Artificial intelligence models can provide textual answers to a wide range of questions, including medical questions. Recently, these models have incorporated the ability to interpret and answer image-based questions, and this includes radiological images. The main objective of this study is to analyse the performance of ChatGPT-4o compared to third-year medical students in a Radiology and Applied Physics in Medicine practical exam. We also intend to assess the capacity of ChatGPT to interpret medical images and answer related questions.
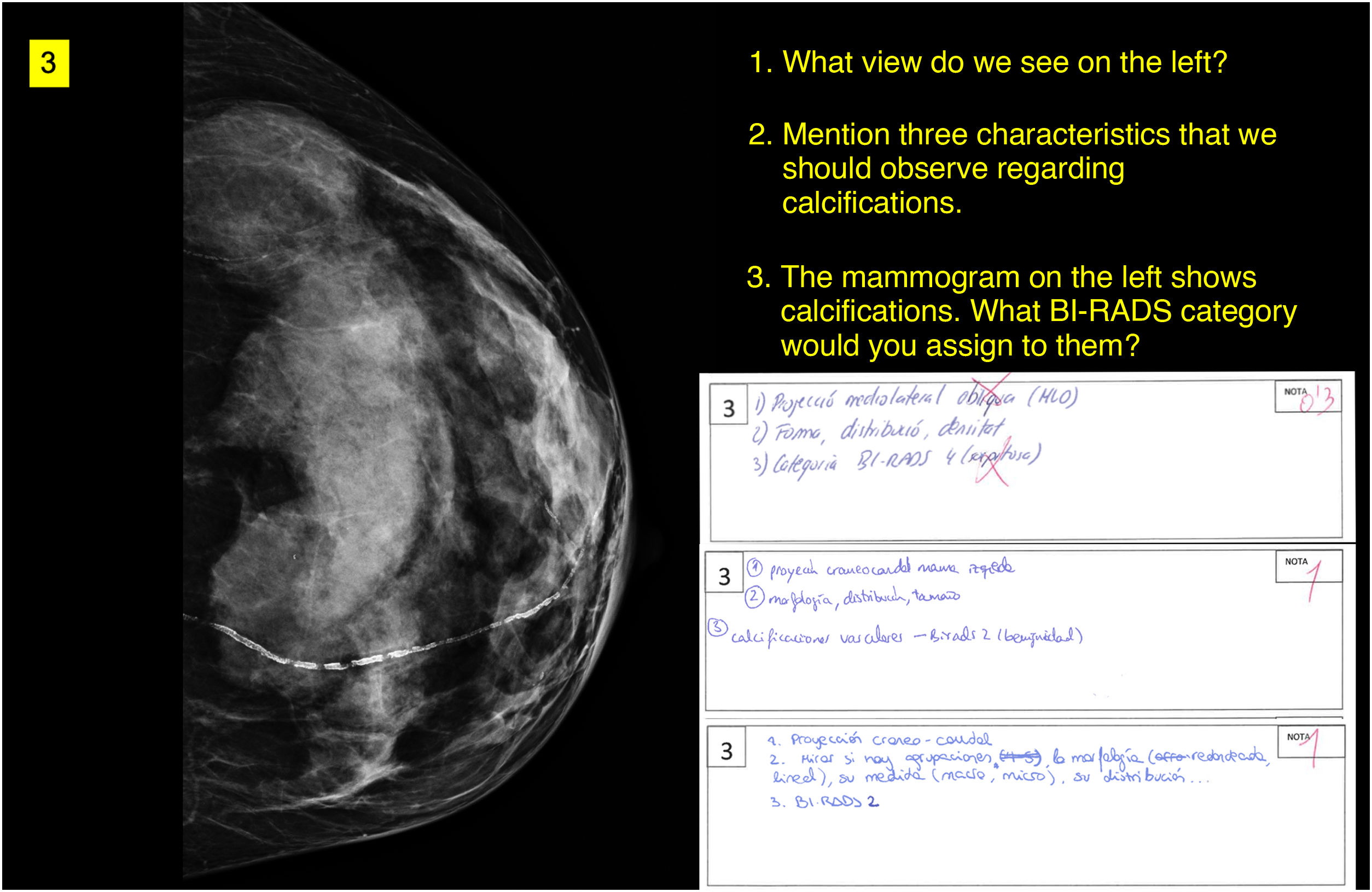
Materials and methodsThirty-three students set an exam of 10 questions on radiological and nuclear medicine images. Exactly the same exam in the same format was given to ChatGPT (version GPT-4) without prior training. The exam responses were evaluated by professors who were unaware of which exam corresponded to which respondent type. The Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the results of the two groups.
