To determine the accuracy of visual analysis and the retention index (RI) with dual-time point 18F-FDG PET/CT for the characterization of indeterminate pulmonary nodules (IPN) with low FDG uptake.
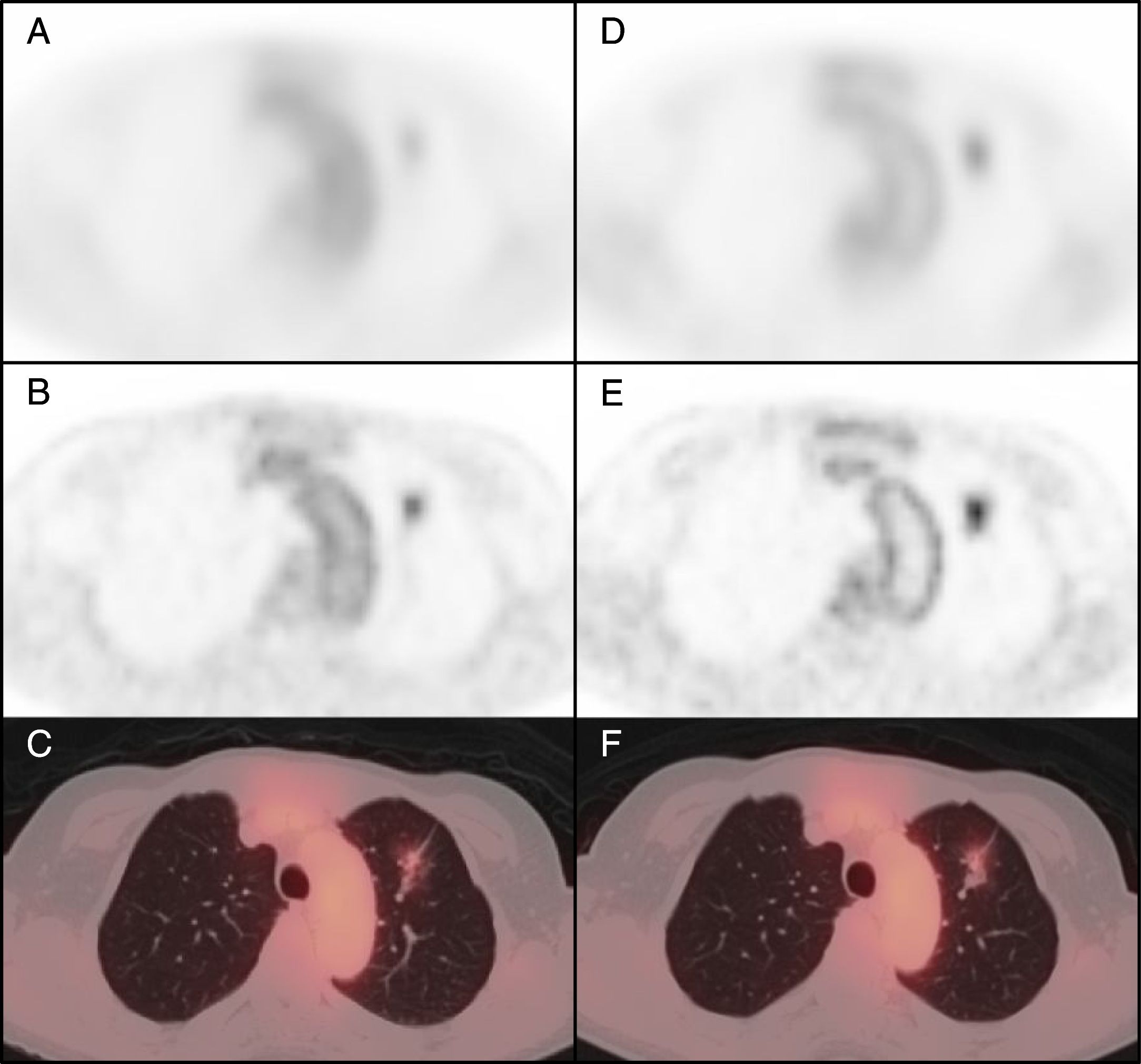
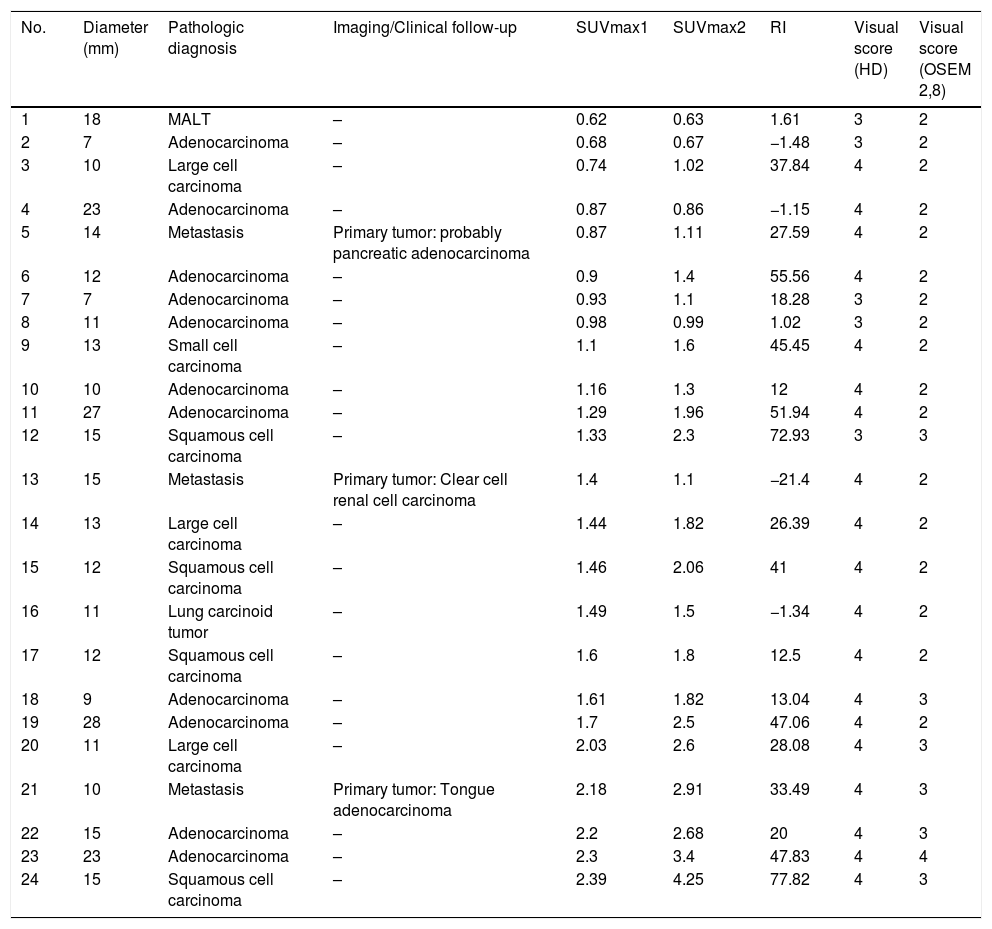
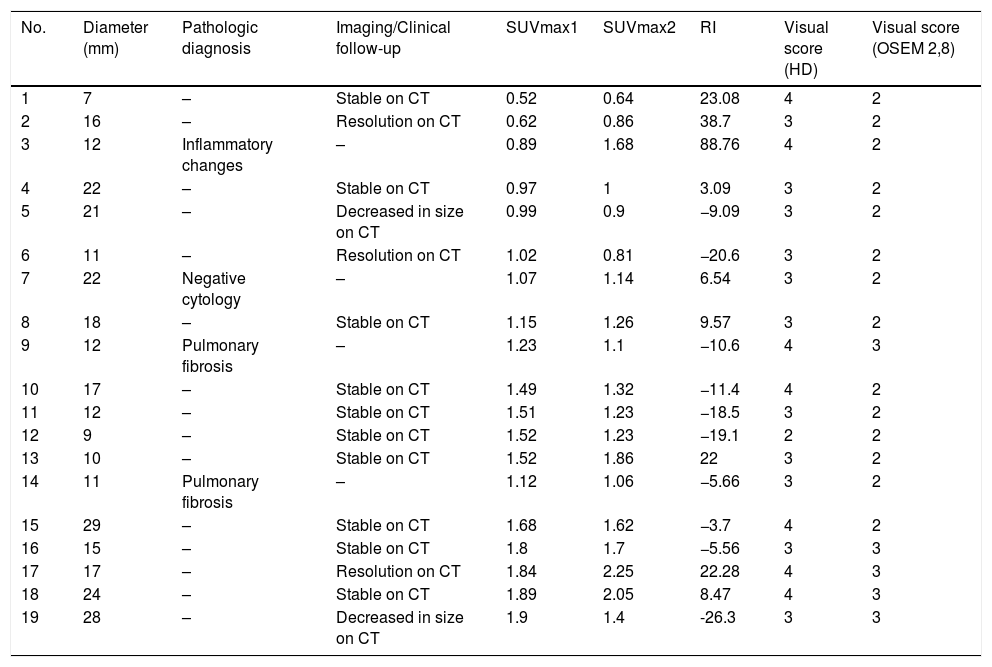
Materials and methodsA retrospective analysis was performed on 43 patients (28 men, 64±11 years old, range 36–83 years) referred for IPN characterization with 18F-FDG-PET/CT and maximum standard uptake value ≤2.5 at 60min post-injection (SUVmax1). Nodules were analyzed by size, visual score for FDG uptake on standard (OSEM 2,8) and high definition (HD) reconstructions, SUVmax1, SUVmax at 180min post-injection (SUVmax2), and RI was calculated. The definitive diagnosis was based on histopathological confirmation (n=28) or ≥2 years of follow-up.
