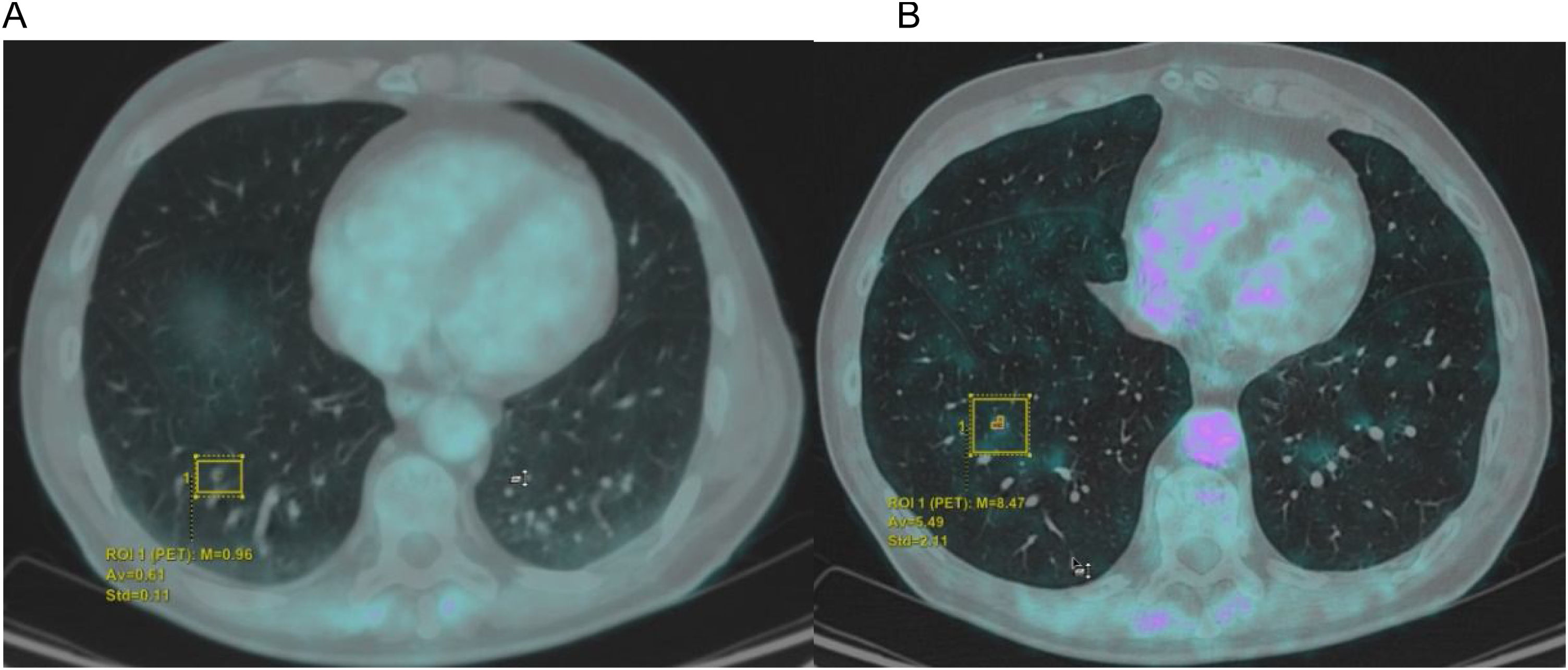
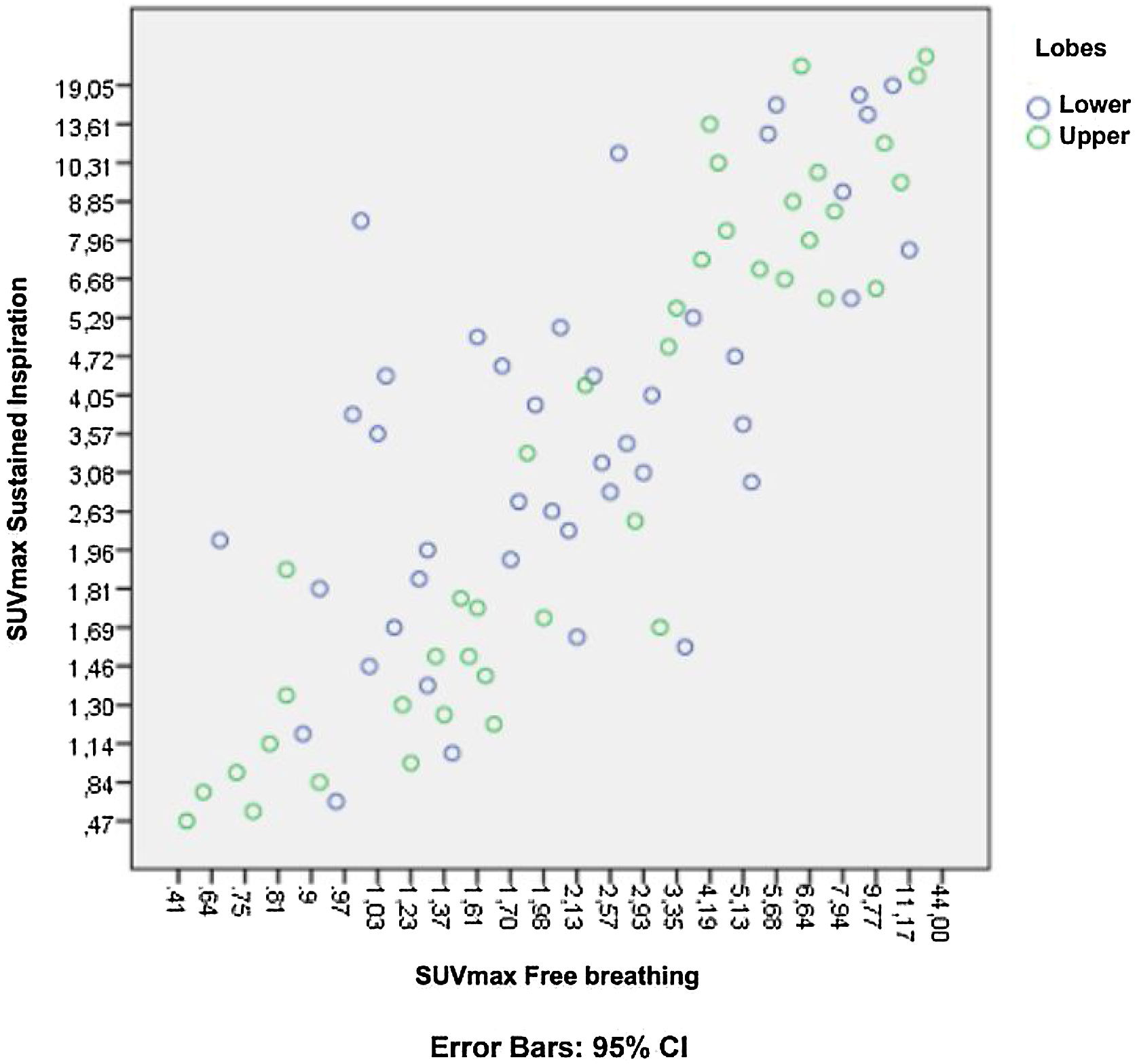
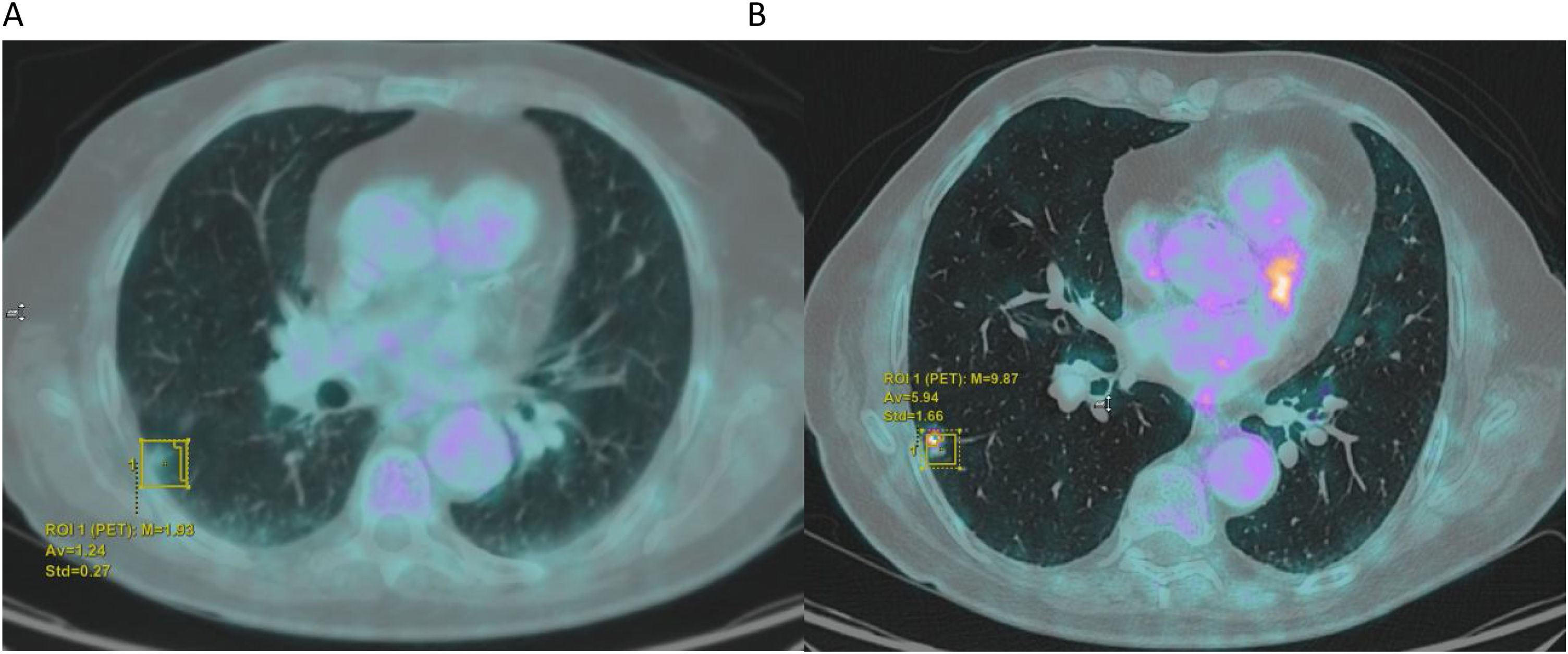
The characterization of pulmonary nodules (PN) is a primary indication for [18F]-FDG PET/CT. However, respiratory movements hinder this characterization, especially for PN located in the