To investigate the association between prostatic-specific antigen (PSA) levels and molecular tumor volume (MTV) measured in the 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT, both done in a short period of time, in prostate cancer patients with biochemical failure.
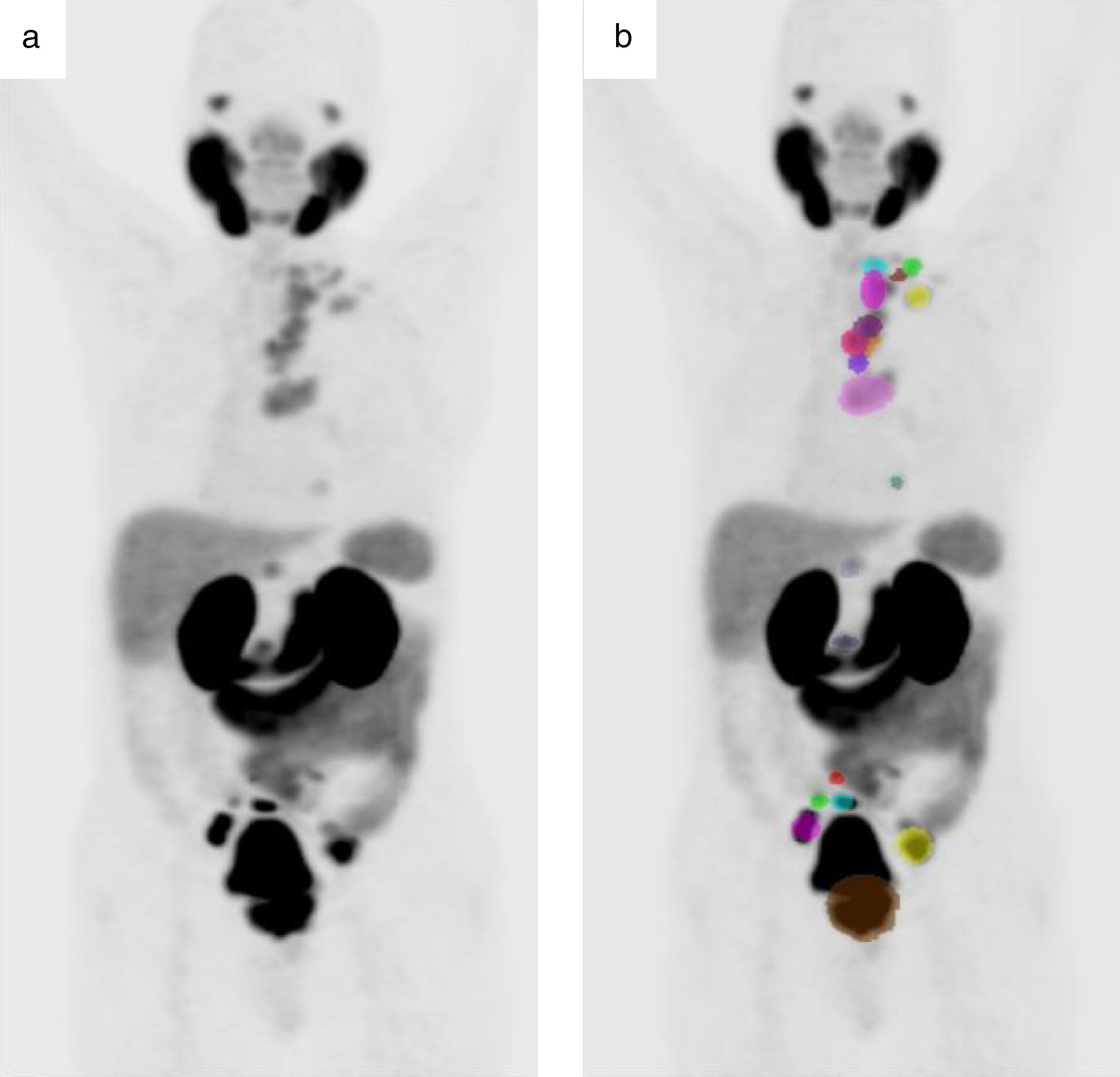
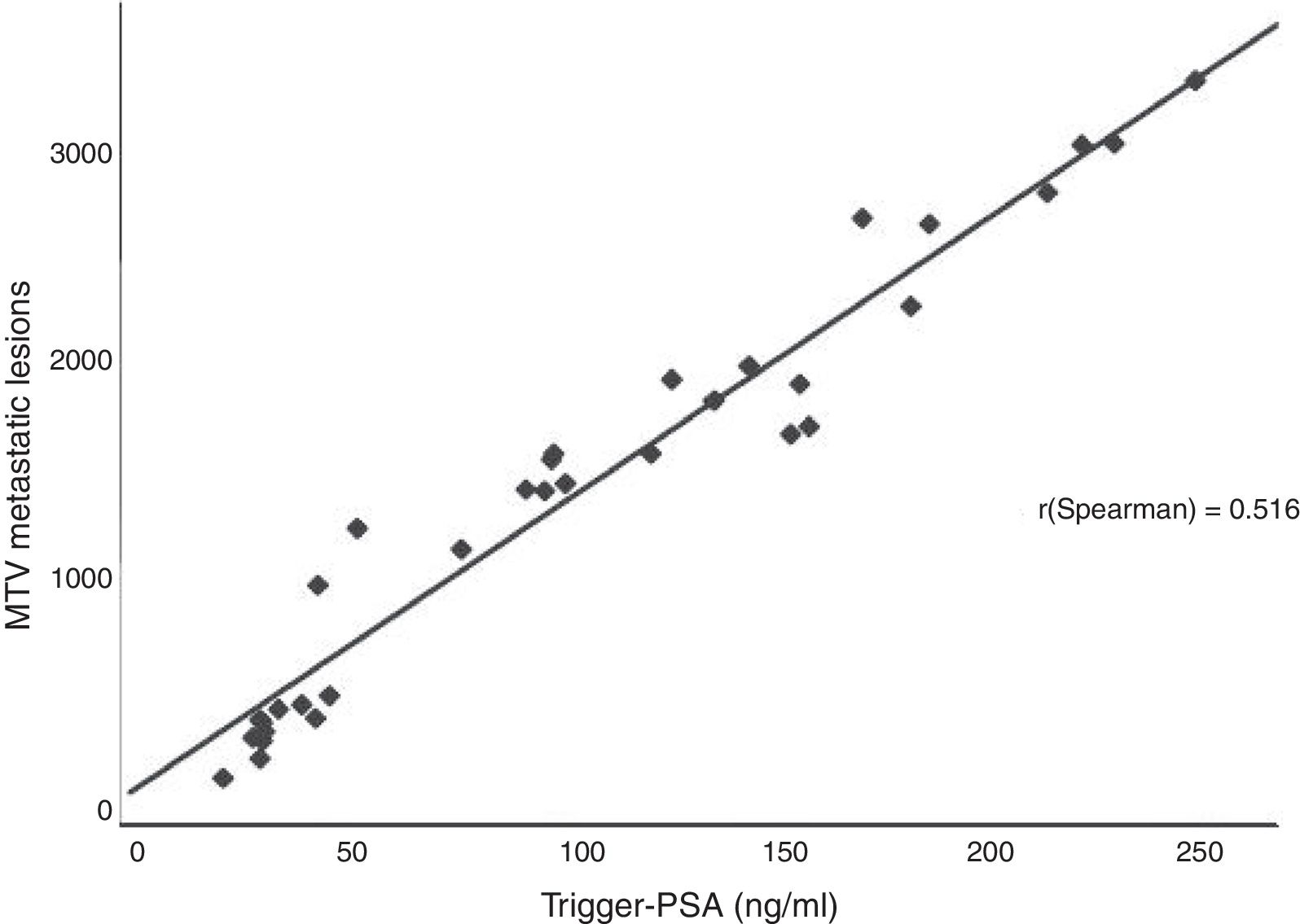
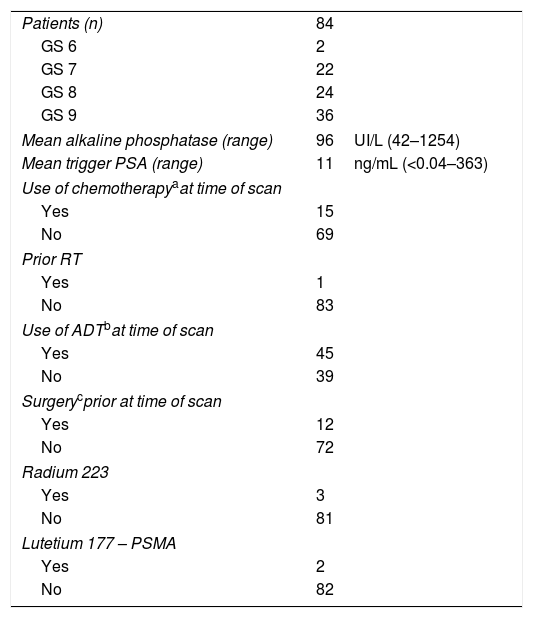
MethodsEighty-four patients who underwent 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT and measurement of PSA levels in the same week (Trigger-PSA) were studied in this retrospective analysis. MTV was calculated from the sum of the metastatic lesions. To determine the association between Trigger-PSA level and PET/CT findings, Spearman rank correlation was used.
