This study aimed to clarify whether quantitative high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) analysis can assess the condition of interstitial lung disease (ILD) associated with anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 positive (anti MDA5+) dermatomyositis (DM) and investigate the efficacy of tofacitinib in the treatment of anti-MDA5+ DM.
Materials and methodsSeventy patients were included in this retrospective study: 39 in the tofacitinib group and 31 in the group without tofacitinib. Patients’ HRCT were uploaded to a deep learning system to assess ILD regression. Based on patients’ quantitative HRCT results, survival and glucocorticoids (GCs) usage, the efficacy of tofacitinib in the treatment of anti-MDA5+ DM were assessed. The safety was assessed by recording the incidence of adverse reactions. Data were analyzed using SPSS26.0 and R4.4.1.
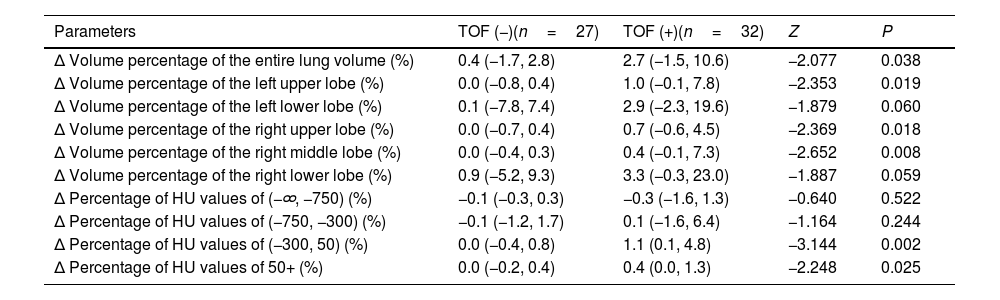
ResultsNo significant differences for baseline characteristics were observed between the two groups of patients, except for cutaneous involvement. Tofacitinib group showed higher 3-year survival and it was an independent protective factor against mortality. Elevated serum ferritin (>1000μg/L) increased the risk of death. Quantitative HRCT analysis showed a significant reduction in the percentage of whole-lung involvement in the tofacitinib group between the baseline and follow-up. The total lesion volume reduction in the whole lung after treatment was substantially higher in the tofacitinib group. The tofacitinib group had a shorter duration of GCs tapering and a higher risk of EBV infection.
ConclusionsQuantitative HRCT analysis can be used to assess the response of ILD to tofacitinib treatment. Tofacitinib is effective in patients with anti-MDA5+ DM-ILD but increases the risk of infection.
Este estudio tiene como objetivo aclarar si el análisis cuantitativo de la tomografía computarizada de alta resolución (HRCT) puede evaluar la condición de la enfermedad pulmonar intersticial (EPI) asociada con la dermatomiositis (DM) con gen 5 positivo asociado a la diferenciación anti-melanoma (anti-MDA5+) e investigar la eficacia del tofacitinib en el tratamiento de la DM anti-MDA5+.
Materiales y métodosEn este estudio retrospectivo se incluyeron 70 pacientes: 39 en el grupo de tofacitinib y 31 en el grupo sin tofacitinib. Las HRCT de los pacientes se cargaron en un sistema de aprendizaje profundo para evaluar la regresión de la EPI. Se evaluó la eficacia de tofacitinib en el tratamiento de la DM anti-MDA5+ a partir de los resultados cuantitativos de la HRCT de los pacientes, la supervivencia y el uso de glucocorticoides (GC). La seguridad se evaluó registrando la incidencia de reacciones adversas. Los datos se analizaron con SPSS® v.26.0 y R4.4.1.
ResultadosNo se observaron diferencias significativas en las características basales entre los 2 grupos de pacientes, excepto en la afectación cutánea. El grupo de tofacitinib mostró una mayor supervivencia a 3 años y fue un factor protector independiente frente a la mortalidad. La ferritina sérica elevada (>1.000μg/l) aumentó el riesgo de muerte. El análisis cuantitativo por HRCT mostró una reducción significativa del porcentaje de afectación de todo el pulmón en el grupo de tofacitinib entre el inicio y el seguimiento. La reducción del volumen total de la lesión en todo el pulmón tras el tratamiento fue sustancialmente mayor en el grupo de tofacitinib. El grupo de tofacitinib tuvo una menor duración de la reducción de GC y un mayor riesgo de infección por el VEB.
ConclusionesEl análisis cuantitativo de la TCAR puede utilizarse para evaluar la respuesta de la EPI al tratamiento con tofacitinib. Tofacitinib es eficaz en los pacientes con anti-MDA5+ DM-ILD, pero aumenta el riesgo de infección.