Analizar la efectividad y los potenciales problemas de seguridad de nirmatrelvir + ritonavir (NMV-r) (Paxlovid®) en la vida real, en los adultos con enfermedad por COVID-19 leve-moderada con riesgo alto de progresar.
DiseñoEstudio descriptivo observacional transversal.
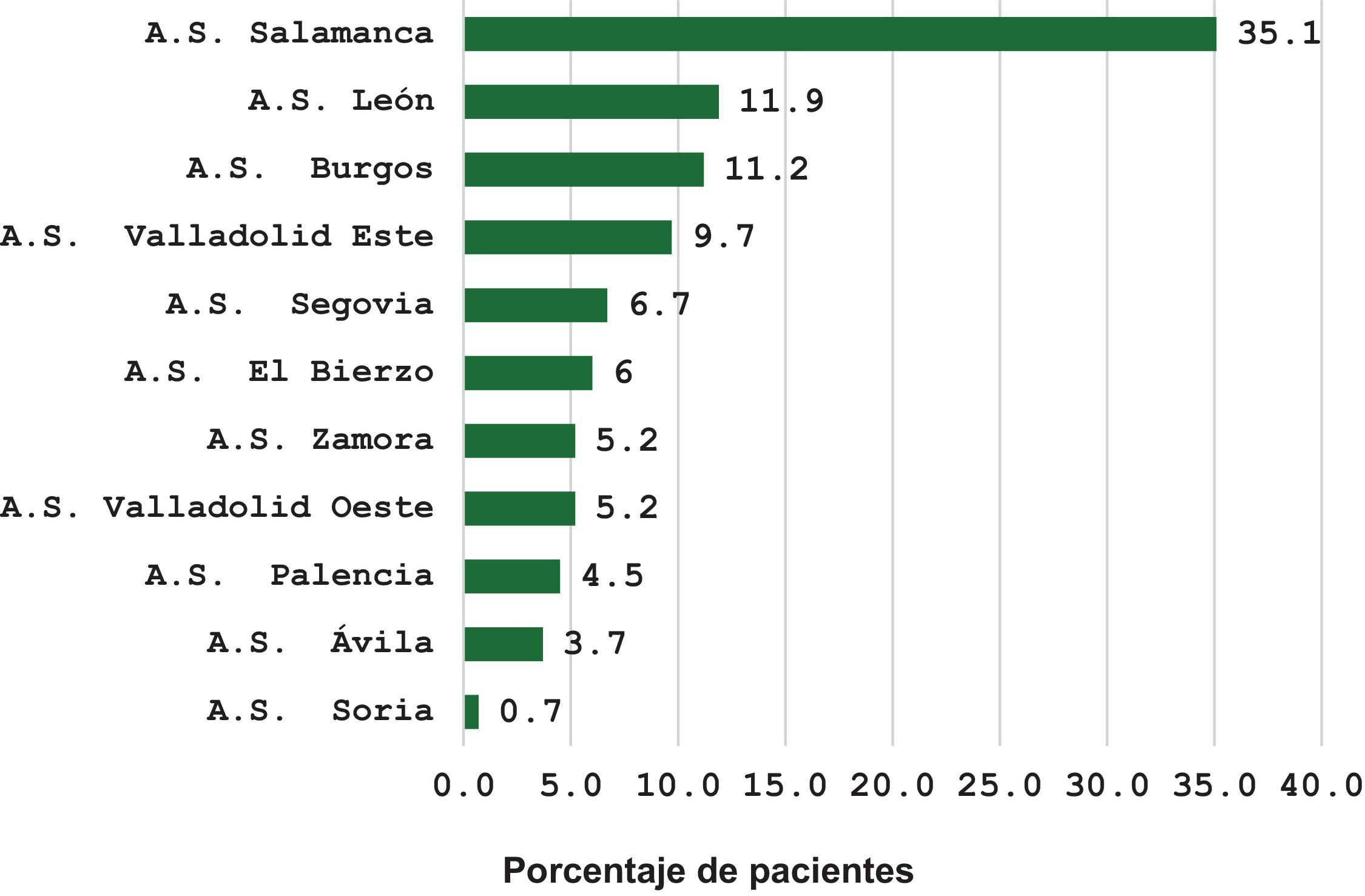
EmplazamientoCastilla y León, España.