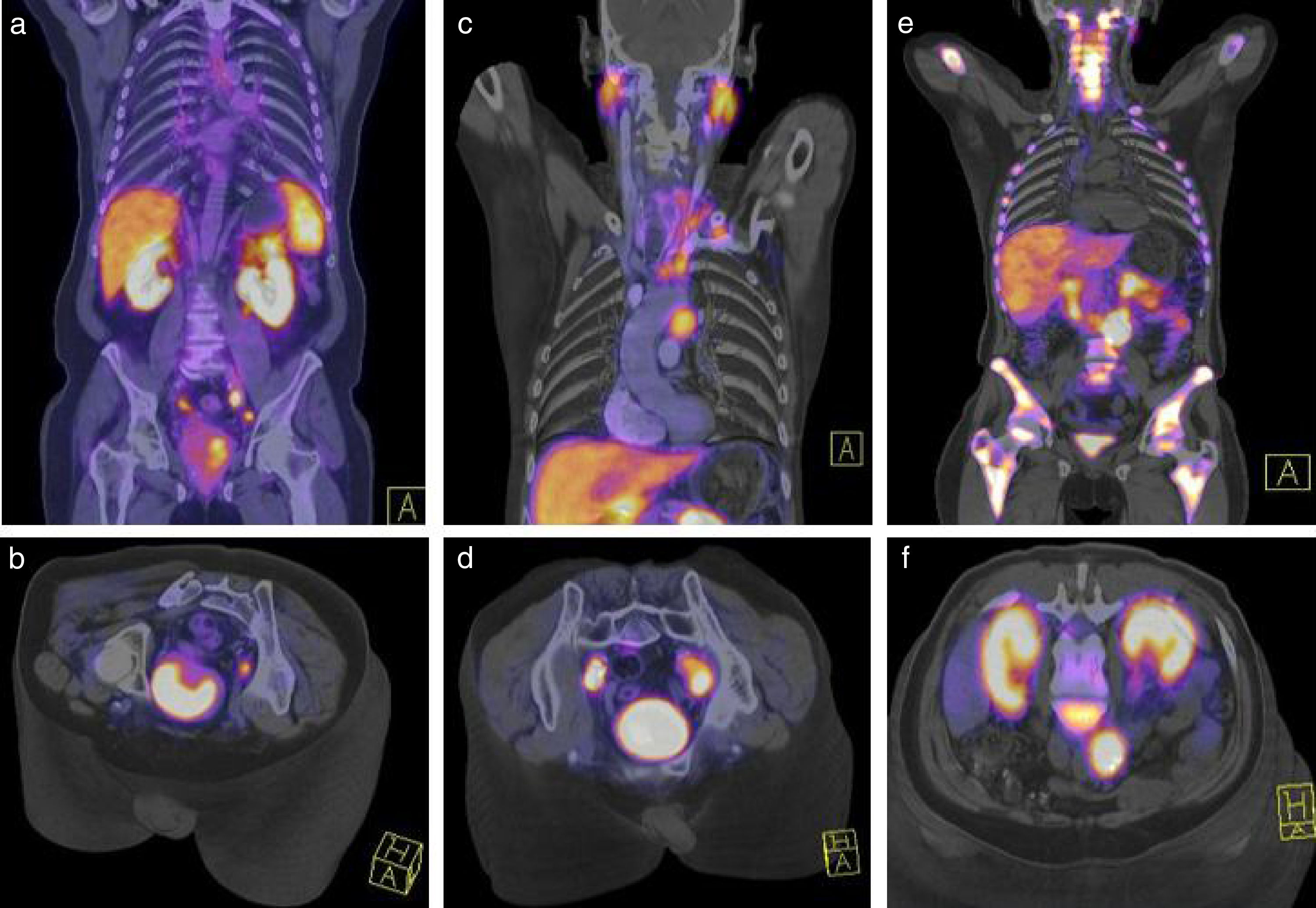
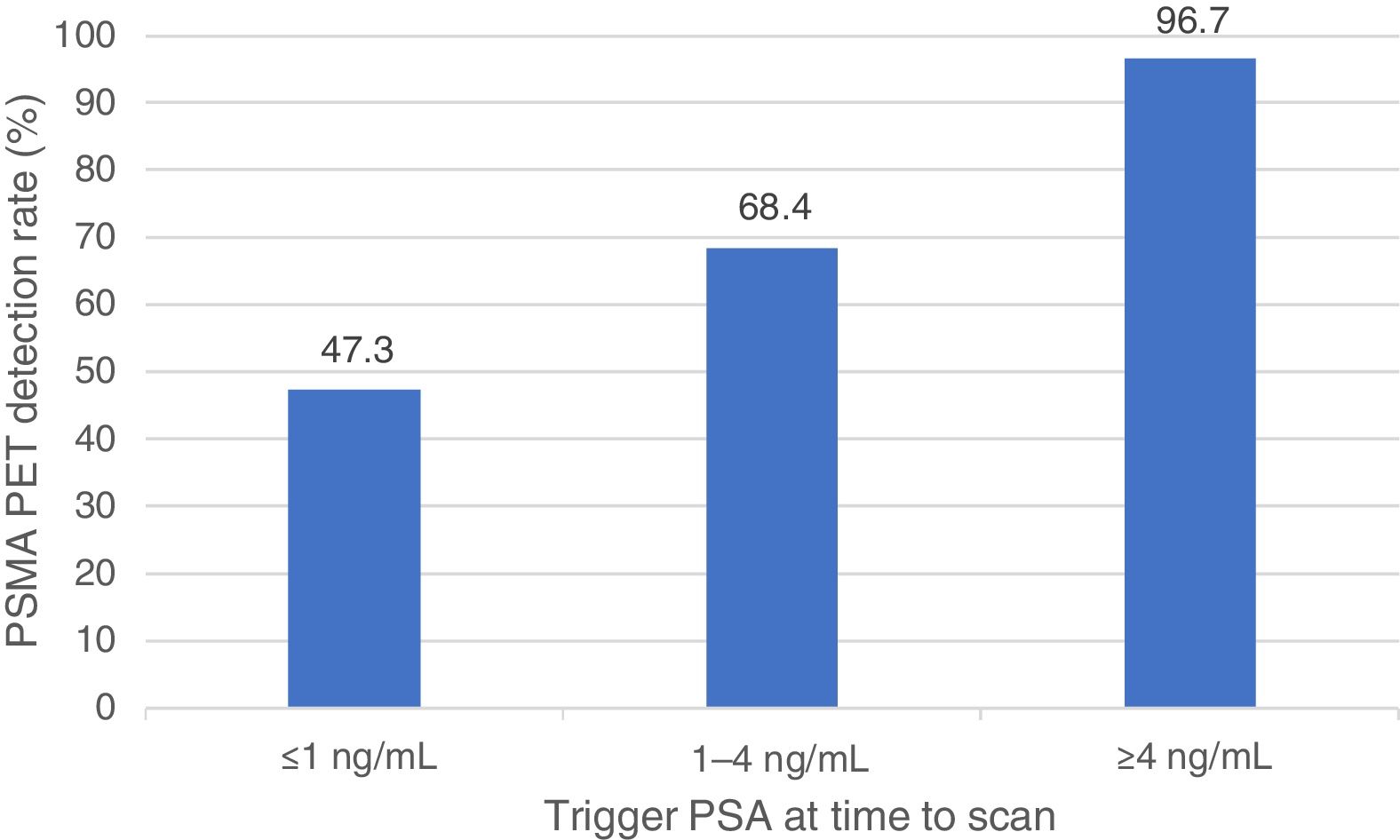
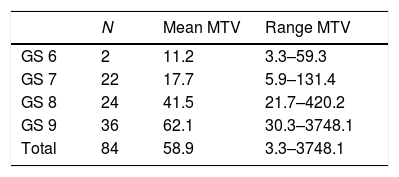
ResultsThe median MTV of metastatic bone disease (mBD) was significantly higher than in metastatic lymph-nodes (mLN) (139.5 versus 17.7; p<0.05). Disease was limited to the prostate (PG) in eight patients (9.5%); mLN in 21 patients (25%); mBD in 32 patients (38.1%); and the three sites (PG, mLN, and mBD) in 17 patients (20.2%). In 6 patients (6.14%), 68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT was not capable of detecting disease. The median Trigger-PSA levels of patients with disease limited to the PG (2.8ng/mL); mLN (6.8ng/mL); and for mBD (16.8ng/mL) was statically significant (p<0.05). Positive patients had a mean Trigger-PSA of 4.3ng/mL vs 1.5ng/mL in negative patients (p<0.05). We established three threshold-points for Trigger-PSA level detection rate: Trigger-PSA ≤1ng/mL, 47.3%; Trigger-PSA 1–4ng/mL, 68.4%; Trigger-PSA ≥4ng/mL, 96.7%. When Trigger-PSA exceeded >4ng/mL, the MTV higher (p<0.001).