lower lobes. Various methods have been developed to improve image resolution.
ObjectiveOur objective was to compare the diagnostic efficacy of [18F]-FDG PET/CT in deep inspiration breath-hold (DIBH) versus free-breathing corrected by software, in the evaluation of PN.
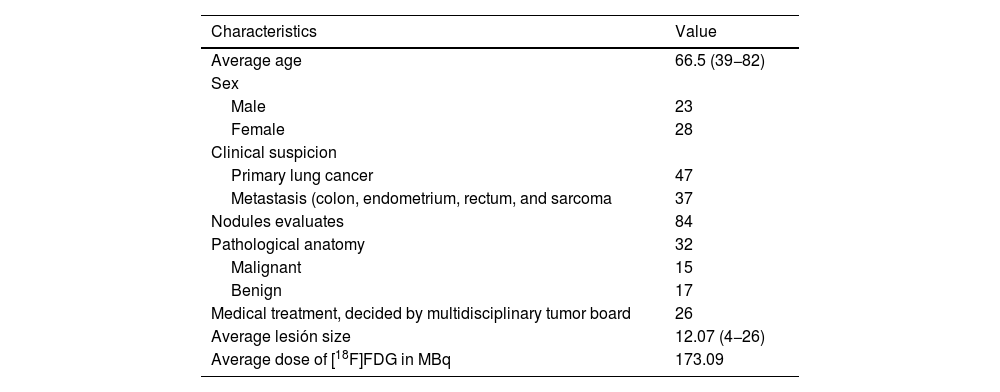
MethodsWe prospectively analyzed 51 patients to assess PN using [18F]-FDG PET/CT in DIBH and free-breathing corrected by software. A total of 84 nodules with an average size of 10 mm were analyzed, with pathological anatomy or medical treatment decide by a multidisciplinary tumor board used as reference.
