Parathyroid adenoma (PA) is the most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism (PHPT). 99mTc-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (99mTc-MIBI) imaging is widely applied in PA diagnosis and location. However, since the individual heterogeneity and adenoma function differences, the diagnostic efficacy of 99mTc-MIBI imaging is limited, which often leads to misdiagnosis and even mistreatment of PA.
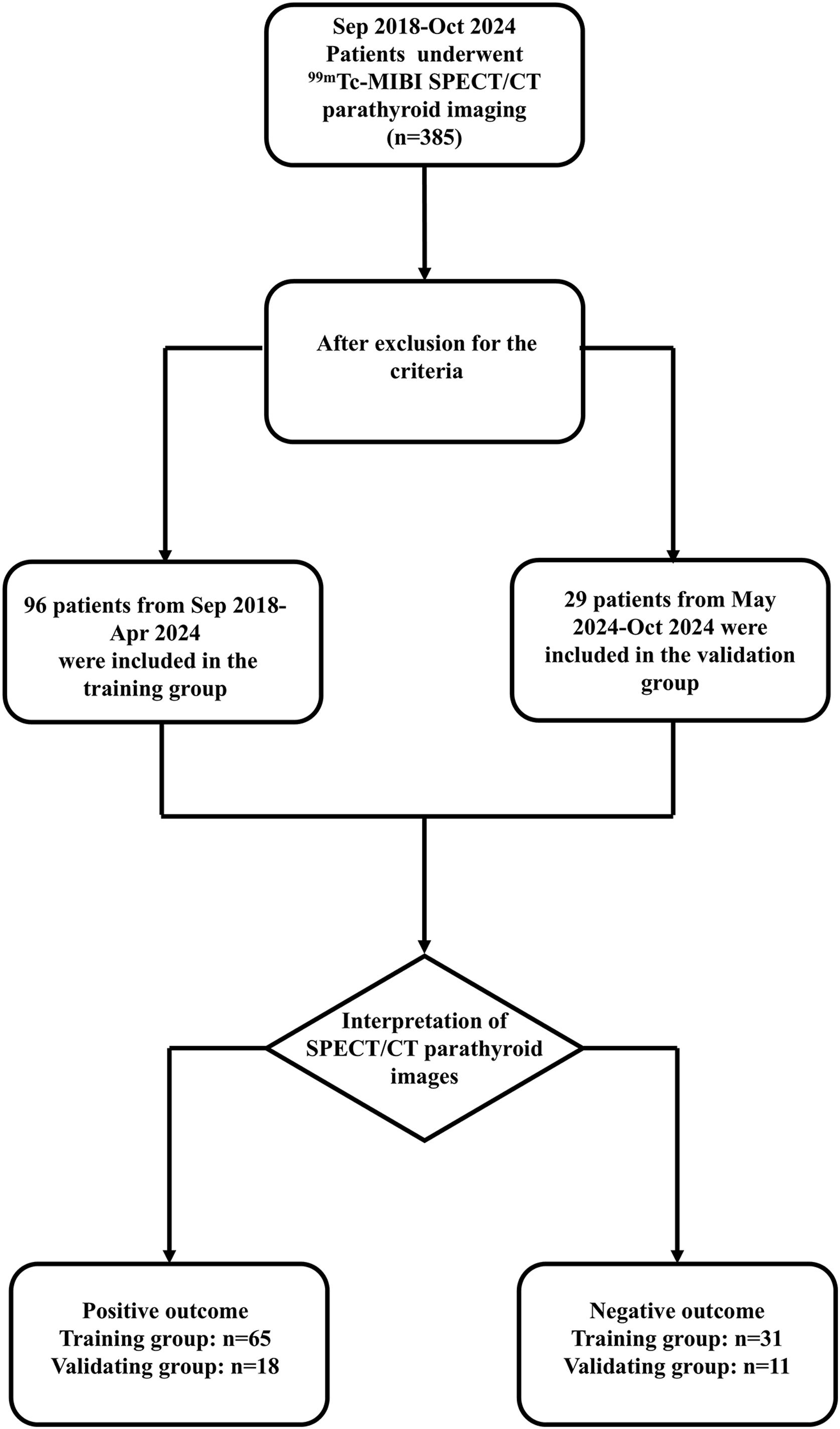
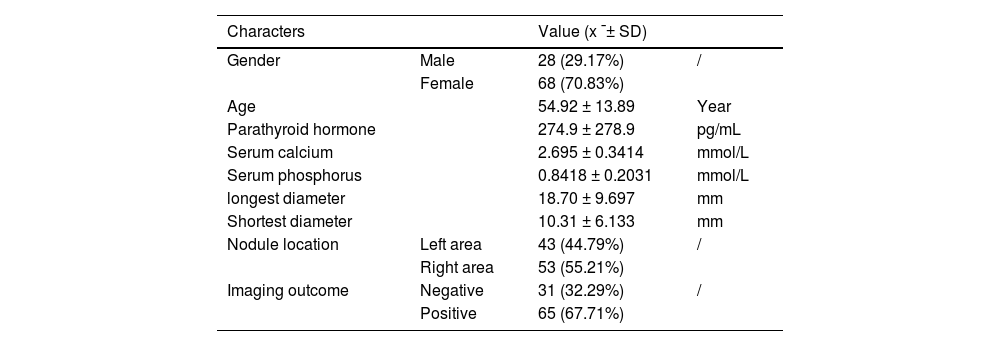
MethodsIn the present study, we established a novel dynamic nomogram model to assist the nuclear imaging diagnosis of PA. A total of 96 PA patients, with 65 cases in the positive group and 31 cases in the negative group, were enrolled for further analyzing.