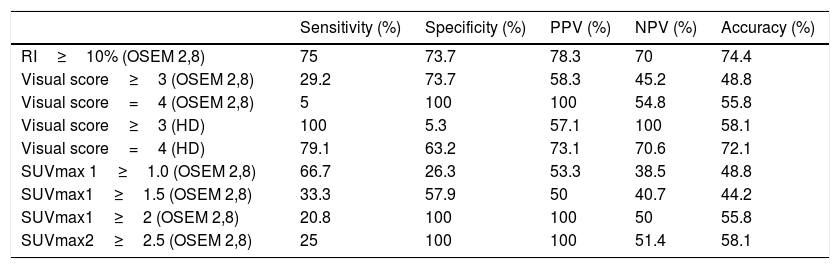
ResultsTwenty-four nodules (56%) were malignant. RI≥10% on standard reconstruction detected 18 nodules that would have been considered negative using the standard SUVmax≥2.5 criterion for malignancy. RI≥10% had a sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and accuracy of 75%, 73.7%, 78.3%, 70%, and 74.4%, respectively, while for FDG uptake>liver on HD these were 79.1%, 63.2%, 73.1%, 70.6%, and 72.1%, respectively. SUVmax1≥2, SUVmax2>2.5 and FDG uptake>liver on standard reconstruction had a PPV of 100%. FDG uptake>mediastinum on HD had a NPV of 100%.
ConclusionsRI≥% was the most accurate criterion for malignancy, followed by FDG uptake>liver on HD reconstruction. On standard reconstruction, SUVmax1≥2 was highly predictive of malignancy, as well as SUVmax2>2.5 and FDG uptake>liver. FDG uptake<mediastinum on HD was highly predictive of benign nodules.
Determinar la precisión del análisis visual y el índice de retención (RI) con el protocolo de imagen tardía con 18F-FDG PET/TC para la caracterización de los nódulos pulmonares indeterminados (NPI) con baja captación de FDG.
Materiales y métodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo en 43 pacientes (28 hombres, 64±11 años, rango 36-83 años) remitidos para la caracterización de NPI con 18F-FDG-PET/TC y SUVmax ≤2.5 a los 60minutos post-inyección (SUVmax1). Los nódulos se analizaron por tamaño, puntuación visual de la captación de FDG en las reconstrucciones estándar (OSEM 2,8) y de alta definición (HD), SUVmax1, SUVmax a 180 minutos post-inyección (SUVmax2), y se calculó el RI. El diagnóstico definitivo se basó en la confirmación histopatológica (n=28) o ≥2 años de seguimiento.
ResultadosVeinticuatro nódulos (56%) eran malignos. El RI≥10% en la reconstrucción estándar detectó 18 nódulos que habrían sido considerados negativos utilizando el criterio estándar SUVmax≥2.5 para malignidad. El RI≥10% obtuvo una sensibilidad, especificidad, VPP, VPN y una precisión del 75%, 73,7%, 78,3%, 70% y 74,4%, respectivamente, mientras que para la captación de FDG >hígado en la HD fueron del 79,1%, 63,2%, 73,1%, 70,6% y 72,1%, respectivamente. SUVmax1≥2, SUVmax2>2,5 y la captación de FDG>hígado en la reconstrucción estándar tuvieron un VPP del 100%. La captación de FDG>mediastino en la HD obtuvo un VPN del 100%.
ConclusionesEl RI≥10% fue el criterio más preciso para malignidad, seguido de la captación de FDG>hígado en la reconstrucción de la HD. En la reconstrucción estándar, el SUVmax1≥2 fue altamente predictivo de malignidad, así como el SUVmax2>2,5 y la captación de FDG >hígado. La captación de FDG
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)