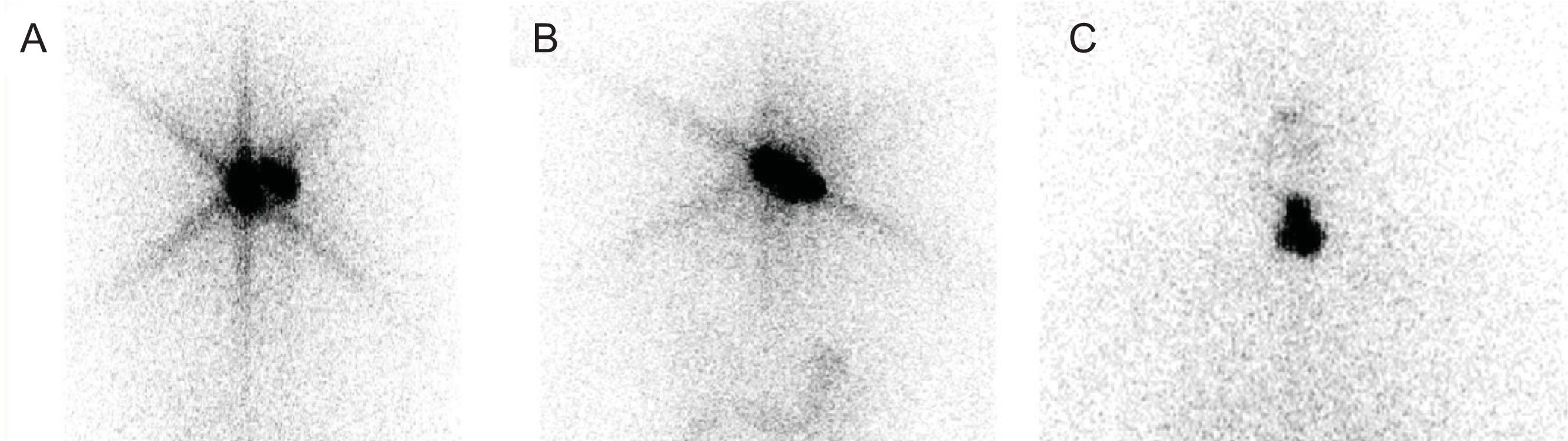
After 131I treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC), we sometimes find a star-shaped intense uptake of 131I on therapeutic whole body scans (Rx-WBS), called star artifacts. Therefore, we analyzed the relevant clinical factors and prognostic value of star artifacts in DTC patients.
Methods809 DTC patients who received 131I treatment were retrospectively evaluated and divided into 2 groups of patients with and without star artifacts. We evaluated the therapeutic response which was divided into excellent response (ER), biochemical incomplete response (BIR), indeterminate response (IR), and structural incomplete response (SIR). Clinical factors for the presence of star artifacts were analyzed. We also compared the rate of ER, BIR, IR, SIR and recurrence rate between group 1 and group 2.
