To see the influence of interlukin-6 (IL-6) as an inflammatory mediator in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and sepsis, assessing whether their serum levels during their stay in intensive care unit (ICU) serve as an early mortality prognostic marker.
Material and methodsA prospective observational cohort study with 203 ICU patients from a third level hospital. A descriptive analysis was made, X2 test used to compare qualitative variables, T-Student test to compare quantitative ones. We made a logistic regression multivariant analysis on admission, third and seventh day of stay with dependent variable mortality and independent variables age, gender and IL-6, lactate and C-reactive protein plasma levels as well as APACHE II and SOFA scores. The biomarkers’ prognostic accuracy was established through ROC curves with their sensitivity and specificity. Finally, a survival curve was performed at 28 days.
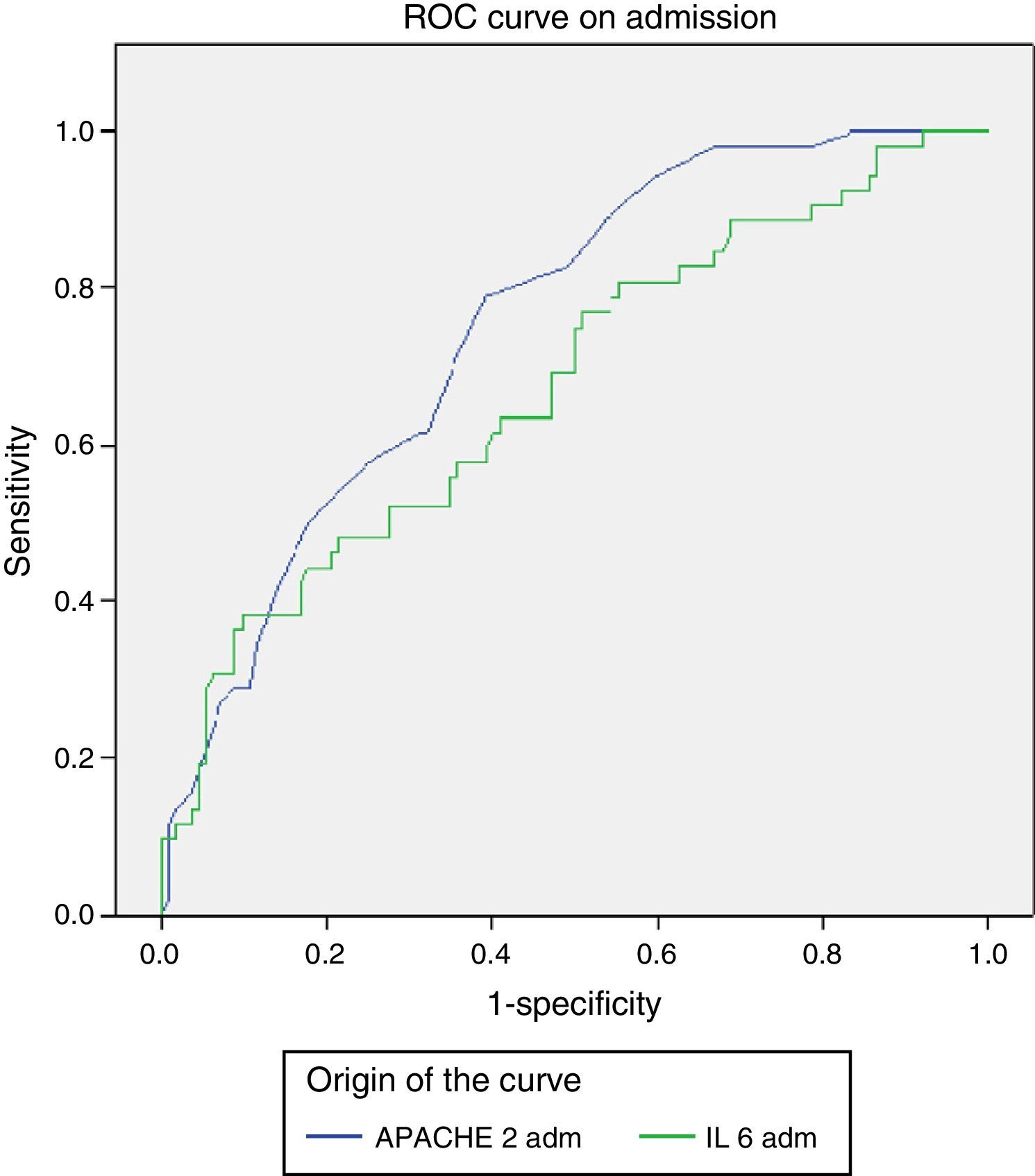
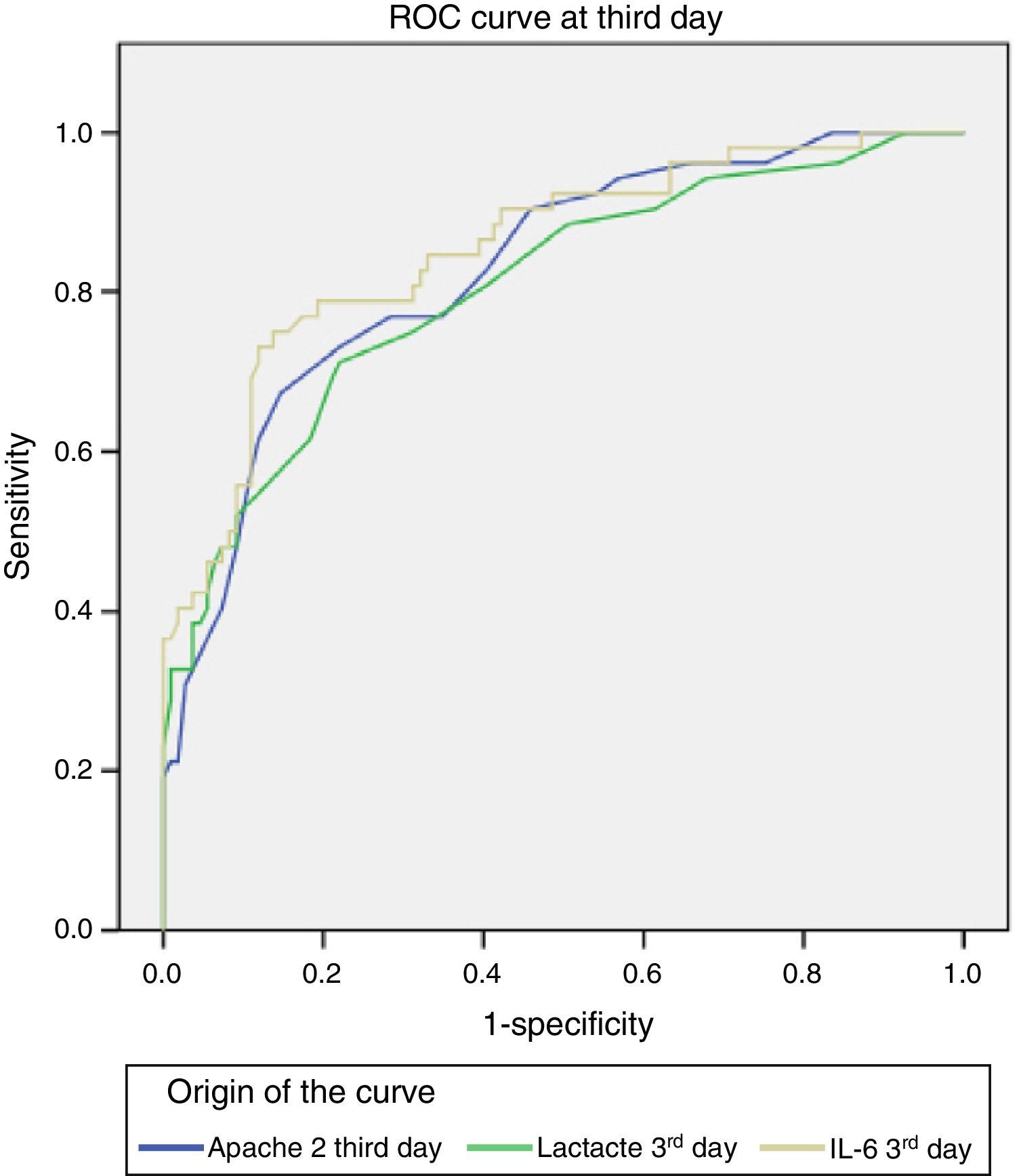
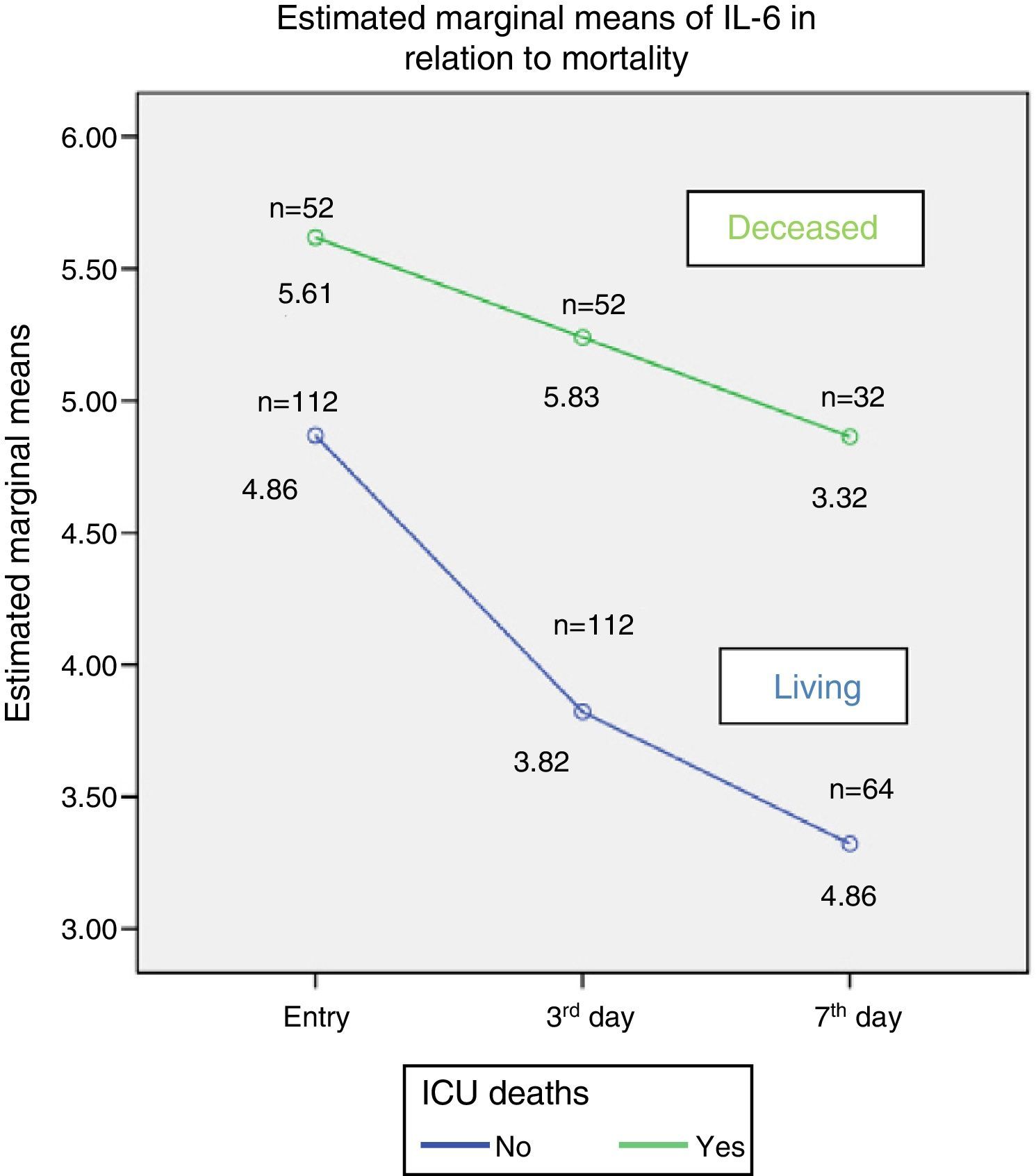
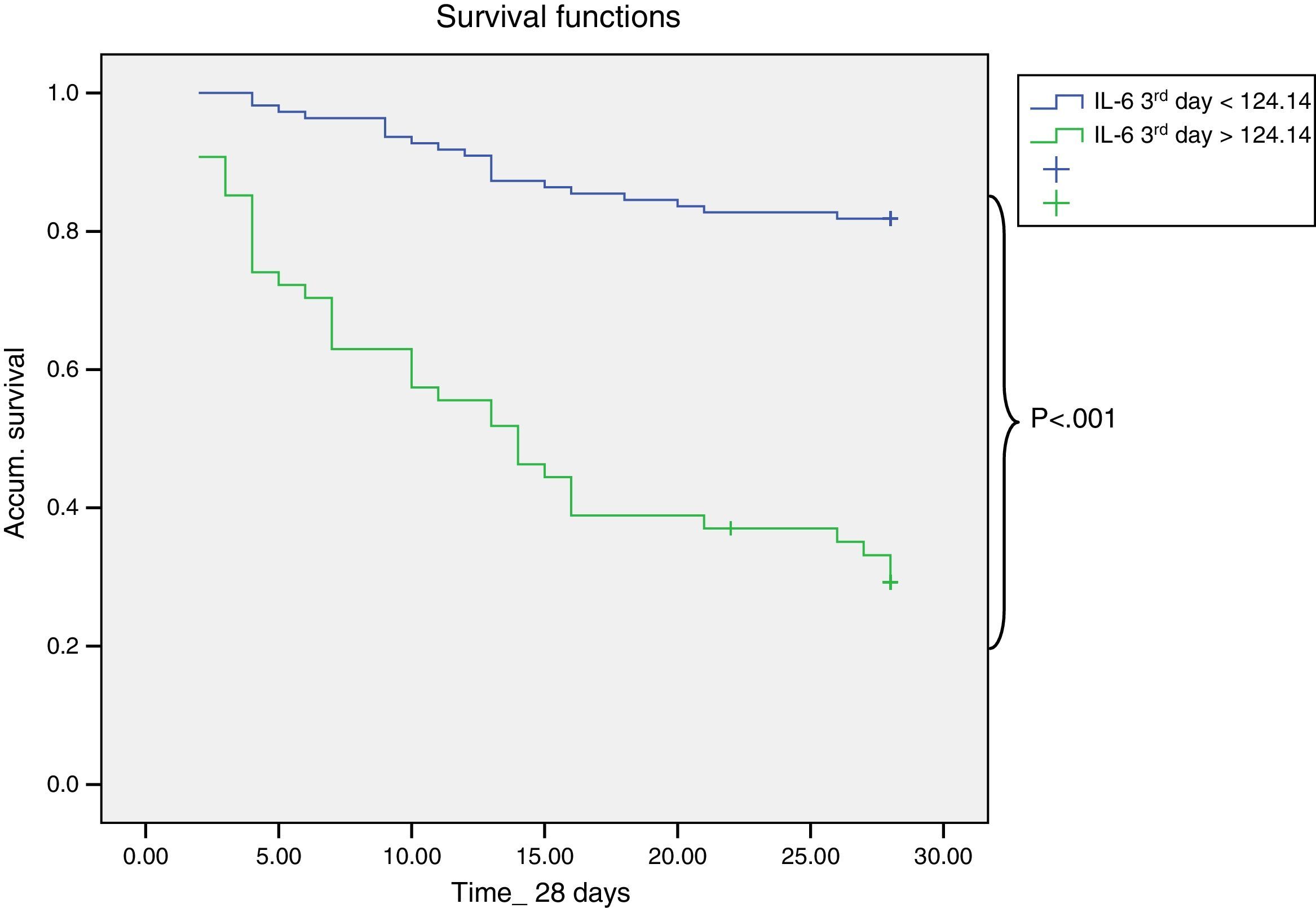
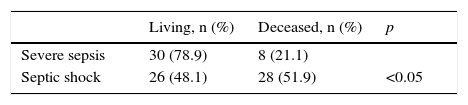
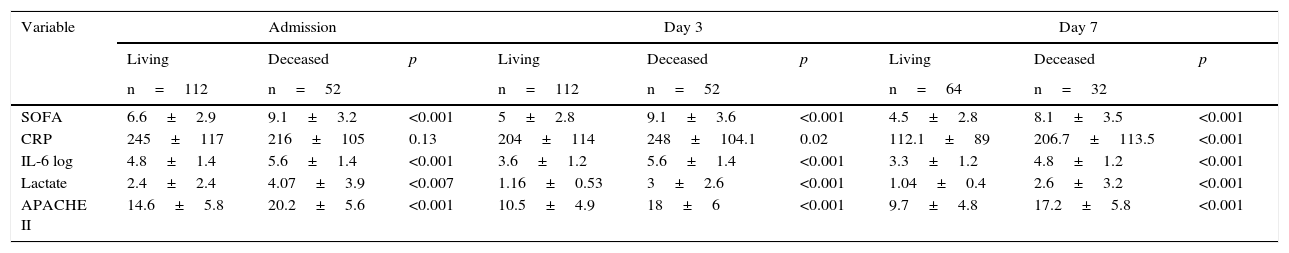
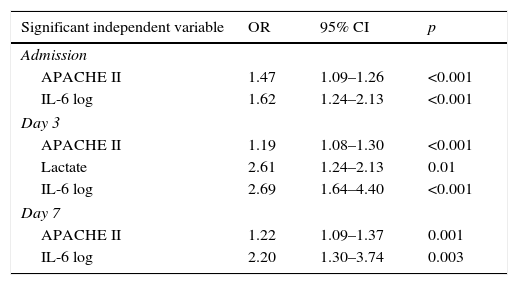
ResultsOf 203 patients, 52 (26%) died and 151 (74%) survived. Ninety-eight (48,3%) had SIRS of infectious aetiology (sepsis). There were no significant differences between age, gender and mortality. More patients died in the sepsis group. The persistence of high IL-6 plasma levels was associated with mortality. On the third