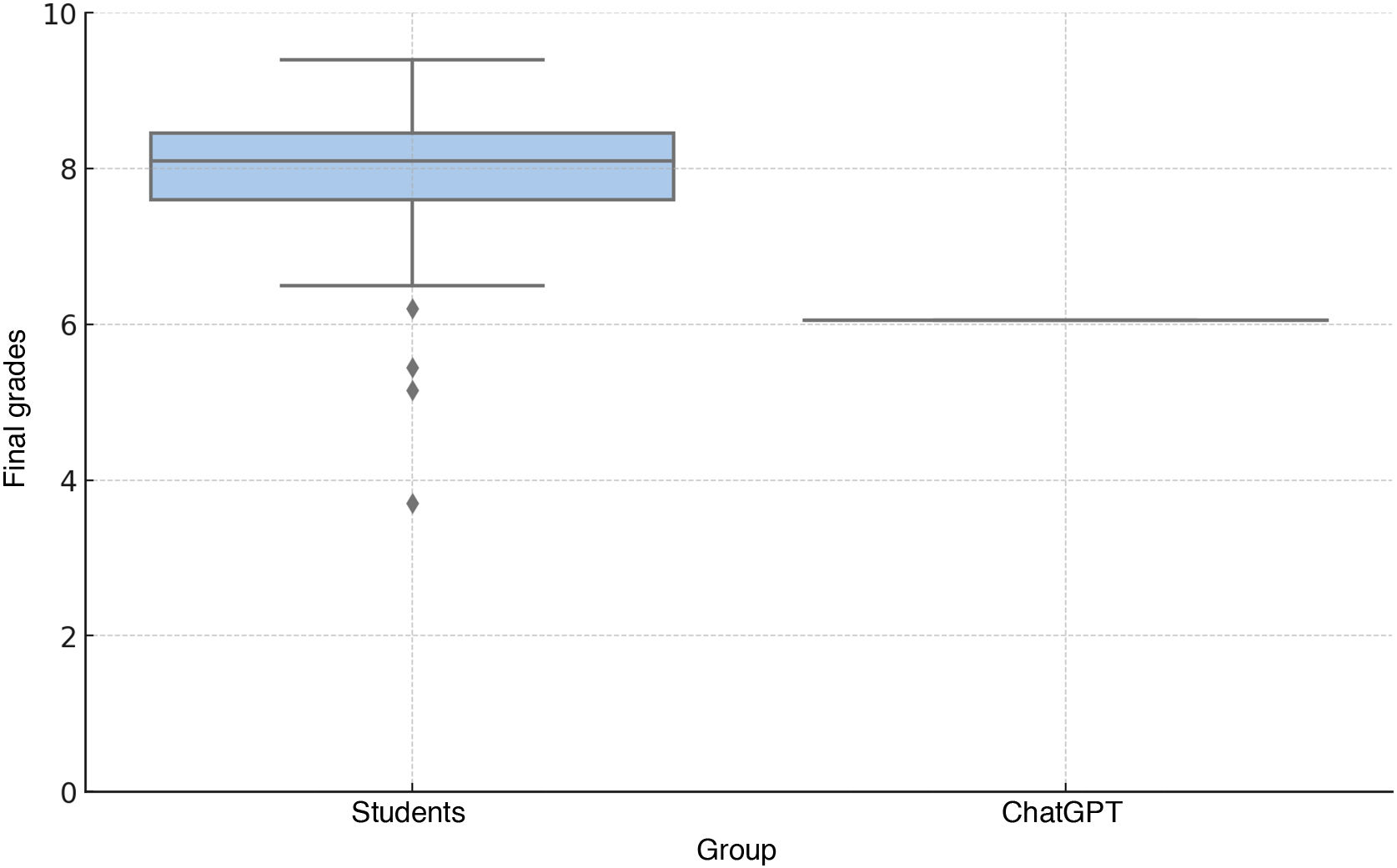
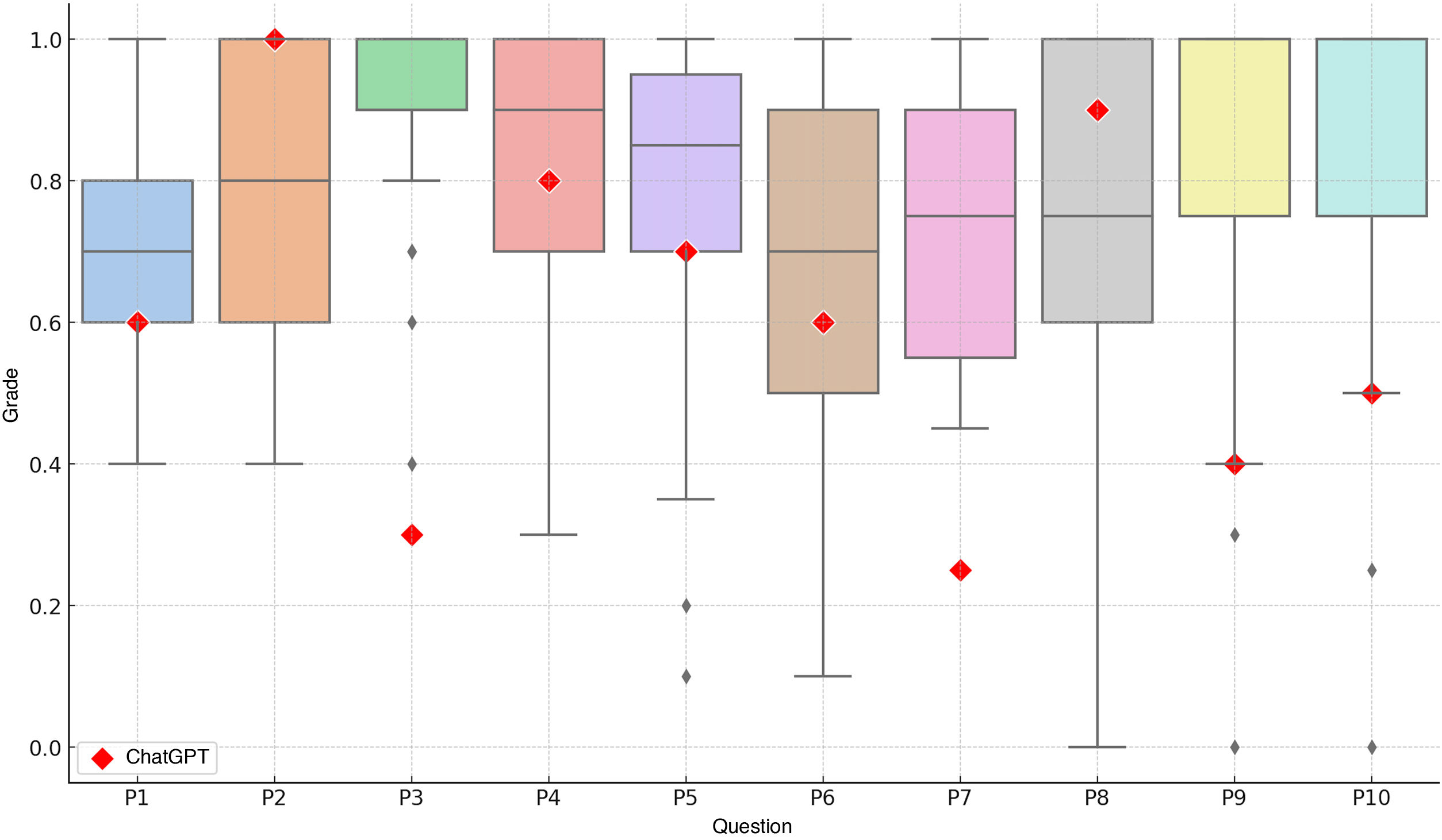
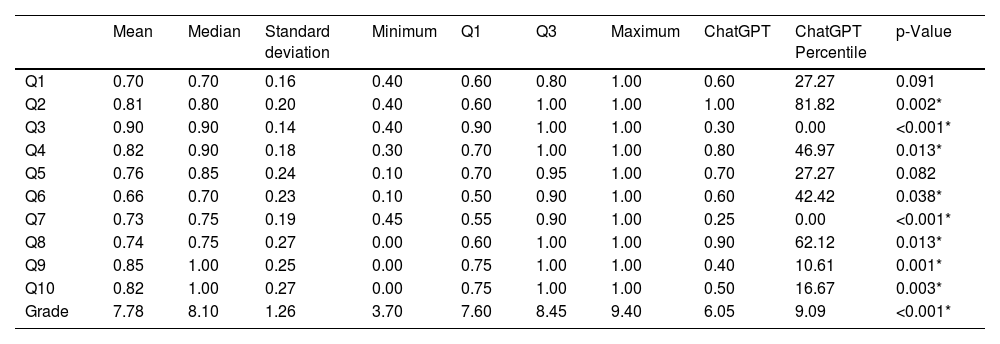
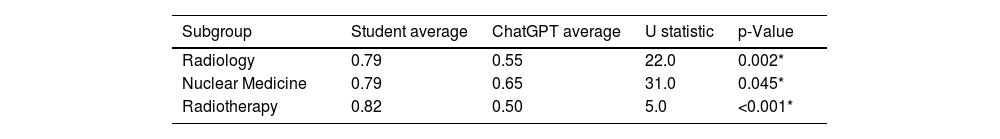
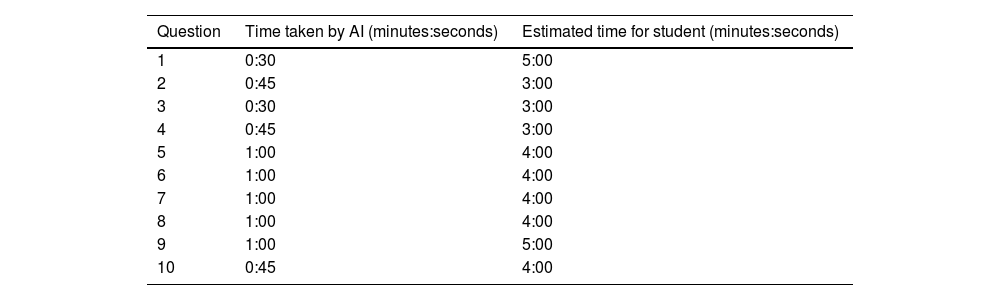
ResultsThe students outperformed ChatGPT on eight questions. The students’ average final score was 7.78, while ChatGPT’s was 6.05, placing it in the 9th percentile of the students’ grade distribution.
DiscussionChatGPT demonstrates competent performance in several areas, but students achieve better grades, especially in the interpretation of images and contextualised clinical reasoning, where students’ training and practical experience play an essential role. Improvements in AI models are still needed to achieve human-like capabilities in interpreting radiological images and integrating clinical information.
