To compare the diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/MR and PET/CT preliminarily for the thoracic staging of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with a special focus on pleural invasion evaluation.
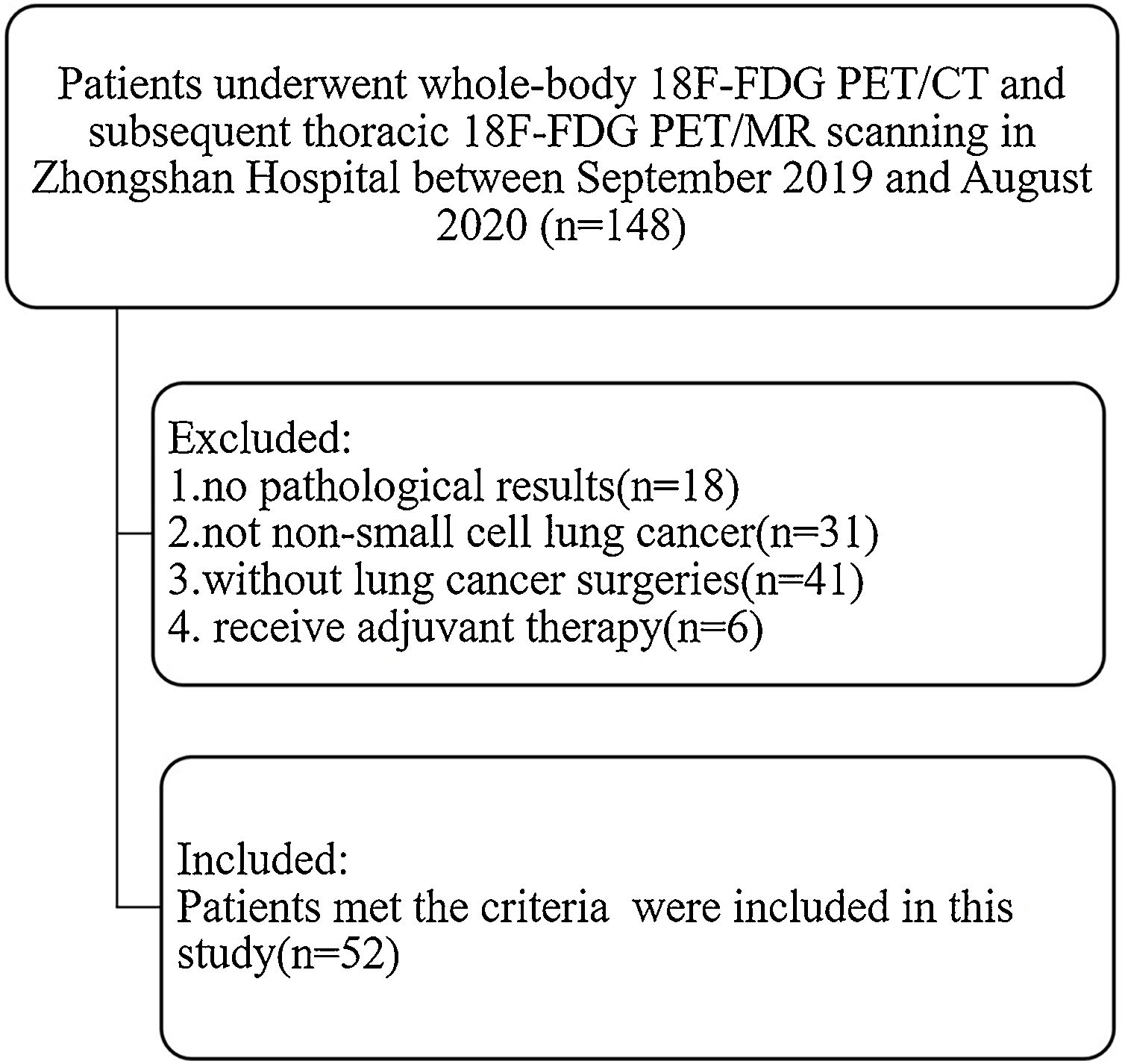
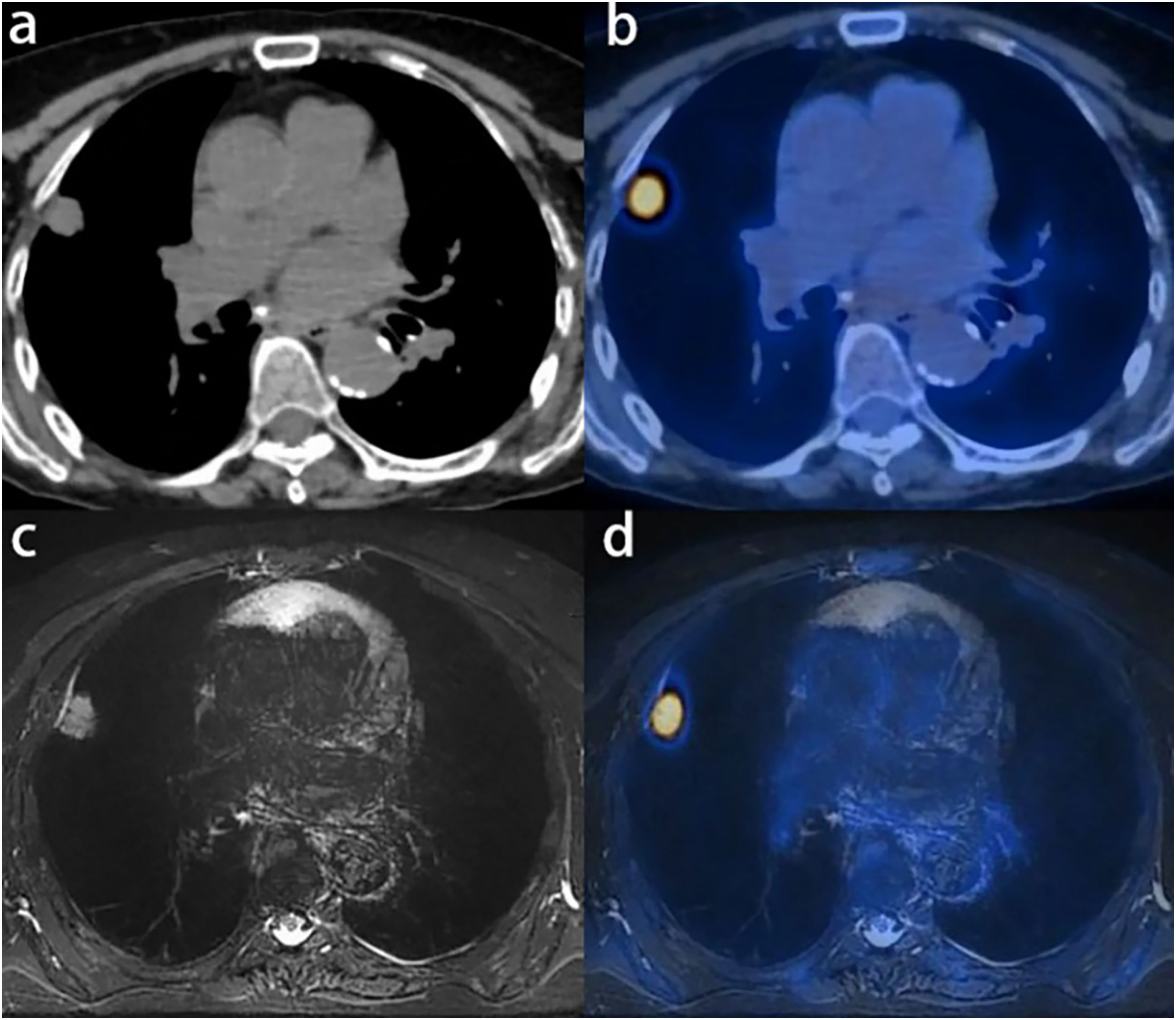
Methods52 patients with pathologically confirmed NSCLC were included and followed for another year. Whole-body 18F-FDG PET/CT and subsequent thoracic PET/MR were performed for initial thoracic staging. Thoracic (simultaneous) PET/MR acquired PET images and MRI sequences including T2 weighted imaging, with and without fat saturation, T1 weighted imaging, and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI). Two radiologists independently assessed the thoracic T, N staging and pleural involvement. The McNemar Chi-square test was used to compare the differences between PET/CT and PET/MR in the criteria. The area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curves (AUC) was calculated.