day of stay, IL-6 was the most significant variable in relation to mortality with 75% sensitivity and 86% specificity. Patients with IL-6 plasma levels greater than 124.14pg/ml on the 3rd day were 6.1 times more likely to die than those with lower levels
ConclusionsPatients with SIRS-sepsis who died had higher IL-6 plasma levels than those who survived. IL-6 was an early marker of intra-ICU mortality.
Ver la influencia de la interleucina 6 (IL-6) como mediador inflamatorio en pacientes con criterios de systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS, «síndrome de respuesta inflamatoria sistémica») y sepsis valorando si su determinación plasmática durante el ingreso en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI) sirve como marcador precoz de mortalidad.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo de cohortes con 203 pacientes ingresados en UCI de un Hospital de tercer nivel. Se efectuó análisis descriptivo comparando las variables cualitativas con el test X2, las cuantitativas con la T-Student. También análisis multivariante tipo regresión logística al ingreso, tercer y séptimo día con variable dependiente mortalidad e independientes edad, sexo, niveles plasmáticos de IL-6, lactato, proteína C reactiva, scores APACHE II y SOFA. La exactitud pronóstica de los biomarcadores se efectuó mediante curvas ROC con su sensibilidad y especificidad. Por último, se llevó a cabo curva de supervivencia a los 28 días.
ResultadosDe 203 pacientes fallecieron 52 (26%) y sobrevivieron 151 (74%). Noventa y ocho (48,3%) presentaron SIRS de etiología infecciosa (sepsis). No hubo diferencias significativas entre edad, sexo y mortalidad. Más pacientes fallecidos en el grupo sepsis. La persistencia de cifras elevadas de IL-6 se relacionó con la mortalidad. Al tercer día, la IL-6 fue la variable con mayor significación en relación con la mortalidad, con sensibilidad del 75% y especificidad del 86%. Los pacientes que al 3tercer día mantuvieron una cifra de IL-6 mayor de 124,14pg/ml tuvieron 6,1 veces mayor probabilidad de fallecer que los de niveles inferiores.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con SIRS-sepsis que fallecieron presentaron cifras de IL-6 más elevadas que los que sobrevivieron. La IL-6 fue un marcador pronóstico precoz de mortalidad intra-UCI.