DC cardioversion (DCCV), when performed early, effectively restores sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). This audit aimed to evaluate the outcomes of patients undergoing DCCV at our institution and assess the factors predicting restoration of sinus rhythm.
MethodsThis retrospective audit included patients who underwent elective DCCV in 2021 at our hospital. We excluded patients where data was incomplete. Data was collected from the electronic case records of the patients.
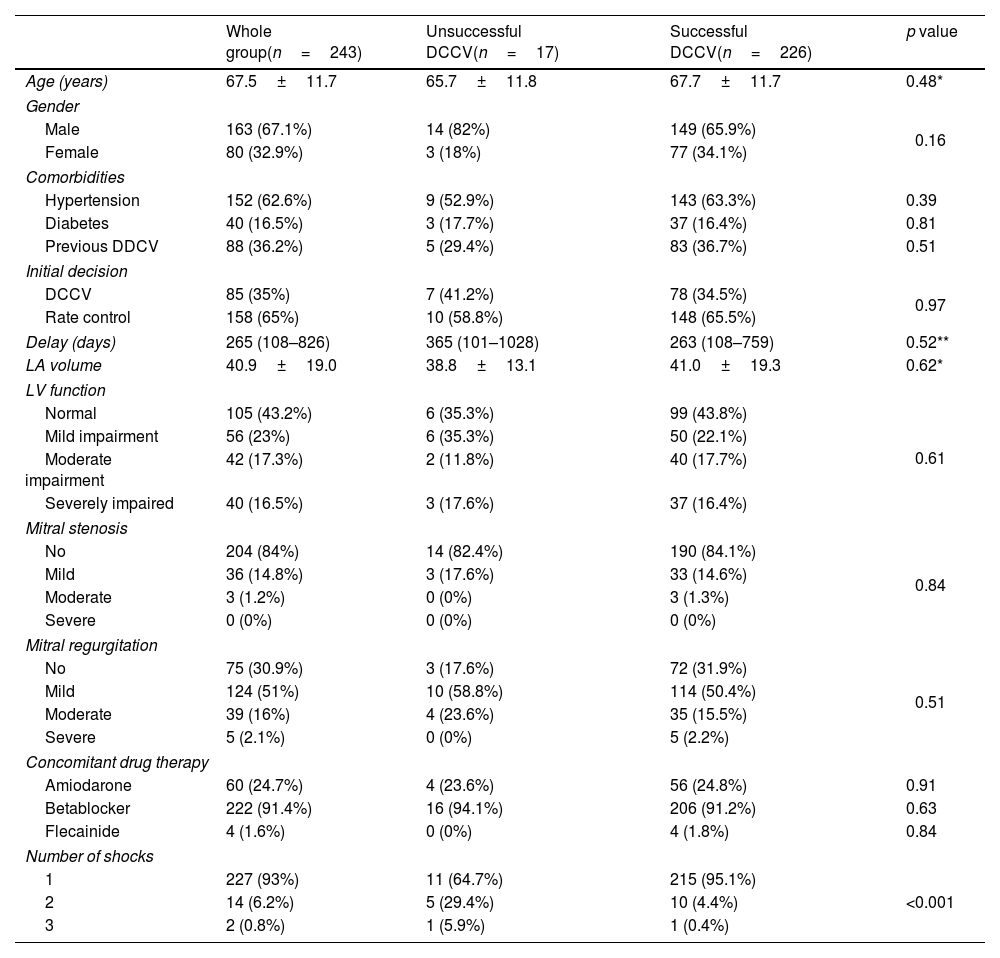
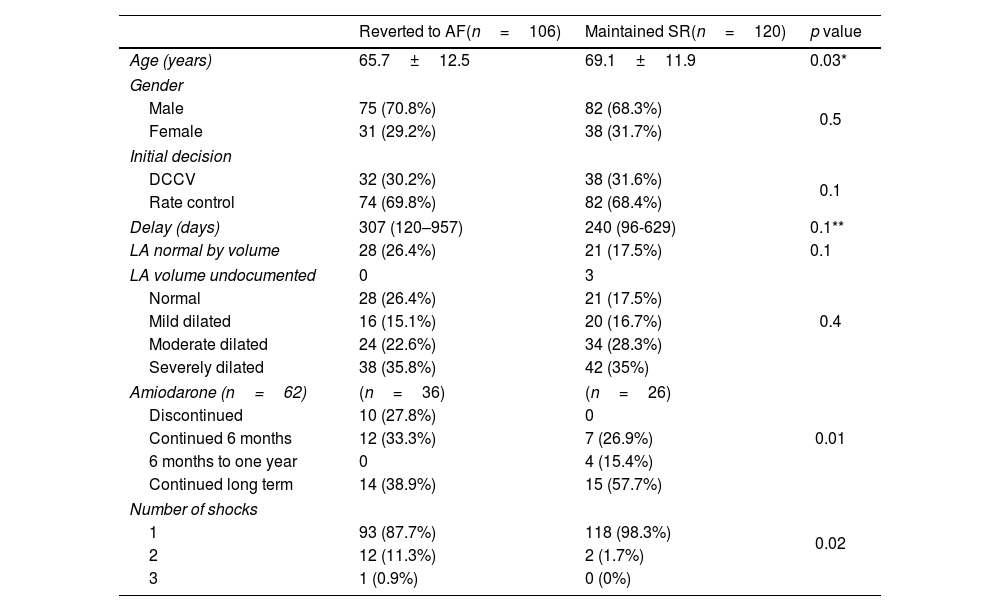
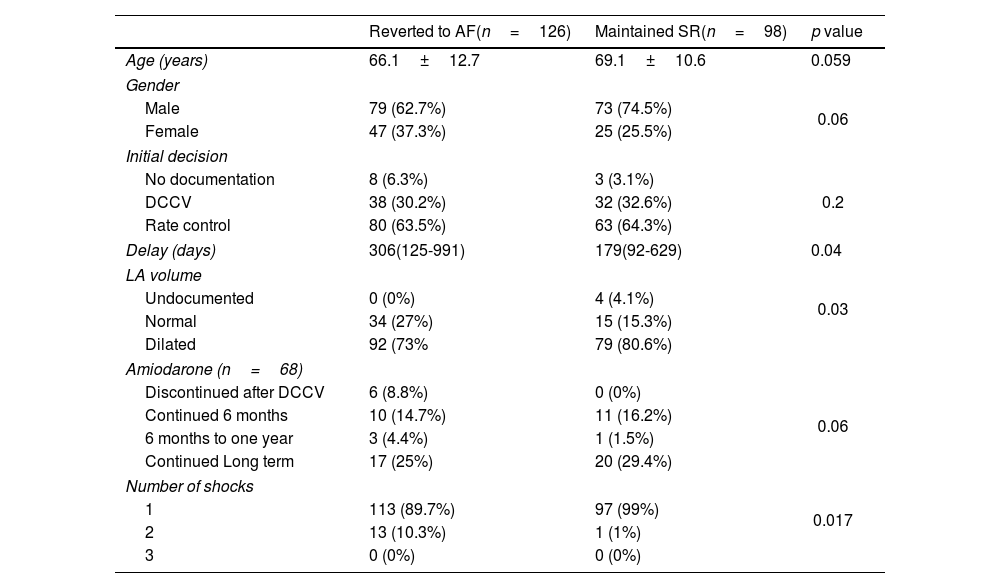
ResultsTwo hundred forty-three patients (mean age 67.5±11.7 years, 67.1% male) were included in the analysis. The median delay from DCCV decision was 265 (108–826) days. Patients who were initially managed with rate control (158 (65%) patients) had longer DCCV wait times compared to those where DCCV was considered as the first line treatment (308 vs. 114 days, p<0.001). DCCV was immediately successful in 232 (93.1%) patients, with 226 (91.5%) maintaining sinus rhythm at discharge, 120 (48.6%) at 6 months and 98 (39.7%) at one year. Fewer shocks predicted sinus rhythm maintenance at discharge, 6 months, and one year (p<0.001). Amiodarone continued post-DCCV also predicted maintenance of sinus rhythm at one year (p=0.01). No significant differences were found in demographics, risk factors, DCCV delay, or LA size between those who maintained sinus rhythm and those who reverted to AF.
ConclusionAt our institution, most patients experienced significant delays before elective cardioversion. Decision to perform DCCV should be taken early and not after an initial trial of rate control. In our patients, amiodarone helped maintain sinus rhythm after successful DCCV.