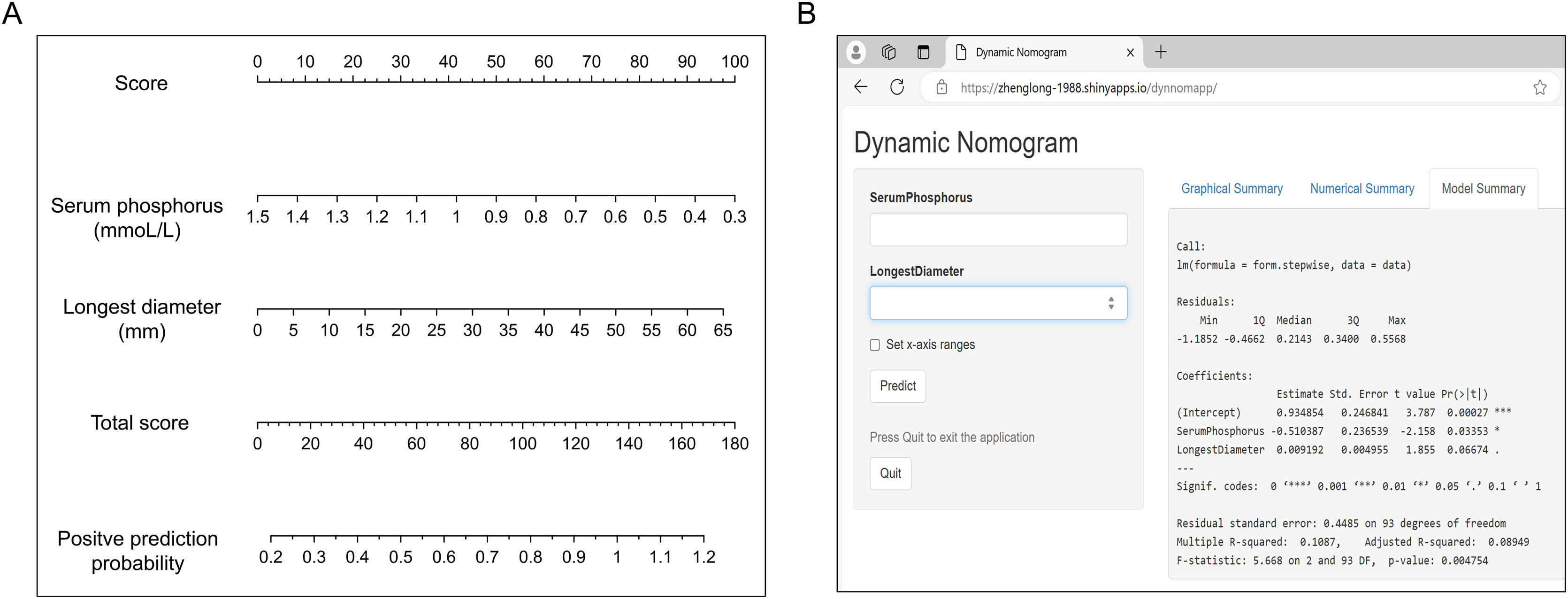
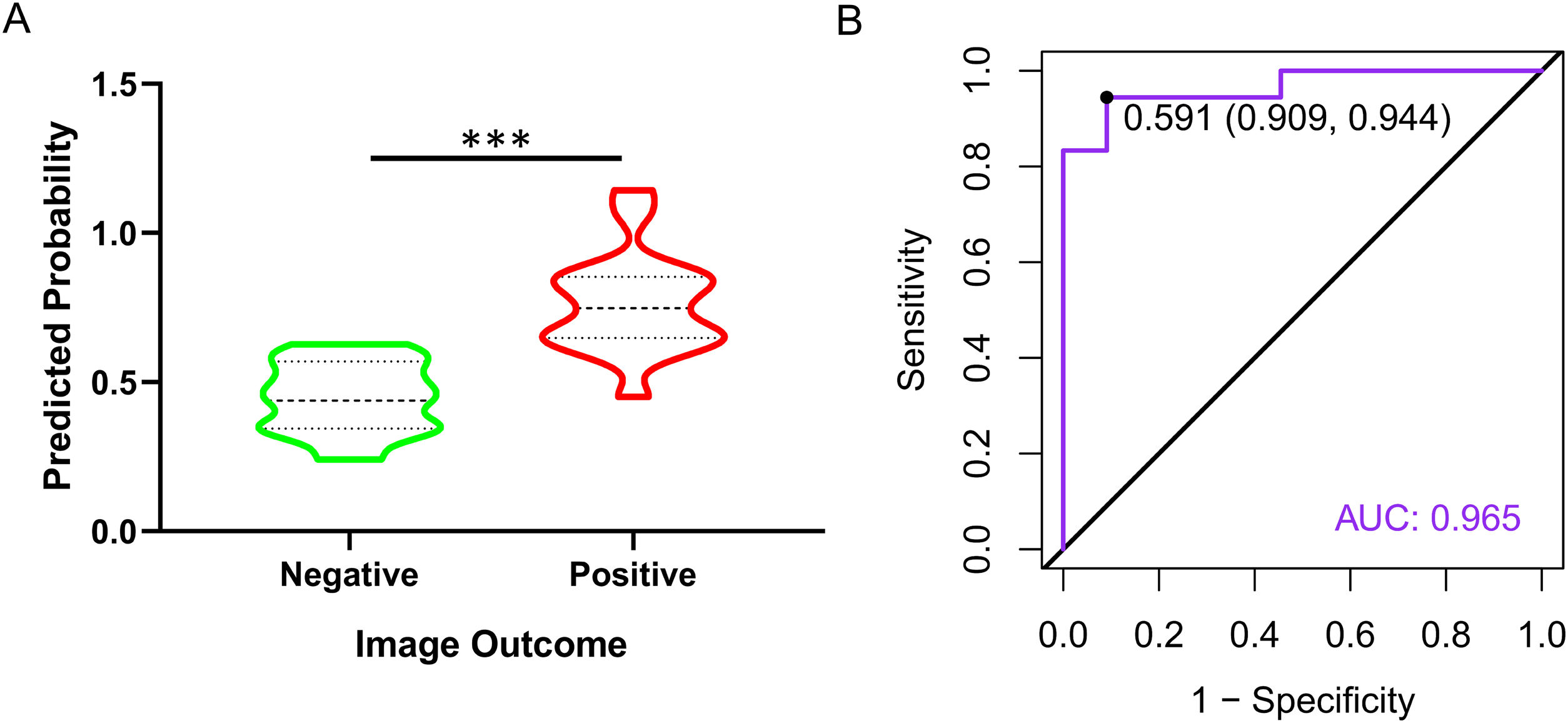
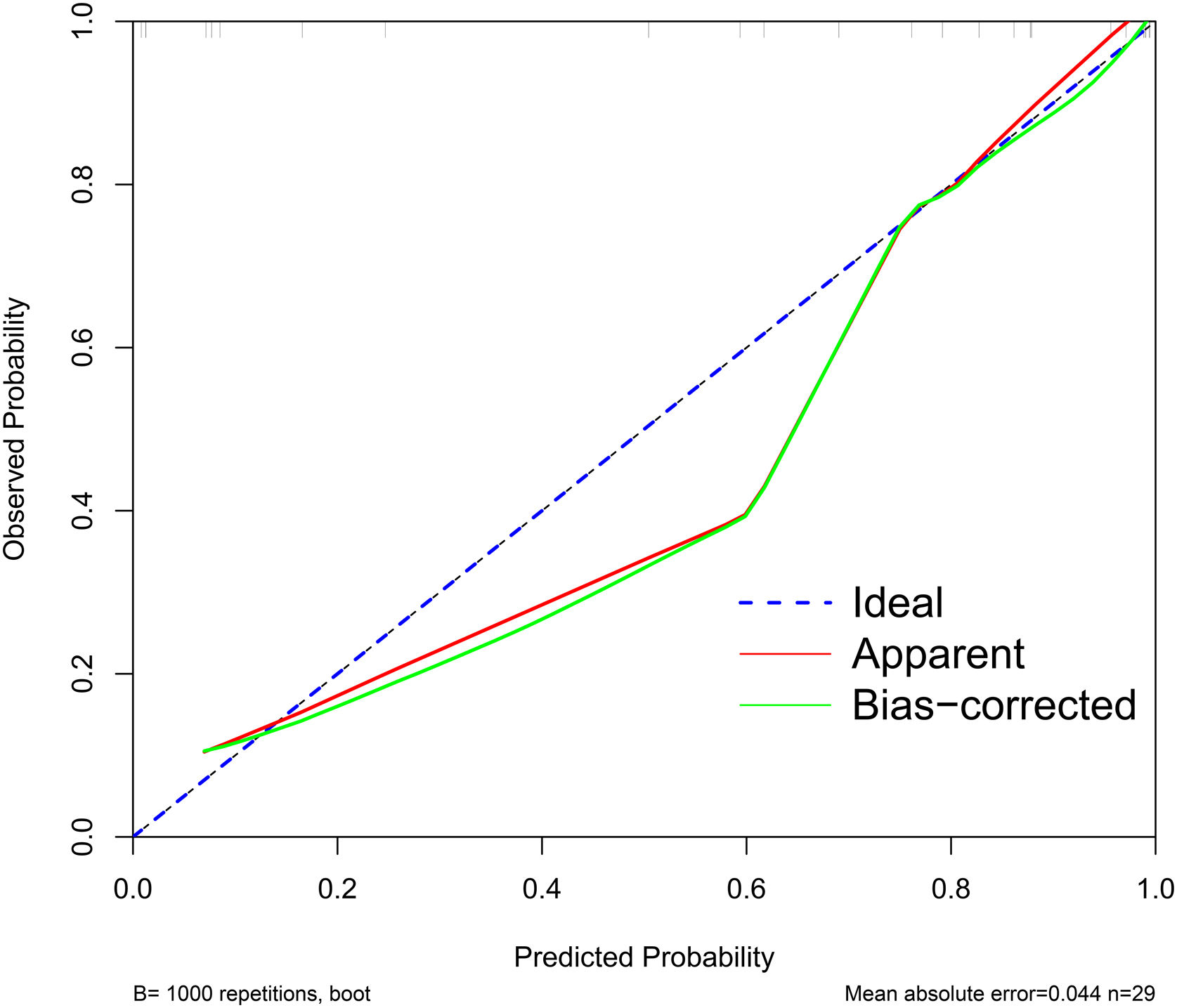
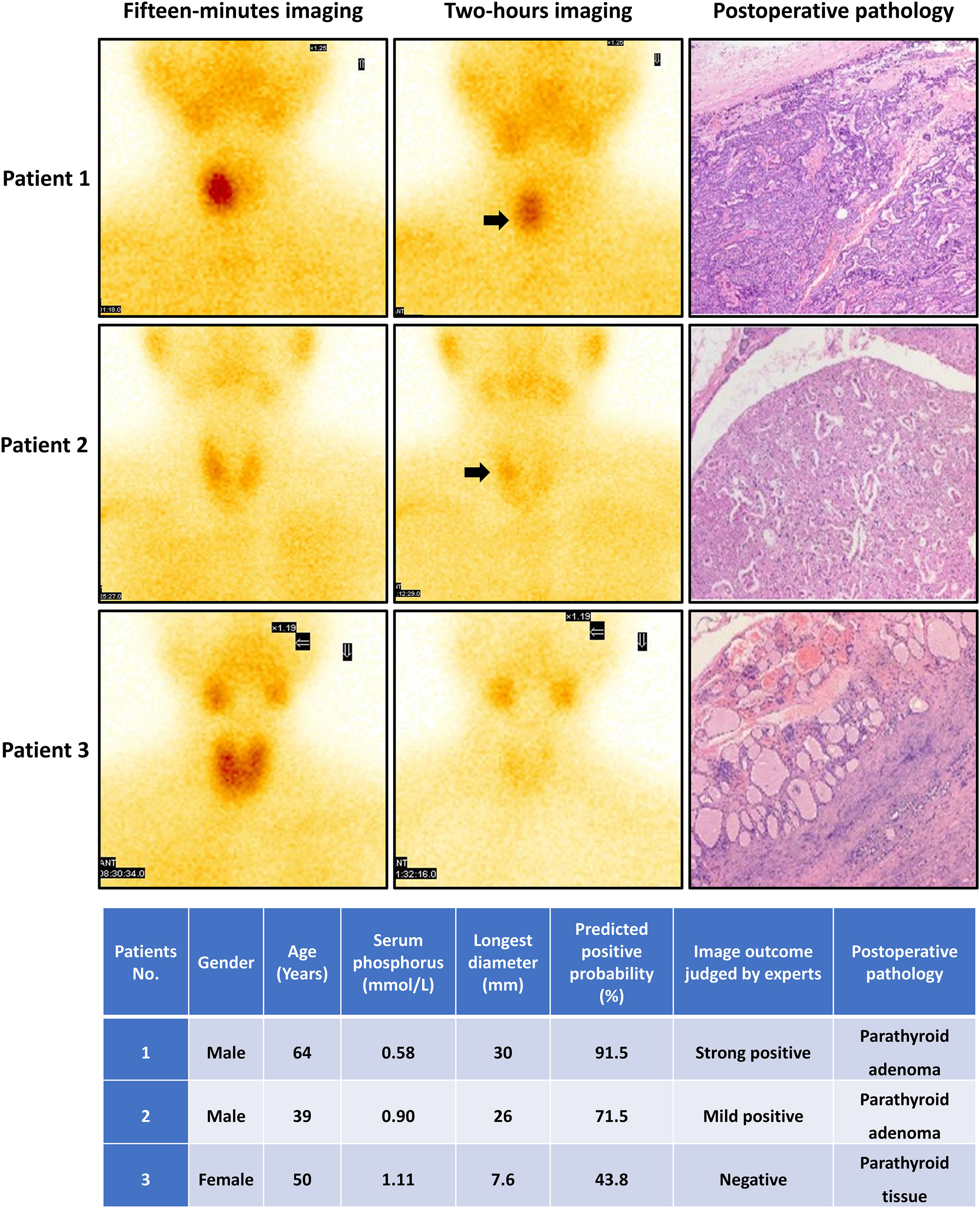
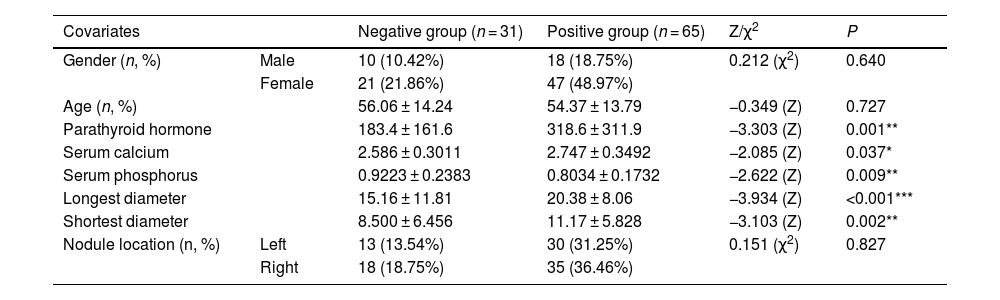
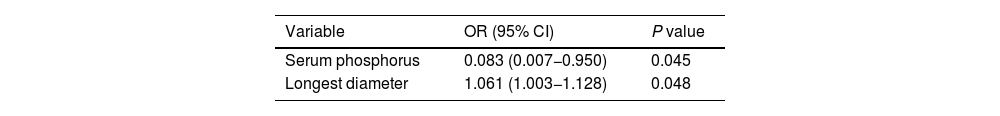
ResultsUnivariate analysis showed there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in terms of gender, age, and adenoma location. The patients in the positive group had significantly higher levels in PTH, serum calcium, longest diameter and shortest diameter of adenoma, compared to those in the negative group. But the serum phosphorus