ParticipantesCiento treinta y cuatro pacientes ≥18 años con COVID-19 con alto riesgo de progresión a enfermedad grave, que fueron tratados entre junio y septiembre de 2022 con NMV-r.
Mediciones principalesLas interacciones farmacológicas más relevantes con la medicación concomitante se obtuvieron de los registros de validación farmacéutica. De la monitorización de ingresos y fallecimientos en los 28 días siguientes al inicio de tratamiento se obtuvo información relativa a la efectividad del tratamiento.
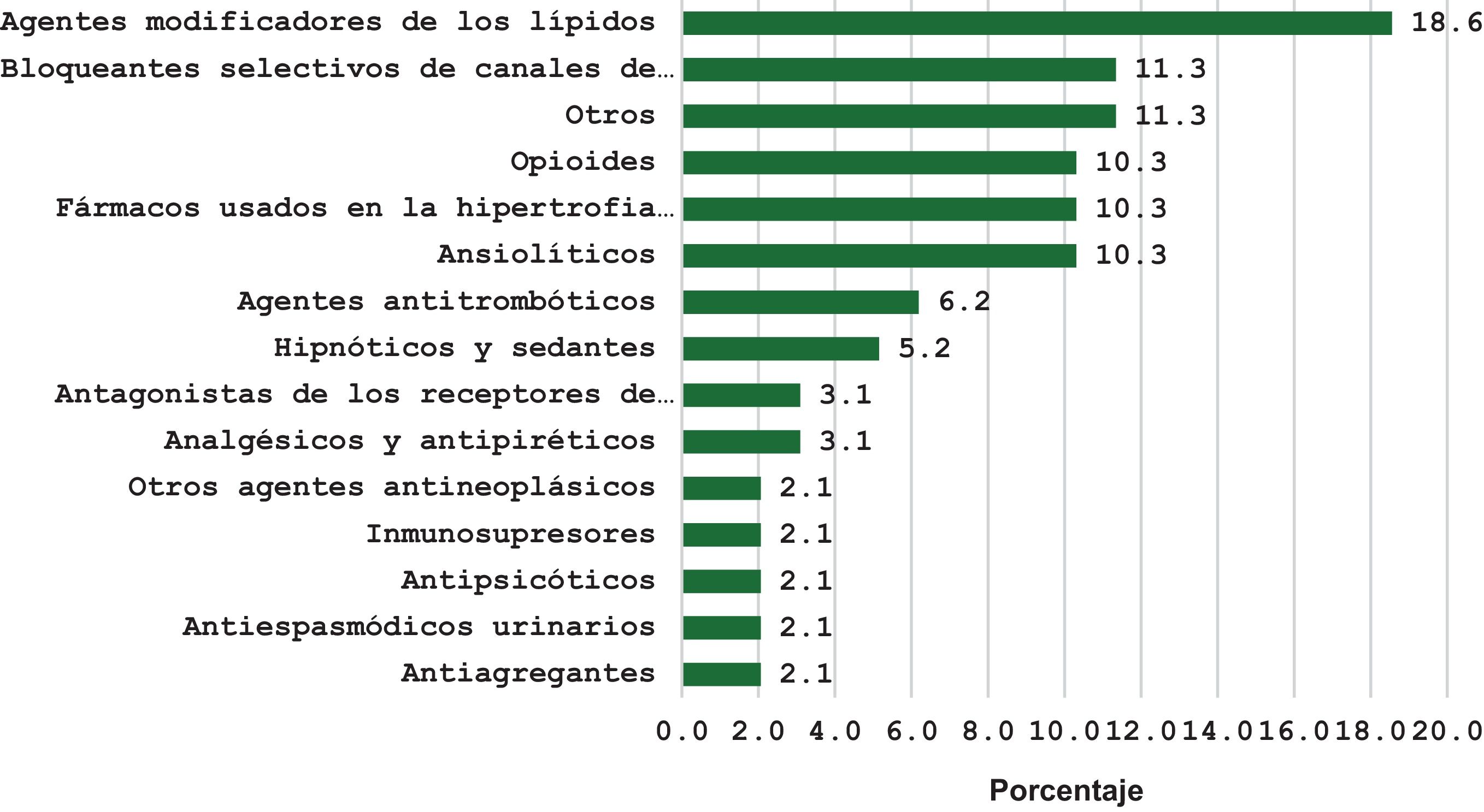
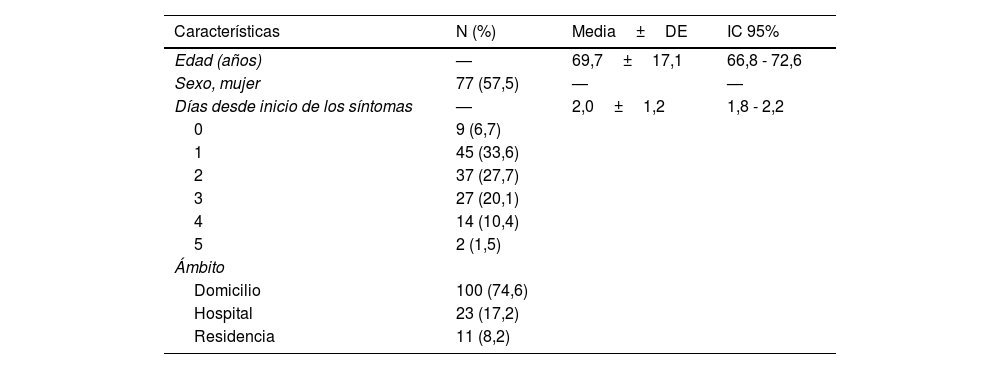
ResultadosEl 57,5% eran mujeres, la edad media±DE de 69,7±17,1 años, el 68,0% recibieron NMV-r en los 2 primeros días tras el inicio de los síntomas, el 74,6% eran domiciliarios y el 95,7% estaban vacunados. La principal condición de riesgo para progresión de la enfermedad fue ser paciente inmunocomprometido (74,5%) seguido de ser >65 años, vacunado, pero con factores de riesgo (21,2%). El 62,9% presentaron interacciones relevantes, con un promedio±DE de 1,7±1,0 por paciente. El 2,2% precisó ingreso hospitalario y el 3,0% falleció.
ConclusionesNMV-r ha sido efectivo para evitar las formas graves de la COVID-19 y los ingresos hospitalarios en población de riesgo con alta tasa de vacunación. La prevalencia de potenciales interacciones es elevada, sin embargo, la colaboración entre médicos de familia y farmacéuticos permite emplear NMV-r en condiciones de seguridad.
To analyze the effectiveness and potential safety concerns of Nirmatrelvir + ritonavir (NMV-r) (Paxlovid®) in adults with mild-moderate COVID-19 disease at high risk of progression.