La cardioversión eléctrica (DCCV, por sus siglas en inglés), cuando se realiza de forma temprana, restablece eficazmente el ritmo sinusal en los pacientes con fibrilación auricular (FA). Esta auditoría tuvo como objetivo evaluar los resultados de los pacientes sometidos a DCCV en nuestra institución, y analizar los factores que predicen la restauración del ritmo sinusal.
MétodosEsta auditoría retrospectiva incluyó a pacientes que se sometieron a DCCV electiva durante 2021 en nuestro hospital. Se excluyeron los pacientes con datos incompletos. Los datos se recopilaron a partir de los registros clínicos electrónicos de los pacientes.
ResultadosSe incluyeron en el análisis 243 pacientes (edad media 67,5±11,7 años, el 67,1% varones). La mediana del tiempo de espera desde la decisión de realizar la DCCV fue de 265 (108-826) días. Los pacientes que inicialmente fueron manejados con control de frecuencia (158 pacientes, 65%) tuvieron tiempos de espera más prolongados para la DCCV en comparación con aquellos en los que se consideró como tratamiento de primera línea (308 vs. 114 días; p<0,001). La DCCV fue exitosa de forma inmediata en 232 (93,1%) pacientes, con 226 (91,5%) pacientes manteniendo el ritmo sinusal al alta, 120 (48,6%) pacientes a los 6 meses y 98 (39,7%) pacientes al año. Un menor número de descargas predijo el mantenimiento del ritmo sinusal al alta, a los 6 meses y al año (p<0,001). La administración continuada de amiodarona después de la DCCV también predijo el mantenimiento del ritmo sinusal al año (p=0,01). No se encontraron diferencias significativas en cuanto a demografía, factores de riesgo, demora en la DCCV o tamaño de la aurícula izquierda entre quienes mantuvieron el ritmo sinusal y quienes recayeron en FA.
ConclusiónEn nuestra institución, la mayoría de los pacientes experimentaron retrasos significativos antes de la cardioversión electiva. La decisión de realizar DCCV debe tomarse de forma temprana y no después de un intento inicial de control de frecuencia. En nuestros pacientes, la amiodarona contribuyó a mantener el ritmo sinusal tras una DCCV exitosa.