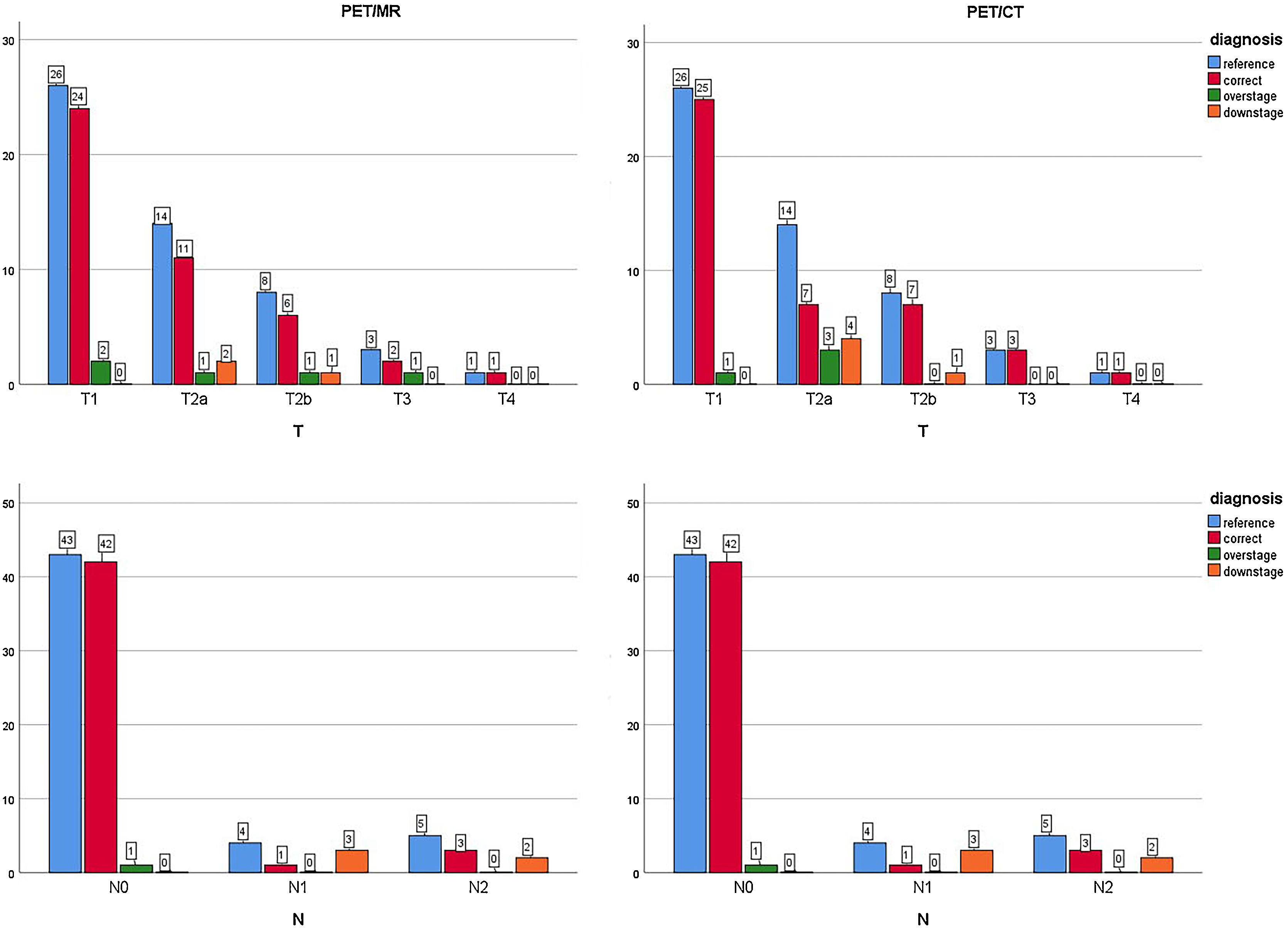
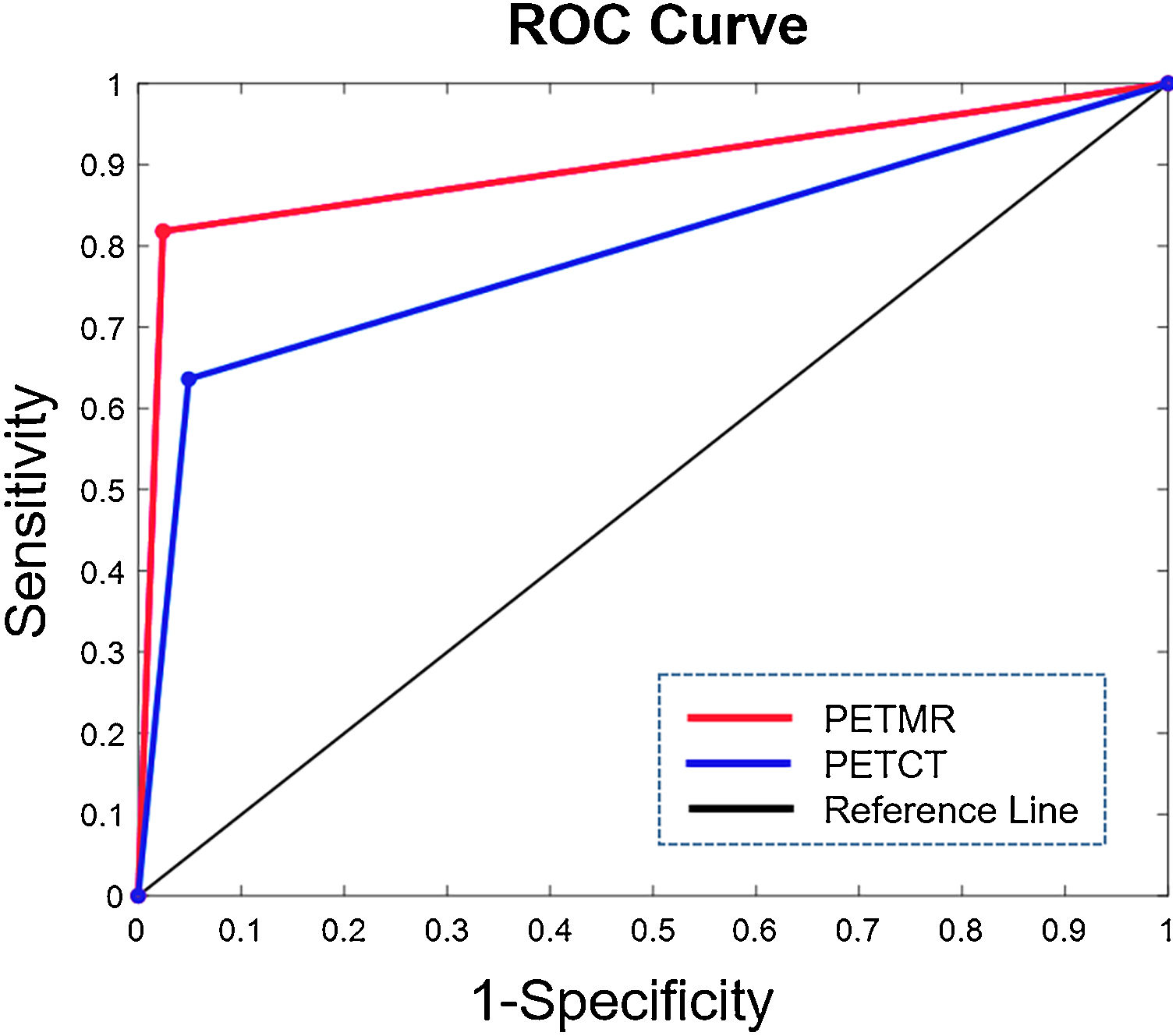
ResultsCompared to PET/CT, PET/MR exhibited higher sensitivity, specificity in the detection of pleural invasion; 82 % vs. 64% (p = 0.625), 98 % vs. 95% (p = 1.000), PET/MR to PET/CT respectively. The receiver-operating-characteristic analysis results of PET/CT vs PET/MR for the pleural invasion were as follow: AUCPET/CT = 0.79, AUCPET/MR = 0.90, p = 0.21. Both T staging results and N staging results were approximately identical in PET/CT and PET/MR. Differences between PET/CT and PET/MR in T staging, N staging as well as pleural invasion accuracy were not statistically significant (p > 0.05, each).
ConclusionPET/MR and PET/CT demonstrated equivalent performance about the evaluation of preoperative thoracic staging of NSCLC patients. PET/MR may have greater potential in pleural invasion evaluation for NSCLC, especially for solid nodules, crucial to clinical decision-making, though our results did not demonstrate statistical significance.