DesignDescriptive cross-sectional observational study.
SettingCastilla y León, Spain.
Participants134 patients ≥18 years old with COVID-19 at high risk of progression to severe disease, who were treated between June and September 2022 with NMV-r.
Main measurementsThe most relevant drug interactions with concomitant medication were obtained from pharmaceutical validation records. From the monitoring of hospital admissions and deaths in the 28 days following the start of treatment, information regarding the effectiveness of the treatment was obtained.
Results57.5% were women, the average age±SD was 69.7±17.1, 68.0% received NMV-r in the first two days of the start of symptoms, 74.6% were at home, and 95.7% were vaccinated. The main risk condition for disease progression was being immunocompromised (74.5%), followed by being >65 years old, vaccinated, but with risk factors (21.2%). A total of 62.9% had relevant interactions, with an average±SD of 1.7±1.0 per patient. 2.2% required hospital admission and 3.0% died.
ConclusionsNMV-r has been effective in preventing severe forms of COVID-19 and hospital admissions in at-risk populations with a high vaccination rate. The prevalence of potential interactions is high, however, collaboration between family physicians and pharmacists allows NMV-r to be used safely.
Artículo
Diríjase al área privada de socios de la web de la SEMERGEN, (https://www.semergen.es/index.php?seccion=biblioteca&subSeccion=revistaSEMERGEN ) y autentifíquese.