Osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS) is of the most feared rare brain complications that could lead to protracted neurological consequences or death. Its occurrence is strongly associated with rapid correction of chronic hyponatremia.
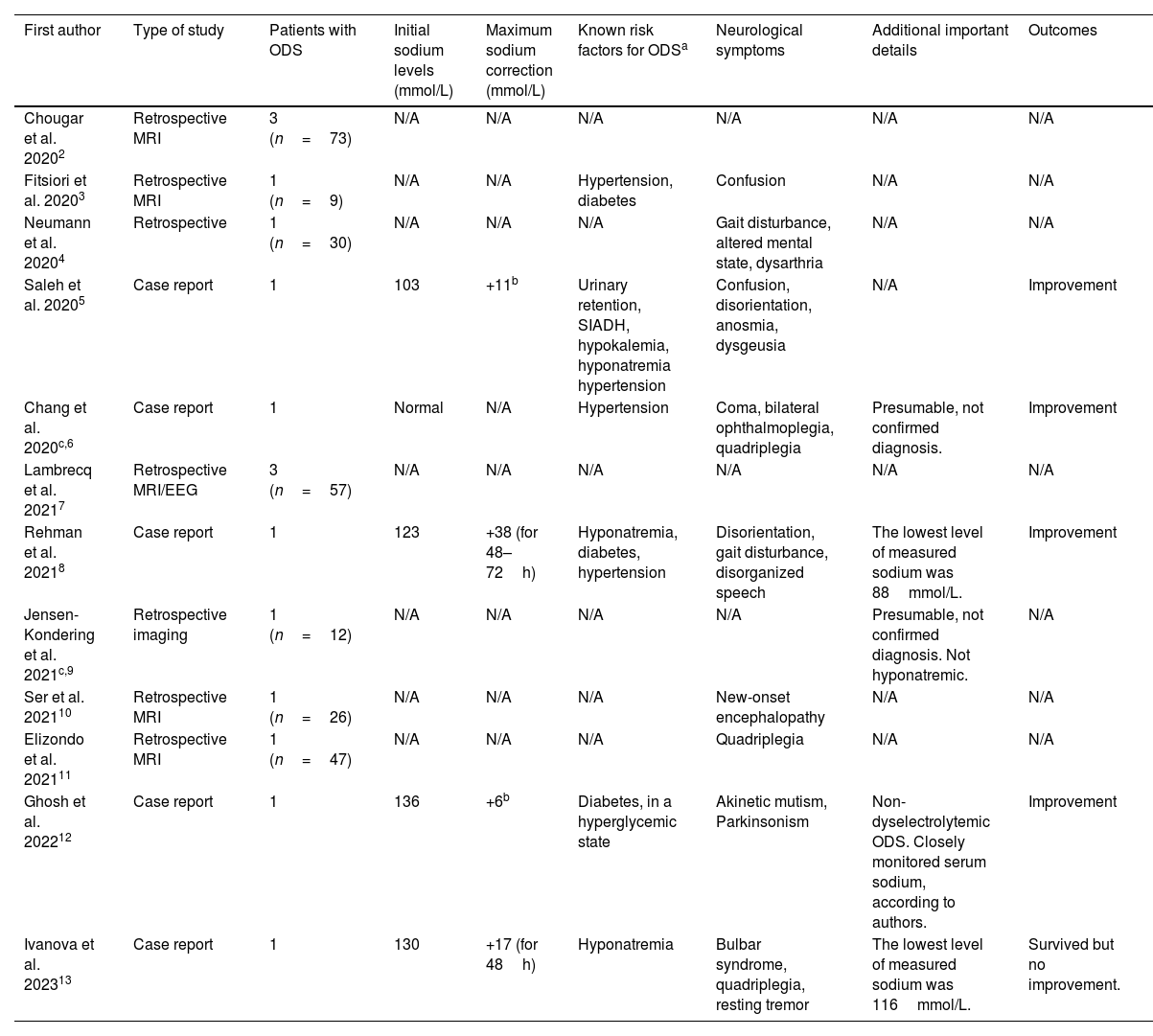
Hyponatremia is common in COVID-19 patients and is associated with poor prognosis.1 However, few publications have described ODS in COVID-19 patients. As of May 2023, we found 12 papers in English, five case reports and seven retrospective studies, containing a total of 16 COVID-19 patients with certain (n=14) or presumable (n=2) ODS2–13 (Table 1).
