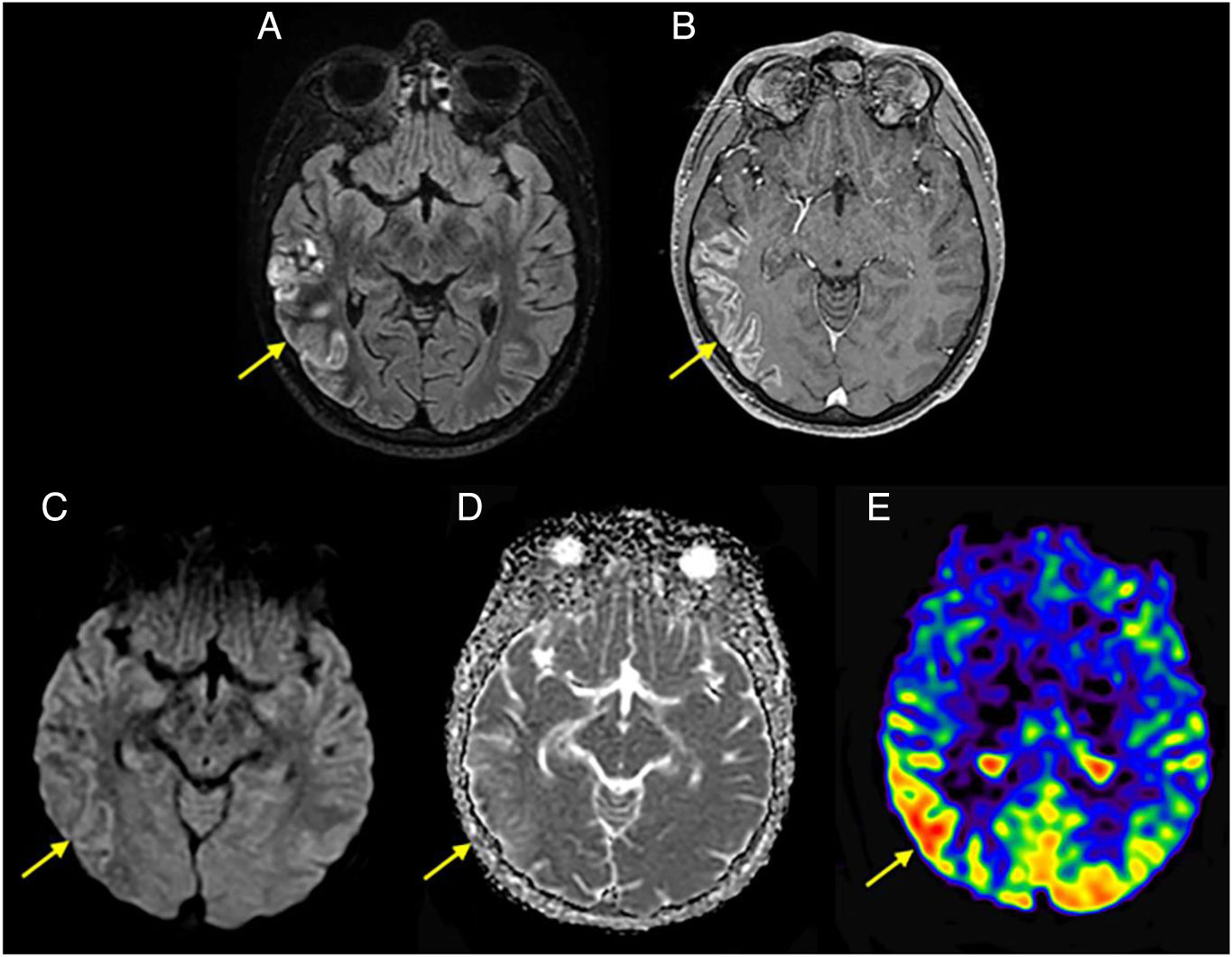
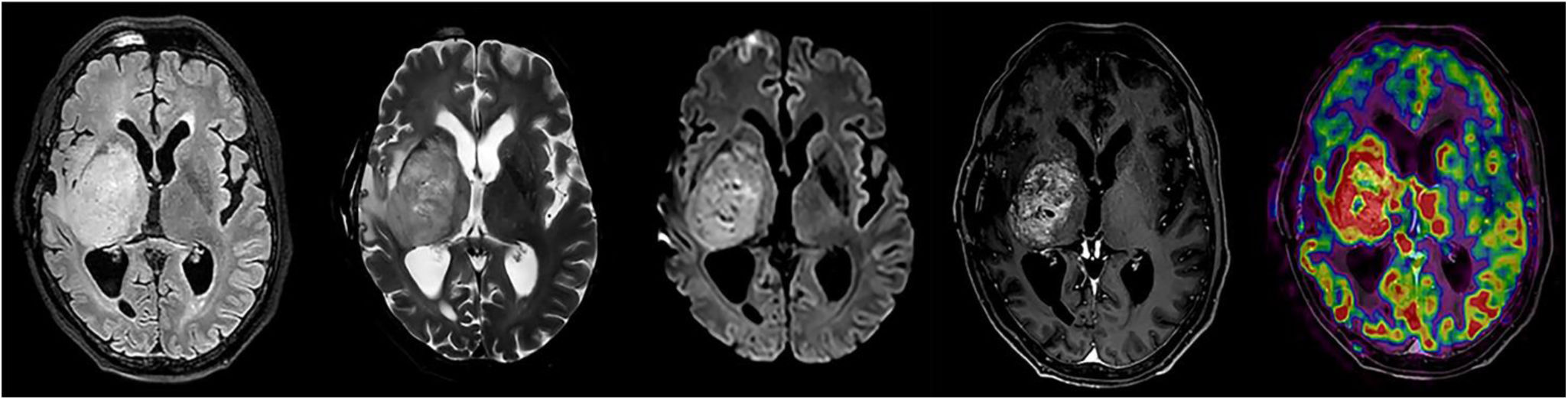
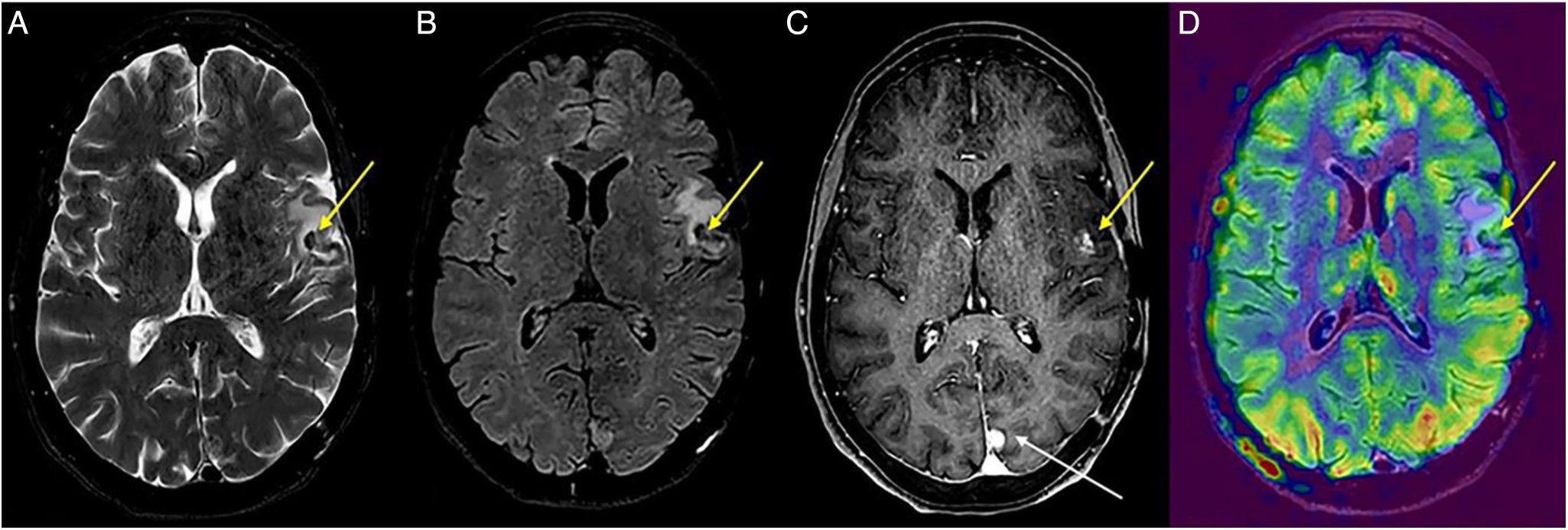
Arterial spin labelling (ASL) is a magnetic resonance imaging perfusion technique used to study cerebral blood flow. It differs from magnetic susceptibility-based perfusion sequences in that it does not require contrast media, but rather uses the signals emitted by pre-labelled protons. It is useful in the exploration of several different kinds of neurological pathologies including ischaemic stroke, brain tumours, dementia and epilepsy. However, it presents numerous artifacts that radiologists must be familiar with to ensure a correct interpretation of findings.
Arterial spin labelling (ASL) es una técnica de perfusión cerebral por de resonancia magnética utilizada para el estudio del flujo sanguíneo cerebral. Se diferencia de las secuencias de perfusión basadas en susceptibilidad magnética por no requerir medios de contraste, sino que aprovecha la señal emitida por los protones previamente marcados. Tiene utilidad en el estudio de diversas patologías neurológicas de diferente naturaleza como el ictus isquémico, los tumores cerebrales, las demencias o la epilepsia entre otros. No obstante, presenta numerosos artefactos que deben ser conocidos por el radiólogo para una correcta interpretación de los hallazgos.