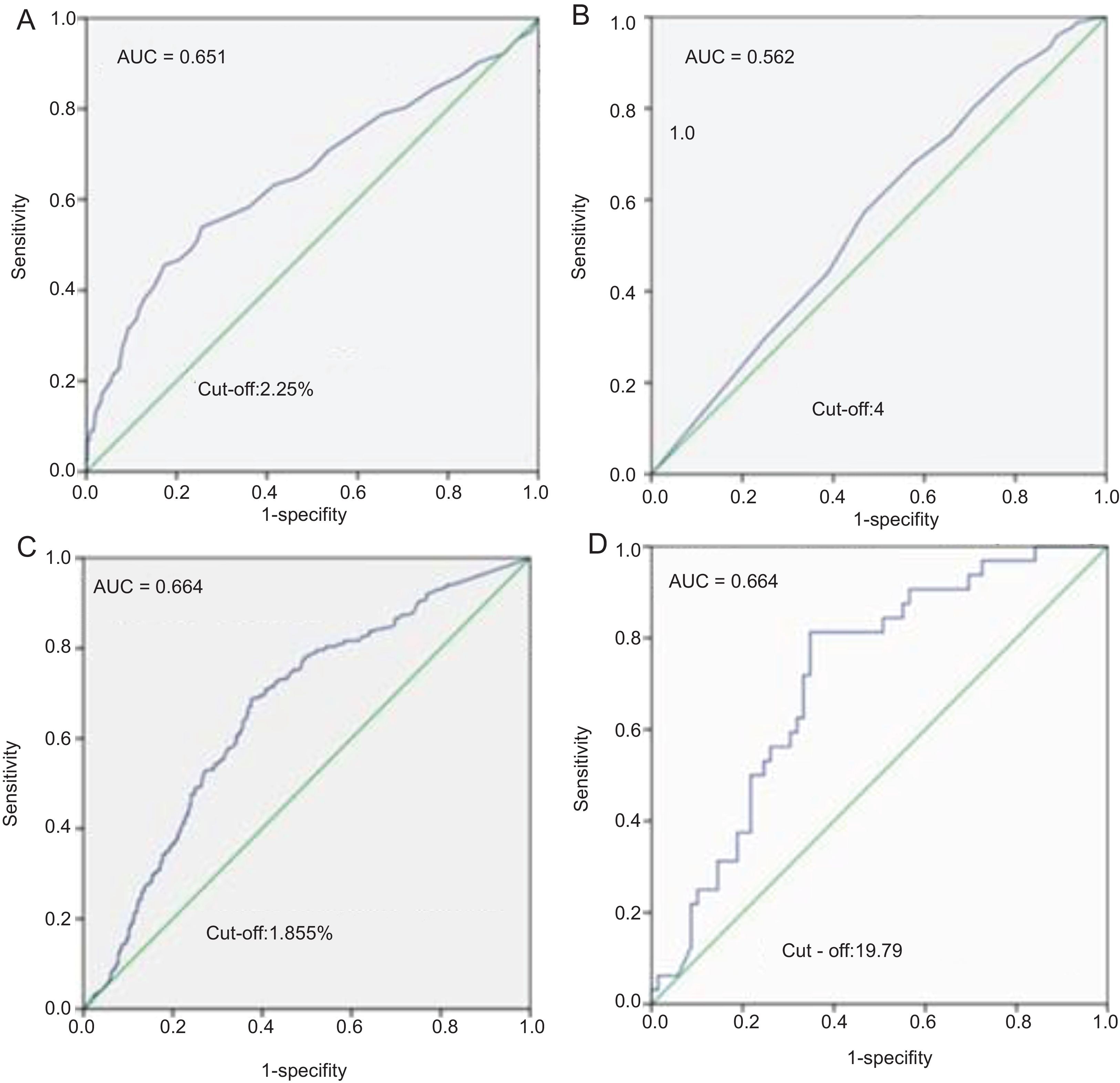
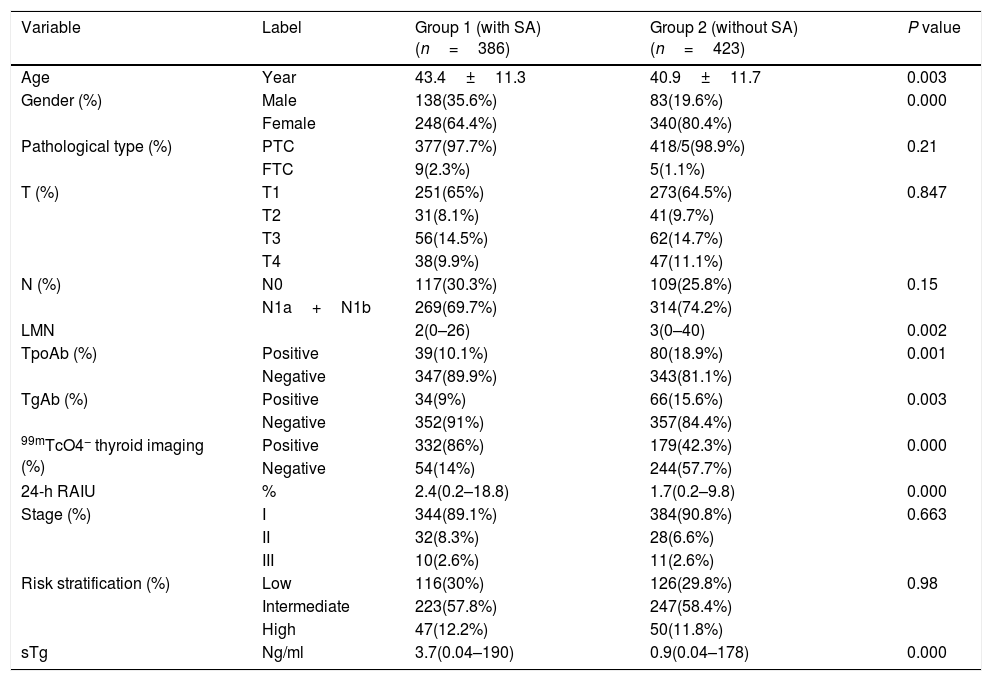
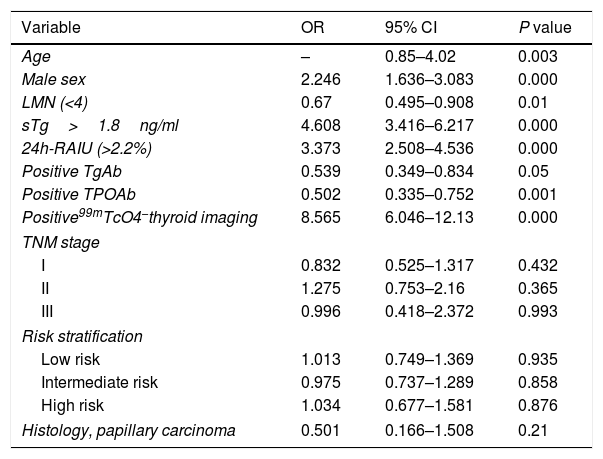
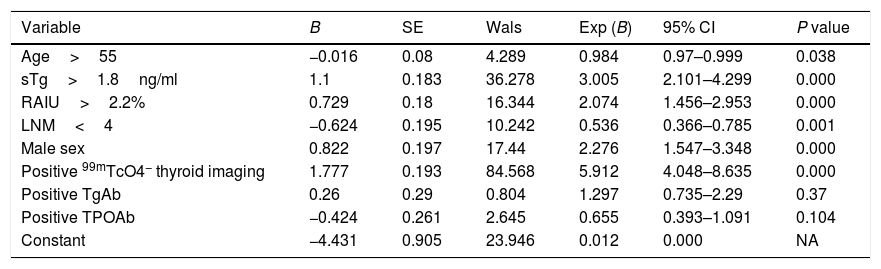
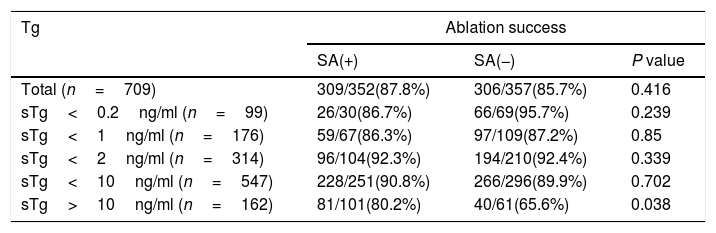
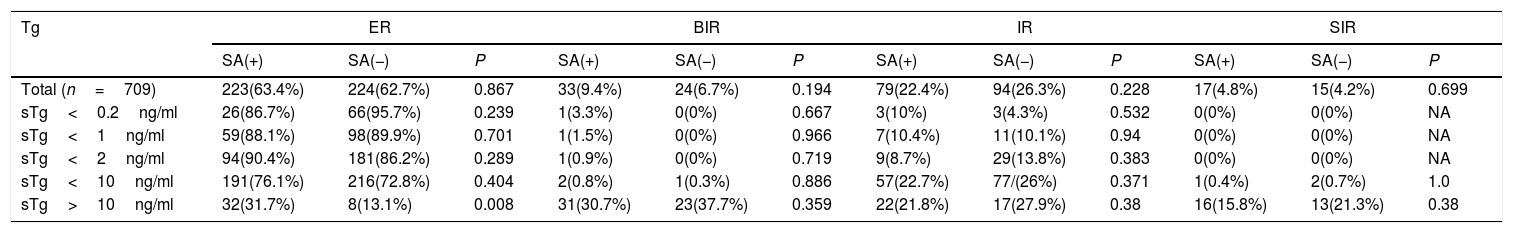
ResultsThe major clinical factors included stimulated thyroglobulin (sTg)>1.8ng/ml, 24h radioiodine uptake (RAIU)>2.2%, and positive 99mTcO4− thyroid imaging for the presence of star artifacts. In patients with sTg levels>10ng/ml, patients in group 1 had a higher rate of ablation success and ER than patients in group 2 (80.2% vs 65.6%, P=0.038, 31.6% vs 13.1%, P=0.008, respectively) and had a similar rate of BIR, IR, SIR. Recurrence rate was similar between group 1 and group 2 (5.2% vs 3.1%, P=0.13).
ConclusionMore remnant thyroid tissue is one of the factors associated with the presence of star artifacts on Rx-WBS. Patients with star artifacts exhibit a better therapeutic response (ER) when sTg levels are >10ng/ml. However, star artifacts have no effect on the recurrence rate.
