Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease of complex aetiology. Several microRNAs (miR) have been linked to the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
To analyze the possible association of miR-22 and miR-150 with autoimmunity and clinical severity of T1D.
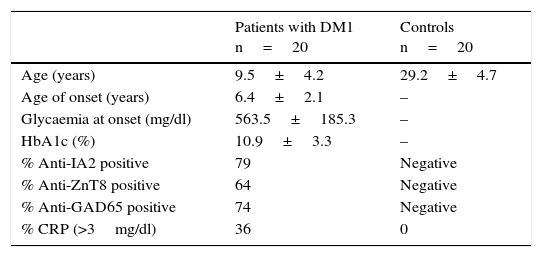
Patients and methodsThe study was performed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of 20 patients with T1D and 20 control subjects. The expression of miR-22 and miR-150 was performed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells using TaqMan probes to different glucose concentrations (baseline, 11mm, 25mm).
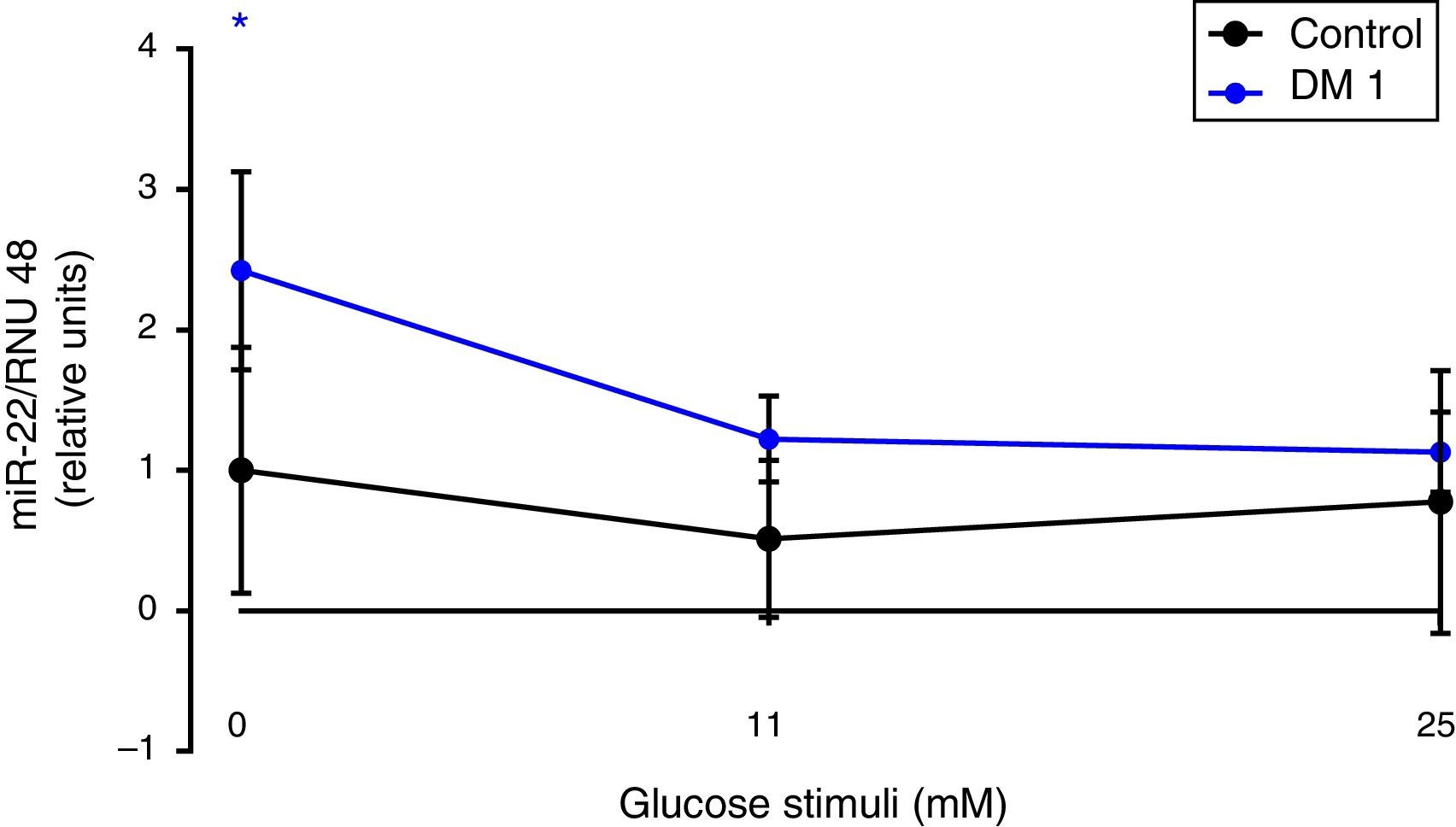
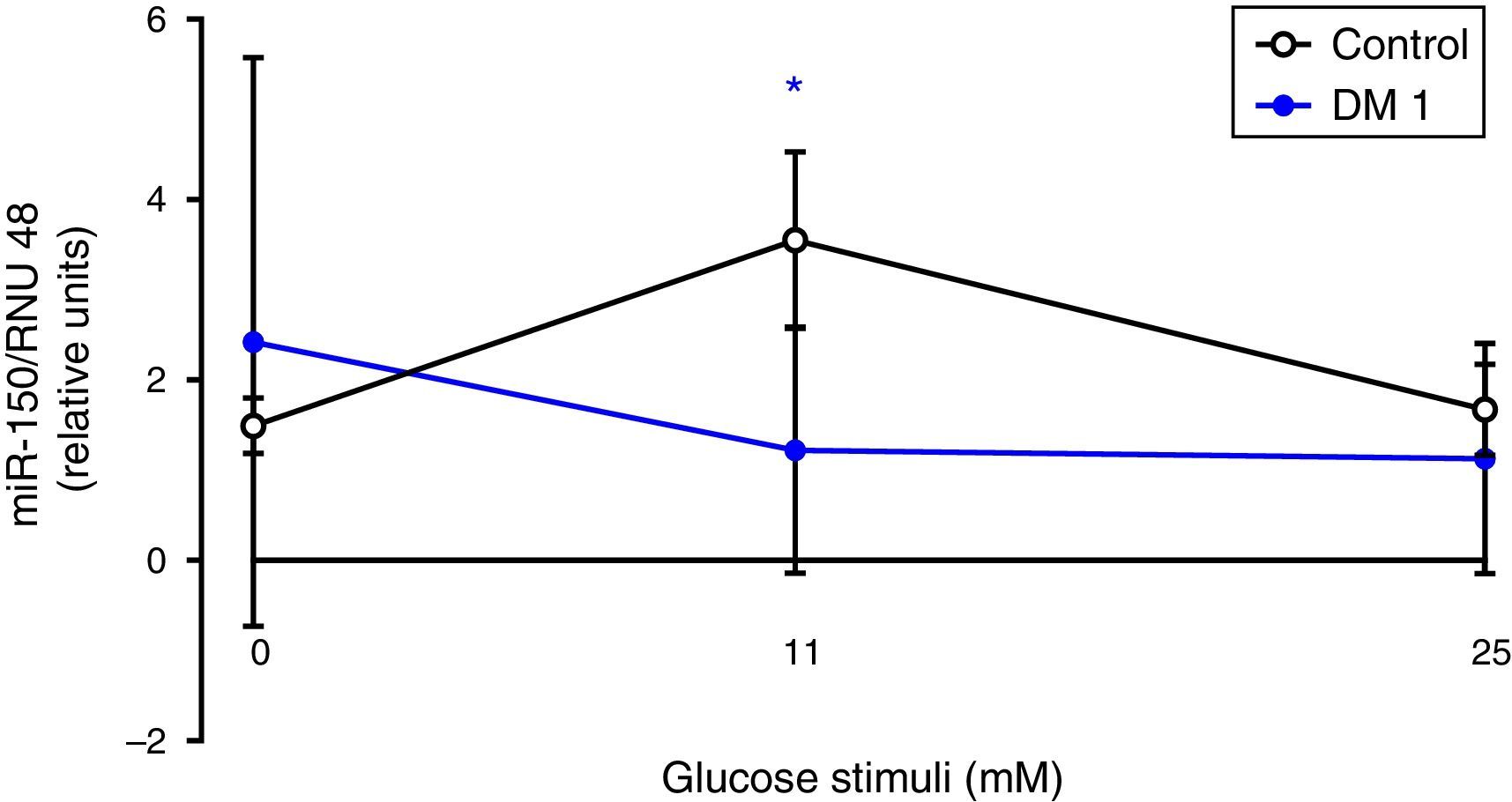
ResultsOur results suggest that the expression of miR-22 is increased in T1D patients compared to the controls. This effect was observed in baseline glucose conditions and decreased in 11 and 25mM of glucose. The expression of miR-150 was lower in T1D patients versus the controls. There was no correlation between the autoimmune profile and the two studied miRNAs. miR-22 (baseline condition) and miR-150 (11mM condition) or the ketoacidosis component.