Review of publications about COVID-19 and osmotic demyelination syndrome as of May 2023.
| First author | Type of study | Patients with ODS | Initial sodium levels (mmol/L) | Maximum sodium correction (mmol/L) | Known risk factors for ODSa | Neurological symptoms | Additional important details | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chougar et al. 20202 | Retrospective MRI | 3 (n=73) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Fitsiori et al. 20203 | Retrospective MRI | 1 (n=9) | N/A | N/A | Hypertension, diabetes | Confusion | N/A | N/A |
| Neumann et al. 20204 | Retrospective | 1 (n=30) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Gait disturbance, altered mental state, dysarthria | N/A | N/A |
| Saleh et al. 20205 | Case report | 1 | 103 | +11b | Urinary retention, SIADH, hypokalemia, hyponatremia hypertension | Confusion, disorientation, anosmia, dysgeusia | N/A | Improvement |
| Chang et al. 2020c,6 | Case report | 1 | Normal | N/A | Hypertension | Coma, bilateral ophthalmoplegia, quadriplegia | Presumable, not confirmed diagnosis. | Improvement |
| Lambrecq et al. 20217 | Retrospective MRI/EEG | 3 (n=57) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Rehman et al. 20218 | Case report | 1 | 123 | +38 (for 48–72h) | Hyponatremia, diabetes, hypertension | Disorientation, gait disturbance, disorganized speech | The lowest level of measured sodium was 88mmol/L. | Improvement |
| Jensen-Kondering et al. 2021c,9 | Retrospective imaging | 1 (n=12) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Presumable, not confirmed diagnosis. Not hyponatremic. | N/A |
| Ser et al. 202110 | Retrospective MRI | 1 (n=26) | N/A | N/A | N/A | New-onset encephalopathy | N/A | N/A |
| Elizondo et al. 202111 | Retrospective MRI | 1 (n=47) | N/A | N/A | N/A | Quadriplegia | N/A | N/A |
| Ghosh et al. 202212 | Case report | 1 | 136 | +6b | Diabetes, in a hyperglycemic state | Akinetic mutism, Parkinsonism | Non-dyselectrolytemic ODS. Closely monitored serum sodium, according to authors. | Improvement |
| Ivanova et al. 202313 | Case report | 1 | 130 | +17 (for 48h) | Hyponatremia | Bulbar syndrome, quadriplegia, resting tremor | The lowest level of measured sodium was 116mmol/L. | Survived but no improvement. |
ODS=osmotic demyelination syndrome, MRI=magnetic resonance imaging, N/A=not available, SIADH=Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion, EEG=electroencephalogram.
Surprisingly, none of the case reports contain information about the 24-h change in serum sodium, which is of utmost importance in current guidelines.14
Herein, we present the case of a 44-year-old male, who was admitted to our intensive care unit (ICU) with altered consciousness, positive for COVID-19. His complaints started two weeks prior when he felt nauseous, vomited several times daily, had fever and cough. On day 10 of symptom onset, the patient experienced a single tonic–clonic seizure with loss of consciousness for the first time. The nationwide shortage of hospital beds due to the pandemic has restricted his immediate hospitalization. Subsequent blood tests at a laboratory revealed severe hyponatremia of 112mmol/L.
On admission (three days later), repeated blood tests revealed hyponatremia of 122mmol/L, or +10mmol/L, indicating that the patient had experienced sodium autocorrection, where the exact correction rate is unknown.
Notable features in the patient's medical history exist. He had managed hypertension with a thiazide diuretic. Thiazide diuretics are a well-known cause of hyponatremia. He also maintained a restrictive diet for a year. In addition, he lost appetite and had been eating less for a week. Finally, he had multiple episodes of vomiting prior to hospital admission. The loss of gastrointestinal fluid results in the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which could cause hyponatremia.
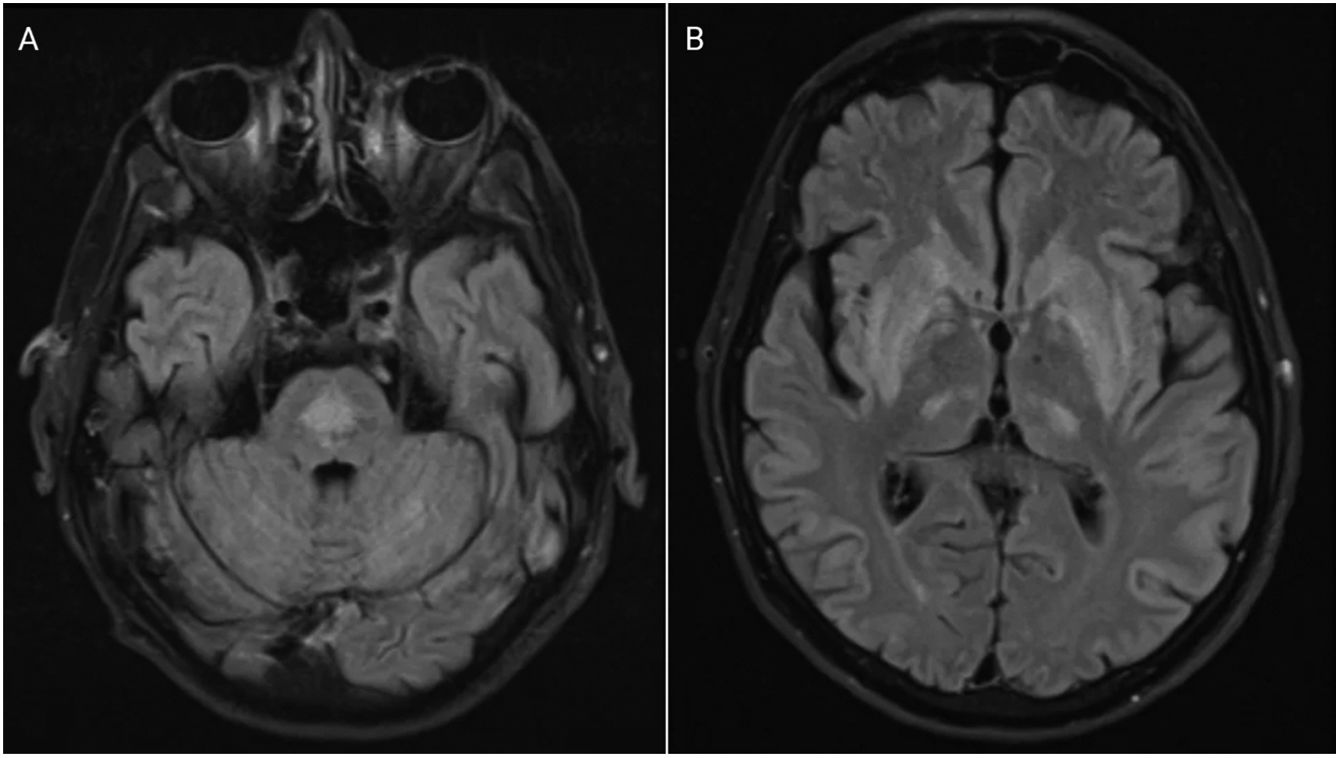
