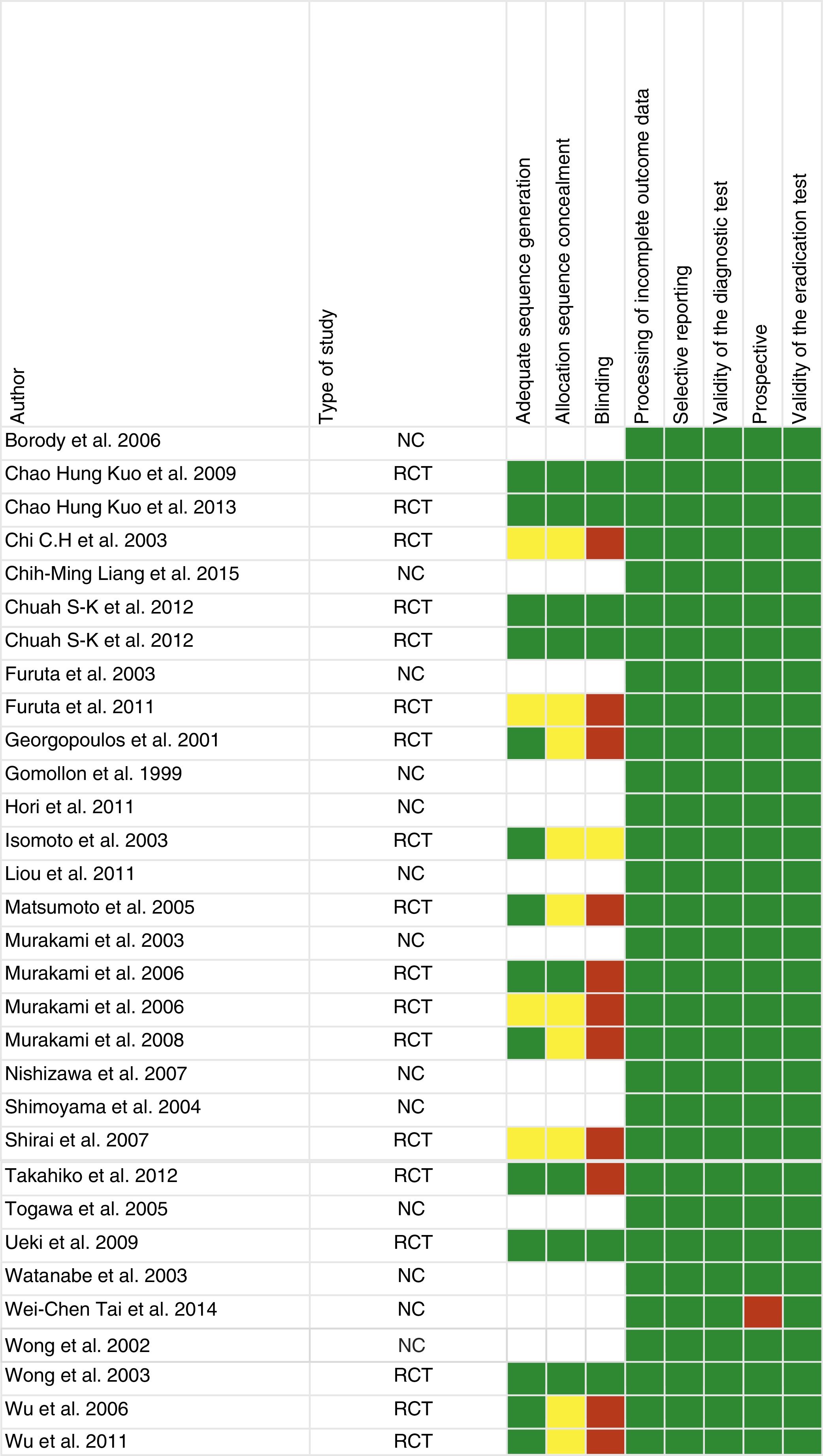
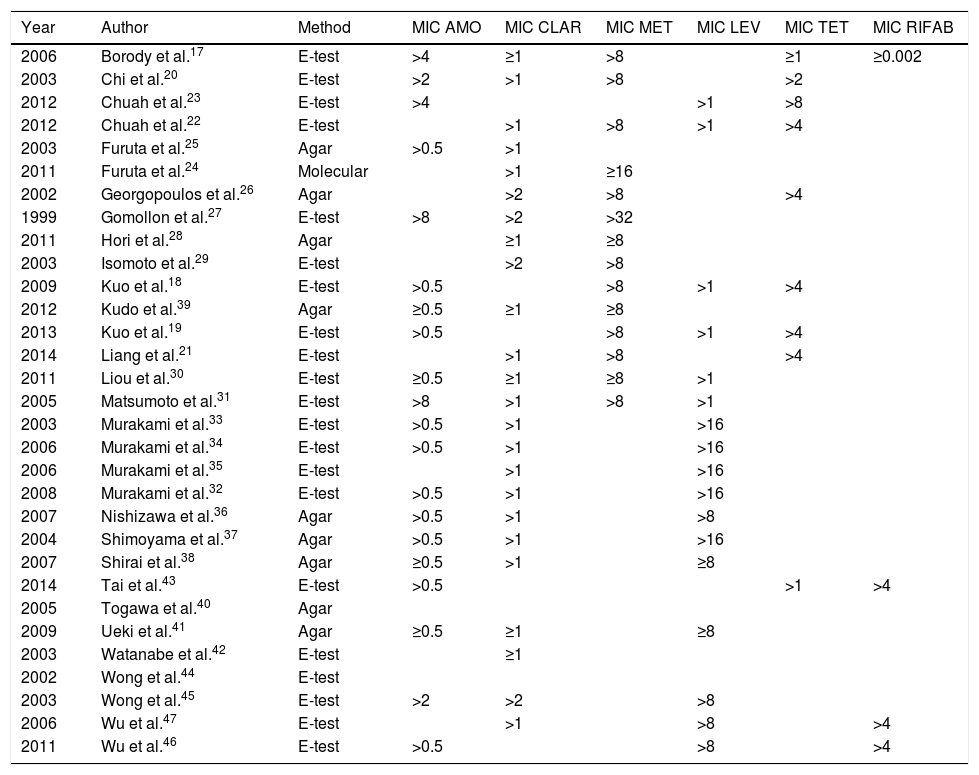
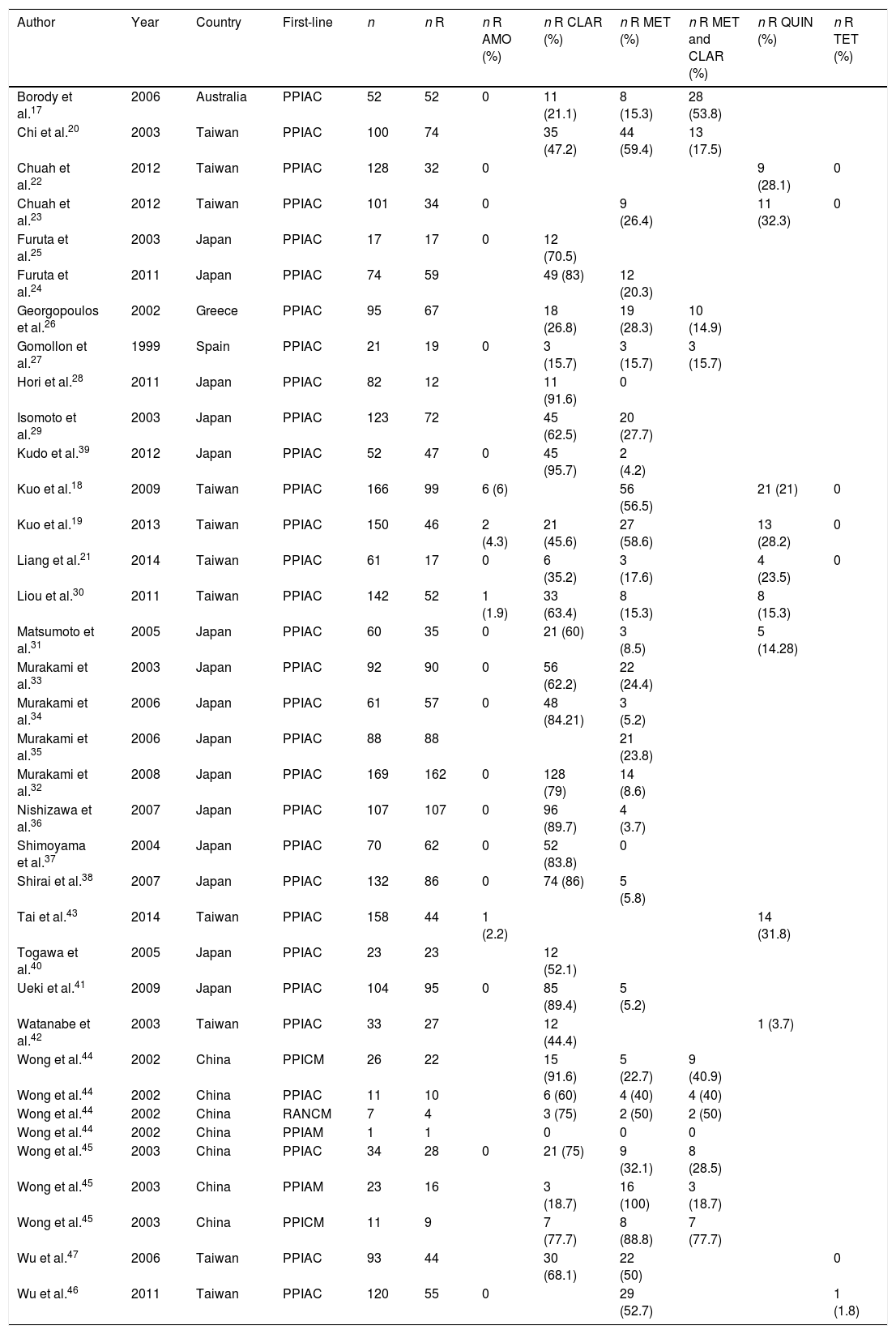
There are no systematic data on the rates of antibiotic resistance after the failure of a first eradication treatment. The objective of this study was to determine the prevalence of secondary resistance to antibiotics by conducting a systematic review of studies evaluating the secondary resistance of Helicobacter pylori. We identified 31 studies (2787 patients). Resistance was determined in 1764 patients. A percentage of 99.1 of patients received clarithromycin as first-line treatment and 58.7% developed resistance. A percentage of 24.3 received metronidazole and 89.7% developed resistance. Secondary resistance to amoxicillin was extremely rare. Secondary resistance after first-line treatment was very common. These findings support the recommendation not to repeat clarithromycin or metronidazole after the failure of a first eradication treatment.
No hay datos sistemáticos sobre cuáles son las tasas de resistencia a antibióticos tras el fracaso de un primer tratamiento erradicador. El objetivo del estudio es determinar la prevalencia de las resistencias secundarias a los antibióticos mediante una revisión sistemática de estudios que evaluaban las resistencias secundarias de Helicobacter pylori. Se identificaron 31 estudios (2.787 pacientes). Se determinaron resistencias en 1.764 pacientes. El 99,1% de los pacientes recibieron claritromicina como tratamiento de primera línea, y un 58,7% desarrollaron resistencias. El 24,3% de los pacientes recibieron metronidazol, desarrollando resistencias el 89,7%. La resistencia secundaria a amoxicilina fue excepcional. Las resistencias secundarias tras un primer tratamiento son muy elevadas. Estos hallazgos dan soporte a la recomendación de no repetir claritromicina o metronidazol tras el fracaso de un primer tratamiento erradicador.