Comparar el rendimiento diagnóstico de la PET/RM con 18F-FDG y la PET/TC de forma preliminar para la estadificación torácica del cáncer de pulmón de células no pequeñas (NSCLC) con un enfoque especial en la evaluación de la invasión pleural.
MétodosSe incluyeron 52 pacientes con NSCLC patológicamente confirmado y se les dio seguimiento durante otro año. Se realizaron PET/TC con 18F-FDG de cuerpo entero y PET/RM torácica posterior para la estadificación torácica inicial. Imágenes de PET/RM adquiridas torácicas (simultáneas) y secuencias de RM que incluyen imágenes ponderadas en T2, con y sin saturación de grasa, imágenes ponderadas en T1 e imágenes ponderadas por difusión (DWI). Dos radiólogos evaluaron de forma independiente la estadificación T, N torácica y la afectación pleural. Se utilizó la prueba de Chi-cuadrado de McNemar para comparar las diferencias entre PET/TC y PET/RM en los criterios. Se realizó análisis ROC con calculó el área bajo la curva (AUC) para la invasión pleural.
ResultadosEn comparación con la PET/TC, la PET/RM mostró una mayor sensibilidad y especificidad en la detección de invasión pleural; 82% frente a 64% (p = 0,625), 98% frente a 95% (p = 1.000), PET/RM a PET/TC respectivamente. Los resultados del análisis ROC de PET/TC vs PET/RM para la invasión pleural fueron los siguientes: AUC PET/TC = 0.79, AUC PET/RM = 0.90, p = 0.21. Tanto los resultados de la estadificación T como los resultados de la estadificación N fueron aproximadamente idénticos en PET/TC y PET/RM. Las diferencias entre PET/TC y PET/RM en la estadificación T, la estadificación N y la precisión de la invasión pleural no fueron estadísticamente significativas (p > 0,05, cada una).
ConclusiónLa PET/RM y PET/TC demostraron un rendimiento equivalente en la evaluación de la estadificación torácica preoperatoria de pacientes con NSCLC. La PET/RM puede tener un mayor potencial en la evaluación de invasión pleural para NSCLC, especialmente para nódulos sólidos, cruciales para la toma de decisiones clínicas, aunque nuestros resultados no demostraron significación estadística.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)