levels were lower in the positive group than in the negative group. Binary logistic regression analysis indicated that serum phosphorus and adenoma longest diameter were independent positive predictors. The dynamic nomogram model was generated by R software and logistic regression analysis (https://zhenglong-1988.shinyapps.io/dynnomapp/). The receiver operating characteristics curve (ROC curve) analysis revealed that the cut-off probability for the model to diagnose PA was 59.1%, with AUC values of 0.965.
ConclusionsThe novel dynamic nomogram diagnostic model integrating serum phosphorus levels and longest diameter could effectively improve the diagnostic accuracy of radionuclide imaging for PA.
El adenoma paratiroideo (AP) es la causa más común de hiperparatiroidismo primario (HPTP). La imagenología con 99mTc-metoxisobutilisonitrilo (99mTc-MIBI) se aplica ampliamente en el diagnóstico y localización del AP. Sin embargo, debido a la heterogeneidad individual y las diferencias en la función del adenoma, la eficacia diagnóstica de la imagenología con 99mTc-MIBI es limitada, lo que a menudo conduce al diagnóstico erróneo e incluso al mal tratamiento del AP.
MétodosEn el presente estudio, establecimos un nuevo modelo de nomograma dinámico para ayudar en el diagnóstico por imagenología nuclear del AP. Se incluyeron un total de 96 pacientes con AP, 65 casos en el grupo positivo y 31 casos en el grupo negativo, para un análisis adicional.
ResultadosEl análisis univariado mostró que no hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre los dos grupos en términos de género, edad y localización del adenoma. Los pacientes del grupo positivo tenían niveles significativamente más altos de PTH, calcio sérico, diámetro más largo y diámetro más corto del adenoma en comparación con los del grupo negativo. Pero los niveles de fósforo sérico fueron más bajos en el grupo positivo que en el grupo negativo. El análisis de regresión logística binaria indicó que el fósforo sérico y el diámetro más largo del adenoma eran predictores positivos independientes. El modelo de nomograma dinámico se generó mediante el software R y el análisis de regresión logística (https://zhenglong-1988.shinyapps.io/dynnomapp/). El análisis de la curva de características operativas del receptor (curva ROC) reveló que la probabilidad umbral para que el modelo diagnosticara AP era del 59,1%, con valores de AUC de 0,965.
ConclusionesEl nuevo modelo de diagnóstico de nomograma dinámico que integra los niveles de fósforo sérico y el diámetro más largo podría mejorar efectivamente la precisión diagnóstica de la imagenología con radionúclidos para el AP.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)