ConclusionThe correlation of MTV with Trigger-PSA is demonstrated, which may have an impact on management. However, Trigger-PSA levels were not capable of distinguishing between localized or distant disease. An accurate detection of disease can lead to a better therapeutic strategy.
Investigar la asociación entre el nivel específico prostático (PSA) en el mismo momento de la realización de PET/CT con 68Ga-PSMA y el volumen tumoral metabólico (MTV) en pacientes con cáncer de próstata en progresión bioquímica.
MétodosEn este análisis retrospectivo se estudió a ochenta y cuatro pacientes sometidos a PET/CT con 68Ga-PSMA, a quienes se midieron los niveles de PSA en la misma semana (Trigger-PSA). Se calculó el MTV a partir de la suma de las lesiones metastásicas. Para determinar las relaciones entre el nivel de Trigger-PSA y los hallazgos de PET/CT, utilizamos la correlación de Spearman.
ResultadosEl MTV medio de la enfermedad ósea (mBD) fue significativamente superior al valor encontrado en los ganglios metastásicos (mLN) (139,5 frente a 17,7; p<0,05). La enfermedad se limitó a la próstata (PG) en ocho pacientes (9,5%,; mLN en 21 pacientes (25%), mBD en 32 pacientes (38,1%),y tres localizaciones en 17 pacientes (20,2%). En 6 pacientes (6,14%), la PET/CT con 68Ga-PSMA no fue capaz de detectar la enfermedad. Los niveles medios de Trigger-PSA en los pacientes con enfermedad limitada a PG (2,8ng/ml), mLN (6,8 ng/ml), y mBD (16,8ng/ml) fueron estadísticamente significativos (p<0,05). Los pacientes positivos tuvieron un Trigger-PSA medio de 4,3ng/ml frente a 1,5ng/ml en los pacientes negativos (p<0,05). Establecimos tres puntos límite para la tasa de detección del nivel de Trigger-PSA: Trigger-PSA ≤1ng/ml, 47.3%, Trigger-PSA 1–4ng/ml, 68,4%, Trigger-PSA ≥4ng/ml, 96,7%. Cuando Trigger-PSA excedió de >4ng/ml, MTV fue superior (p<0,001).
ConclusiónLos resultados evidencian la correlación de MTV con Trigger-PSA, lo cual puede tener impacto sobre el tratamiento. Sin embargo, los niveles de Trigger-PSA no permitieron distinguir entre la enfermedad localizada o a distancia. La estadificación precisa de la enfermedad podría permitir planificar la mejor estrategia terapéutica.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)