Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) is frequently associated with pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and may occur after its surgical treatment.
AimTo determine the incidence, risk factors and management of SUI during and after POP surgery through a review of the available literature.
Materials and MethodNarrative literature review on the incidence and management of SUI after POP surgery after search of relevant manuscripts indexed in PubMed, EMBASE and Scielo published in Spanish and English between 2013 and 2023.
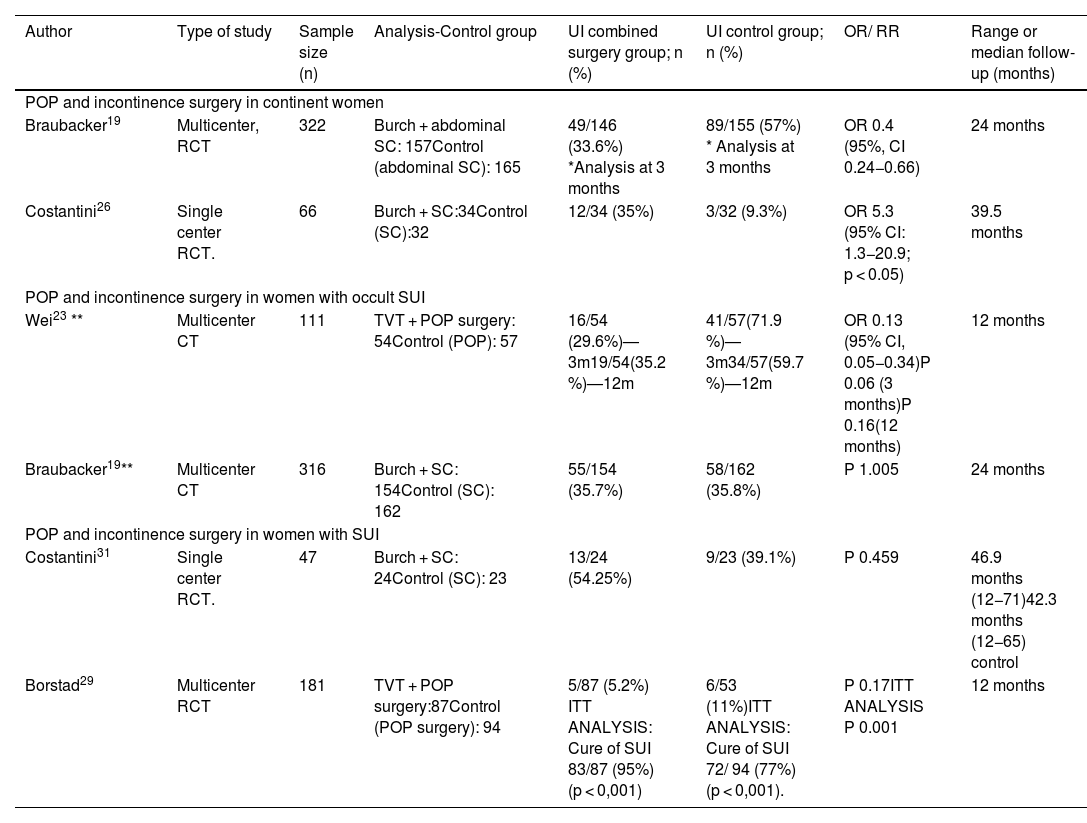
ResultsOccult SUI is defined as visible urine leakage when prolapse is reduced in patients without SUI symptoms. De novo SUI develops after prolapse surgery without having previously existed. In continent patients, the number needed to treat (NNT) to prevent one case of de novo SUI is estimated to be 9 patients and about 17 to avoid repeat incontinence surgery. In patients with occult UI, the NNT to avoid repeat incontinence surgery is around 7. Patients with POP and concomitant SUI are the group most likely to benefit from combined surgery with a more favorable NNT (NNT 2).
ConclusionQuality studies on combined surgery for treatment SUI and POP repair are lacking. Continent patients with prolapse should be warned of the risk of de novo SUI, although concomitant incontinence treatment is not currently recommended. Incontinence surgery should be considered on an individual basis in patients with prolapse and SUI.
La incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo(IUE)es un problema frecuente asociado al prolapso de órgano pélvico(POP),y que además puede aparecer en relación su tratamiento quirúrgico.
ObjetivoDeterminar la incidencia,factores de riesgo y manejo de la IUE durante y después de cirugía del POP,mediante revisión de la literatura disponible al respecto.
Material y métodoRevisión narrativa de la literatura sobre la incidencia y manejo de la IUE tras la cirugía del POP tras búsqueda de manuscritos relevantes indexados en PubMed,EMBASE y Scielo publicados en español e inglés entre 2013-2023.
ResultadosLa IUE oculta se define como la pérdida visible de orina con el prolapso reducido en pacientes sin síntomas de IUE.La IUE de novo es aquella que se desarrolla tras la cirugía del prolapso, sin que existiera previamente.En pacientes continentes el número necesario a tratar (NNT) para prevenir un caso de IUE de novo se estima en 9 pacientes y cerca de 17 para evitar una cirugía antiincontinencia adicional.En pacientes con IU oculta el NNT para evitar una cirugía antiincontinencia posterior se encuentra en torno a 7.Las pacientes con POP e IUE concomitantes son el grupo que más puede beneficiarse de una cirugía combinada con un NNT más favorable(NNT 2).
ConclusionesFaltan estudios de calidad sobre el tratamiento conjunto de la IUE y el POP.Las pacientes continentes con prolapso deben ser advertidas del riesgo de IUE de novo,aunque no se recomienda en la actualidad realizar tratamiento antiincontinencia de manera conjunta.Debe valorarse de manera individualizada la realización de cirugía antiincontinencia en pacientes con prolapso e IUE concomitante.