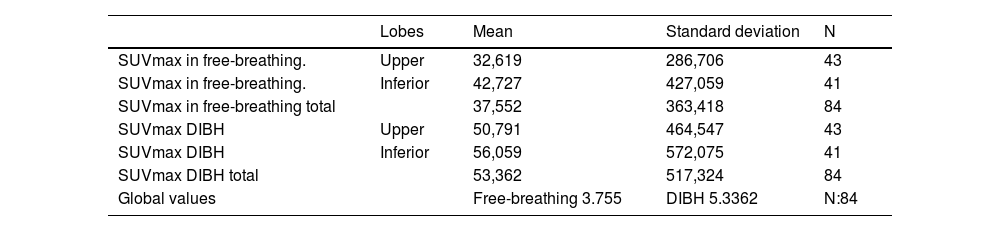
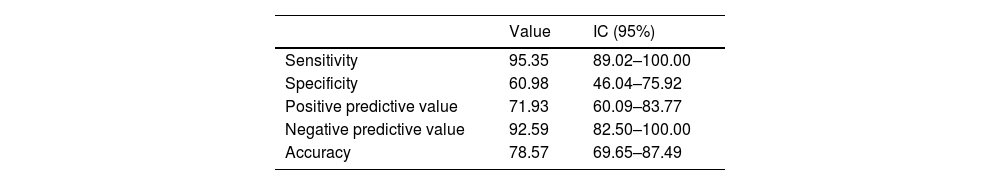
ResultsA total of 84 PN were evaluated, comparing those in DIBH versus free-breathing, finding statistically significant differences in SUVmax values P(< 0.05) (mean SUVmax 3.7 in free-breathing vs. 5.33 in DIBH). When analyzed by location in lobes, we did not find statistically significant differences, though there was a trend towards higher SUVmax values in the lower lobes. [18F]-FDG PET/CT in DIBH showed high sensitivity (95%) and negative predictive value (NPV) (92%), indicating it may be a promising tool for PN characterization.
ConclusionsThe acquisition of [18F]-FDG PET/CT in DIBH significantly improves the sensitivity and diagnostic efficacy in the assessment of PN. Although no statistically significant differences were found based on location, there is a potential benefit for the lower lobes. These findings could support its use in clinical practice.
La caracterización de los nódulos pulmonares (NP) es una indicación principal del [18F]-FDG PET/TC. Sin embargo, los movimientos respiratorios dificultan esta caracterización, en especial la de los NP localizados en lóbulos inferiores (LLII). Existen varios métodos que han mejorado la resolución de las imágenes.
ObjetivoNuestro objetivo fue comparar la eficacia diagnóstica de [18F]-FDG PET/TC en inspiración profunda mantenida (IPM) frente a la respiración libre corregida por software, para evaluar los NP.
MétodosAnalizamos prospectivamente 51 pacientes para evaluar NP mediante [18F]-FDG PET/TC en IPM y en inspiración libre corregidas por software. Se analizaron 84 nódulos con un tamaño medio de 10 mm y se usó como referencia la anatomía patológica o tratamiento médico decidio por un comité de tumores multidisciplinar.
ResultadosSe valoraron 84 NP comparando aquellos en IPM versus respiración libre encontrando diferencias estadísticamente significativas en los valores de SUVmax P(< 0,05) (media SUVmax 3.7 en inspiración libre vs 5,33 IPM). Al analizar por localización en lóbulos no encontramos diferencias estadísticamente significativas, pero si una tendencia a aumentar los valores del SUVmax en LLII. El [18F]-FDG PET/TC en IPM mostró una sensibilidad (95%) y un valor predictivo negativo (VPN) (92%) alto, pudiendo ser una herramienta prometedora para la caracterización de NP.
ConclusionesLa adquisición de [18F]-FDG PET/TC en IPM mejora significativamente la sensibilidad y eficacia diagnóstica en la valoración de NP. Aunque no se encontraron diferencias estadísticas significativas según la localización, hay un beneficio potencial en los LLII. Hallazgos que podrían respaldar su uso en la práctica clínica.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)