The patient became comatose, and required intubation in early hospitalization days, which made adequate neurologic examination difficult, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) impossible. Initial and repeated CT scans of the brain on day 4 were normal. On day 13, his general condition allowed for better examination. Quadriparesis, extraocular muscle palsy, and bulbar syndrome were observed. We performed MRI of the head, which confirmed the diagnosis of ODS (Fig. 1).
Axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance imaging (FLAIR MRI) demonstrating a centrally located area of increased signal in the pons (A) and a moderately homogeneous signal enhancement bilaterally symmetrical in the basal ganglia with symmetrical foci of enhancement in the posterior thalami (B), typical for pontine (A) and extrapontine (B) myelinolysis or osmotic demyelination syndrome.
Diagnosing ODS is difficult in ICU where encephalopathies are common, including during the COVID-19 era.3 The gold standard is using MRI. However, the need for intensive care limits its feasibility. CT of the brain, while being more accessible and performed under these circumstances, is not sufficiently sensitive.
The question arises whether ODS is underdiagnosed and underreported in COVID-19 patients. Existing studies on COVID-19 patients indicate that ODS may not be rare, particularly in severely ill. In a study by Chougar et al., among 35 COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the ICU with neurological symptoms, three (8.6%) were identified with ODS.4 Fitsiori et al. found one ODS case among nine ICU patients (11.1%),5 Neumann et al. identified one case among 30 COVID-19 patients (3.3%), with the patient being in a critical condition,6 and Jensen-Kondering et al. reported one case of ODS in 12 patients (8.3%), with the patient being severely ill.11 However, these studies suffer from small sample sizes, and conclusions would be premature.
Our patient had stable sodium levels during the hospital stay before establishing diagnosis. The maximum measured increase in serum sodium over 24h (+8mmol/L) was within the current recommended therapeutic limits. Multiple cases in literature have also reported ODS, despite adherence to guidelines. Tandukar et al. highlight 19 publications encompassing 21 patients, 19 of whom (90.5%) had risk factors for ODS.15
However, MacMillan et al. recently showed that ODS can develop in the absence of rapid sodium correction, and an accompanying editorial by Ayus and Moritz questioned current guidelines. This is a large study including 22,858 patients, 3632 of whom (17.7%) had rapid correction of hyponatremia, defined as >8mmol/L/24h. ODS appeared to be a rare condition, developing in only 12 (0.05%) patients. Most notably, seven (58%) of the 12 patients were not rapidly corrected.16,17 Yet, they might have undergone uncontrolled sodium correction. As illustrated by our case report, autocorrection may occur at any time and sodium levels may change dramatically, particularly outside the hospital setting. Also, serum sodium levels of patients are unknown prior to first measurement. These limitations apply in general.
Thus, we posit that undocumented correction of hyponatremia could significantly contribute to the uncertainty regarding established therapeutic guidelines. Further research is needed to explore its role.
Ethical standardsThis research was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Informed consentWritten informed consent was obtained from the relative in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to publishThe relative has consented to submitting the case report to the journal.
Availability of data and materialsThe authors take full responsibility for the data, analysis, and interpretation of the research, and have full access to all data.
FundingThis work is supported by the Bulgarian Ministry of Education and Science under National Program “Young Scientists and Postdoctoral Students – 2”.
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.