Sepsis caused by Clostridium perfringens develops rapidly and has a high mortality rate. Although uncommon, it should be suspected in cases of infection by gram-positive bacilli and massive haemolysis. We present two cases of patients with a history of cephalic pancreaticoduodenectomy (CPD) due to cancer who presented with liver abscesses and massive haemolysis secondary to sepsis caused by C. perfringens.
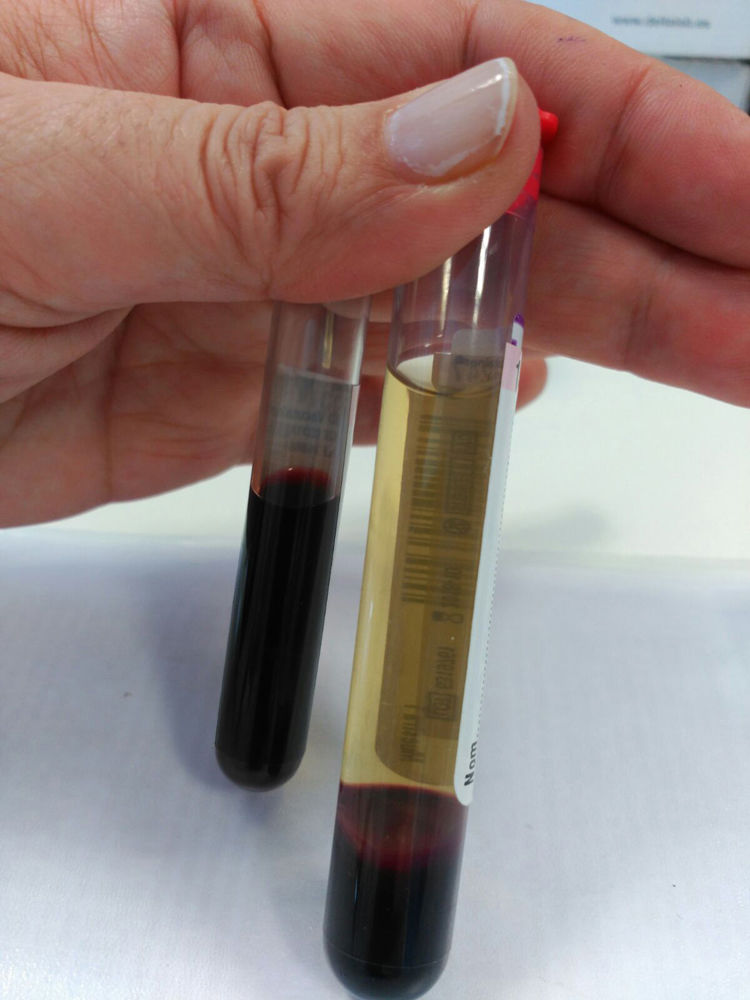
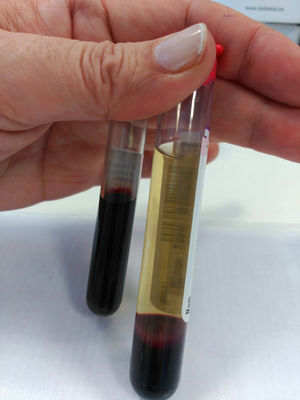
Both were male, aged 66 and 63, respectively. Both went to A&E with pyrexia, mucocutaneous jaundice and poor general condition. In the first case, the patient had undergone surgery for an uncinate process adenocarcinoma two months earlier, while the second case had undergone surgery nine years earlier for a distal cholangiocarcinoma. They both showed signs of shock with hypotension and tachycardia, and blood tests revealed anaemia, elevated markers of infection, hyperbilirubinaemia, haemolysis and metabolic acidosis. Investigations were completed with a computed tomography (CT) scan of abdomen and pelvis, showing liver abscess in both cases. In view of the severity of the shock and the fact that they were haemodynamically unstable, both patients were transferred to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), where they were treated with empirical antibiotics, vasopressor support and blood products. Despite these measures, in both cases, there was similar deterioration in the patient's condition, with massive haemolysis (Fig. 1). and cardiorespiratory arrest, with the first patient dying 3h and the second 6h after being admitted to the ICU.
Prior to their surgical interventions, neither had had endoprostheses or any type of biliary drainage. No Clostridium strains were isolated in postoperative cultures and no stenosis of the hepaticojejunal anastomosis was detected which might be responsible for the infectious complication. The patients had also not received any antibiotic therapy prior to the acute episode.
In our area, pyogenic liver abscess is a rare condition of polymicrobial aetiology, the most common route of infection being via the biliary tract. Gas-forming abscesses account for 7–24%, with associated septic shock being more common in these cases (32.5% versus 11.7% in abscesses not forming gas).1 The most common microorganisms are aerobic and anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria of intestinal origin (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterococcus, Bacteroides spp. and Fusobacterium spp.), with anaerobic Gram-positive (Actinomyces spp. and C. perfringens2) being less common.
C. perfringens is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore-forming bacillus. It is part of the normal flora of the gastrointestinal tract and the female genital tract, but can sometimes become pathogenic.2,3 It can cause skin and soft tissue infections, gastroenteritis, gangrene, cholecystitis, liver abscesses, endophthalmitis, empyema, endocarditis, bacteraemia, septic shock and massive haemolysis.2C. perfringens can double in number in 7min, turning it into a rapidly proliferating pathogen.3 One of its toxins, the alpha-toxin, acts as a phospholipase by hydrolysing the phospholipids of the red blood cell membrane, leading to spherocytosis and lysis of the erythrocytes.2,3
In cases of bacteraemia, 6–20% are polymicrobial. Clostridium can be isolated in 0.5–2% of all blood cultures, with C. perfringens being the most common and responsible for 20–50% of cases.4 Sepsis caused by C. perfringens has a 30-day mortality rate of 27–44%. Massive haemolysis can develop in 7–15% of cases. This factor is associated with a worse prognosis, raising the mortality rate to 70–100%, with an average time from admission to death of 9.7h.2
Growth and identification of C. perfringens in blood cultures is required for definitive diagnosis. When sepsis develops, it tends to progress rapidly, and there is no time to obtain culture growth. Therefore, when massive haemolysis is detected, C. perfringens should be suspected and treatment started as soon as possible in order to improve the prognosis of these patients. The optimal treatment is based on high-dose penicillin G and local control of the focus by way of surgical debridement.5
In our two cases, due to the rapid and difficult-to-manage progression, it was not possible to supplement the antibiotic therapy and support treatment with surgical debridement. In view of the severity of the condition, C. perfringens should be considered in all patients with severe sepsis and gas-forming liver abscess (with or without massive haemolysis).
Please cite this article as: Martí Gelonch L, Jiménez Agüero R, Rodríguez Canas N, Enríquez Navascués JM. Hemólisis masiva debida a sepsis por Clostridium perfringens secundaria a absceso hepático. Presentación de dos casos con un mismo antecedente. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;41:562–563.