Los modelos de inteligencia artificial ofrecen la capacidad de generar respuestas textuales a una amplia variedad de preguntas, incluidas aquellas relacionadas con temas médicos. Recientemente, han incorporado la posibilidad de interpretar y responder a consultas basadas en imágenes, incluyendo imágenes radiológicas. El objetivo principal del estudio es analizar el rendimiento de ChatGPT-4o frente a estudiantes de tercer año de Medicina en una prueba práctica de la asignatura de Radiología y Medicina Física. Como objetivo secundario pretendemos valorar la capacidad de ChatGPT para interpretar imágenes médicas y responder a preguntas sobre las mismas.
Material y métodosSe examinó a un grupo de 33 estudiantes con 10 preguntas sobre imágenes radiológicas y de medicina nuclear. El mismo examen se administró a ChatGPT (versión GPT-4o) sin entrenamiento previo, siguiendo un formato idéntico. Las respuestas al examen fueron evaluadas por profesores que desconocían que examen correspondía al modelo a prueba. Se utilizó la prueba U de Mann-Whitney para comparar los resultados entre los dos grupos.
ResultadosLos estudiantes superaron a ChatGPT en ocho preguntas. La calificación media final de los estudiantes fue de 7,78 y la de ChatGPT fue de 6.05, situándose en el percentil 9 de la distribución de notas de los estudiantes.
DiscusiónChatGPT muestra un rendimiento competente en varias áreas, pero los estudiantes obtienen mejores calificaciones, especialmente en la interpretación de imágenes y en el razonamiento clínico contextualizado, donde la formación y la experiencia práctica de los estudiantes juega un papel esencial. Son necesarias todavía mejoras en los modelos de IA para alcanzar la capacidad humana de interpretar imágenes radiológicas e integrar información clínica.