Después del tratamiento con 131I en pacientes con carcinoma diferenciado de tiroides (DTC), a veces encontramos una captación intensa en forma de estrella de 131I en las exploraciones terapéuticas de todo el cuerpo (Rx-WBS), llamadas artefactos estelares. Por lo tanto, analizamos los factores clínicos relevantes y el valor pronóstico de los artefactos estelares en los pacientes con DTC.
Métodos809 pacientes con DTC que recibieron el tratamiento 131I fueron evaluados retrospectivamente y divididos en 2 grupos de pacientes con y sin artefactos estelares. Evaluamos la respuesta terapéutica que se dividió en respuesta excelente (ER), respuesta bioquímica incompleta (BIR), respuesta indeterminada (IR) y respuesta estructural incompleta (SIR). Se analizaron los factores clínicos de la presencia de artefactos estelares. También comparamos la tasa de ER, BIR, IR, SIR y la tasa de recurrencia entre el grupo 1 y el grupo 2.
Los resultadosLos principales factores clínicos incluyeron tiroglobulina estimulada (sTg) >1.8ng/ml, captación de yodo radioactivo (RAIU) >2.2%, e imagen positiva de la tiroides 99mTcO4− para la presencia de artefactos estelares. En los pacientes con niveles de sTg >10ng/ml, los pacientes del grupo 1 tuvieron una mayor tasa de éxito en la ablación y en la sala de emergencias que los pacientes del grupo 2 (80,2% vs 65,6%, P=0,038, 31,6% vs 13,1%, P=0,008, respectivamente) y tuvieron una tasa similar de BIR, IR, SIR. La tasa de recurrencia fue similar entre el grupo 1 y el grupo 2 (5,2% vs 3,1%, P=0,13).
ConclusiónUn mayor tejido tiroideo remanente es uno de los factores asociados a la presencia de artefactos estelares en Rx-WBS. Los pacientes con artefactos estelares exhiben una mejor respuesta terapéutica (RE) cuando los niveles de sTg son >10ng/ml. Sin embargo, los artefactos estelares no tienen ningún efecto en la tasa de recurrencia.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)