ConclusionmiR-22 and 150 were not associated with the autoimmune component present in T1D patients.
La diabetes tipo 1 (DM1) es una enfermedad autoinmune de etiología compleja. Diversos microARN (miR) han sido relacionados con la patogénesis de enfermedades autoinmunes.
ObjetivoAnalizar la posible asociación de miR-22 y miR-150 con autoinmunidad y gravedad clínica en la DM1.
Pacientes y métodoEl estudio se realizó en células mononucleares periféricas de 20 pacientes con DM1 y 20 sujetos controles. La expresión de miR-22 y miR-150 se realizó por sondas TaqMan en células mononucleares periféricas a diferentes concentraciones de glucosa (basal, 11mM, 25mM).
ResultadosNuestros resultados muestran que la expresión de miR-22 está aumentada en pacientes con DM1 respecto de controles. Este efecto se observó en la condición basal de glucosa y disminuyó en condiciones 11 y 25mM de glucosa. La expresión de miR-150 fue menor en pacientes con DM1 versus controles. No hubo asociación de los niveles de miR-22 (condición basal) y miR-150 (condición 11mM) con el perfil de autoinmunidad ni la presencia de cetoacidosis.
ConclusiónmiR-22 y miR-150 no se asocian a los niveles de autoanticuerpos, pero sí al componente de cetoacidosis en DM1.