Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and cellular antioxidant activity. Overproduction of ROS causes oxidative damage to major macromolecules, alters homeostasis and leads to the generation of different pathologies. At present, there is no totally effective treatment to counteract these diseases involved with oxidative stress, so it is necessary to investigate new treatment alternatives that suppress the ROS generated. One promising alternative is the use of plant extracts, which have demonstrated a potent antioxidant effect. Efficient cells for the study of pathological diseases related to reactive oxygen species are T lymphocytes, which share systems with neurons such as: the dopaminergic system, death signaling and survival. In vitro lymphocytes are an optimal model for the evaluation of oxidative mechanisms.
ObjectiveTo determine the protective effect of ethanolic extract of propolis against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in human lymphocytes in vitro, by means of the cell viability test with trypan blue.
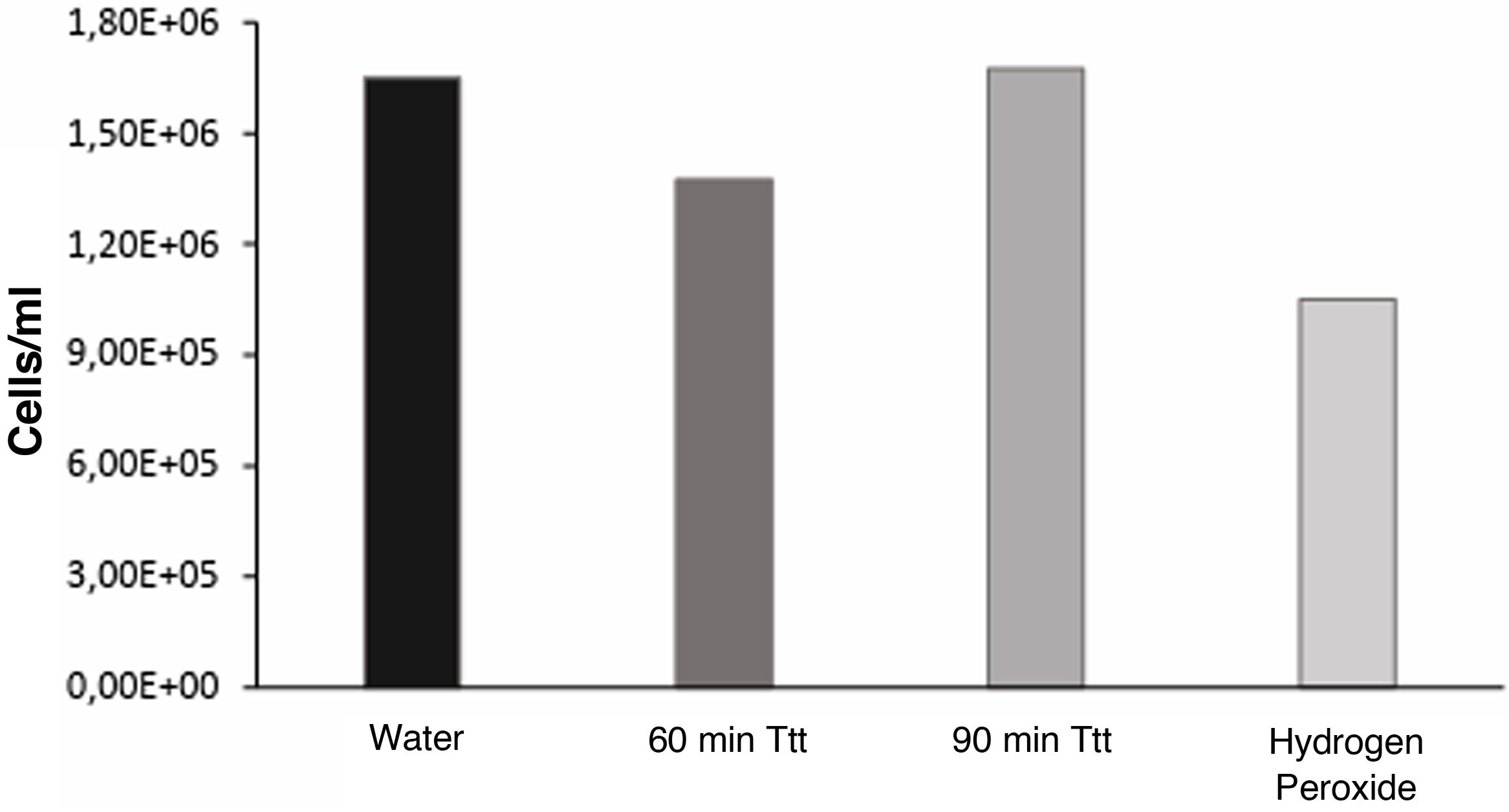
ResultsAnova test shows that the concentrations of 0.0225 and 0.045 mg/mL of ethanolic extract of propolis, present protective activity against cell damage caused by H2O2.
ConclusionThis study proposes the ethanolic extract of propolis as a potential pharmacological, useful for treatments against autoinmune disorders.
El estrés oxidativo ocurre cuando hay un desequilibrio entre la producción de especies reactivas de oxígeno (ROS) y la actividad antioxidante celular. La sobreproducción de ROS causa daño oxidativo en las principales macromoléculas, altera la homeostasis y conlleva la aparición de diferentes patologías. En la actualidad no existe un tratamiento totalmente efectivo para contrarrestar estas enfermedades implicadas con el estrés oxidativo, por lo cual es necesario indagar en nuevas alternativas de tratamientos que supriman las ROS generadas. Una alternativa prometedora es el uso de extractos vegetales, que ha demostrado un potente efecto antioxidante. Las células eficientes para el estudio de enfermedades patológicas relacionadas con las especies reactivas de oxígeno son los linfocitos T, los cuales comparten sistemas con las neuronas, como el sistema dopaminérgico, la señalización de muerte y la supervivencia. Los linfocitos in vitro son un modelo óptimo para la evaluación de mecanismos oxidativos.
ObjetivoDeterminar el efecto protector del extracto etanólico de propóleo frente al daño oxidativo inducido con peróxido de hidrógeno (H2O2) en linfocitos humanos in vitro mediante conteo de linfocitos.
ResultadosEl análisis estadístico con Anova demuestra que las concentraciones de 0,0225 y 0,045 mg/mL del extracto etanólico de propóleo presentan actividad protectora frente al daño celular provocado por H2O2.
ConclusiónEl presente estudio propone al extracto etanólico de propóleo como un potencial farmacológico, útil para tratamientos contra las patologías autoinmunes.