Hypercholesterolemia represents a major risk factor in the onset and progression of cardiovascular diseases. While statins have long been the cornerstone of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reduction, the occurrence of adverse events associated with their use has prompted the development and adoption of alternative lipid-lowering agents. These include ezetimibe, bempedoic acid, and proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors, such as alirocumab, evolocumab, and inclisiran.
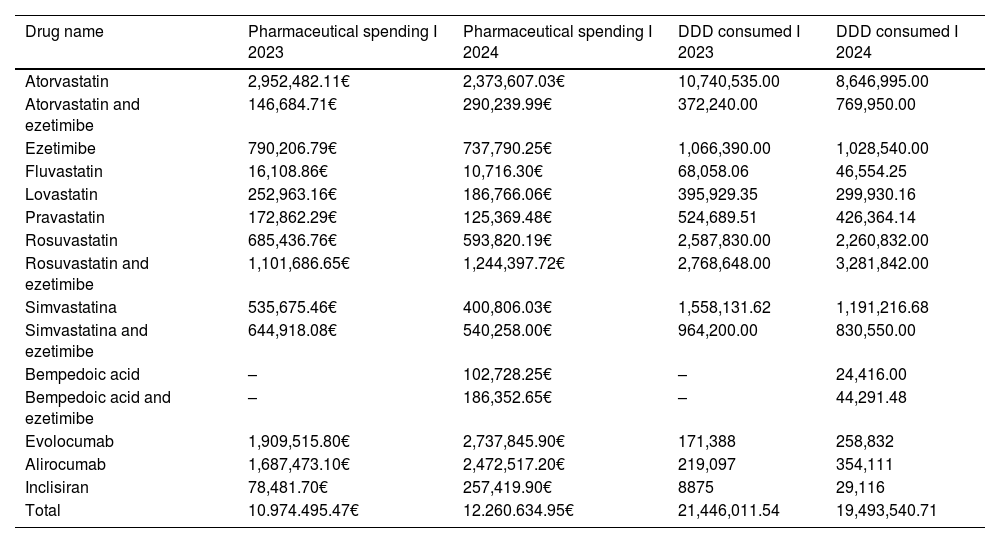
MethodsThis study aims to assess and compare the consumption patterns and associated costs of lipid-lowering medications during the first half of 2023 and 2024. The objective is to evaluate the economic implications of emerging therapies in the management of dyslipidemia and the extent of adherence to clinical guidelines. Data were collected from both private community pharmacies and public healthcare facilities, including hospital and district pharmacies. Drug utilization was analyzed using the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification system and expressed in defined daily doses (DDD).
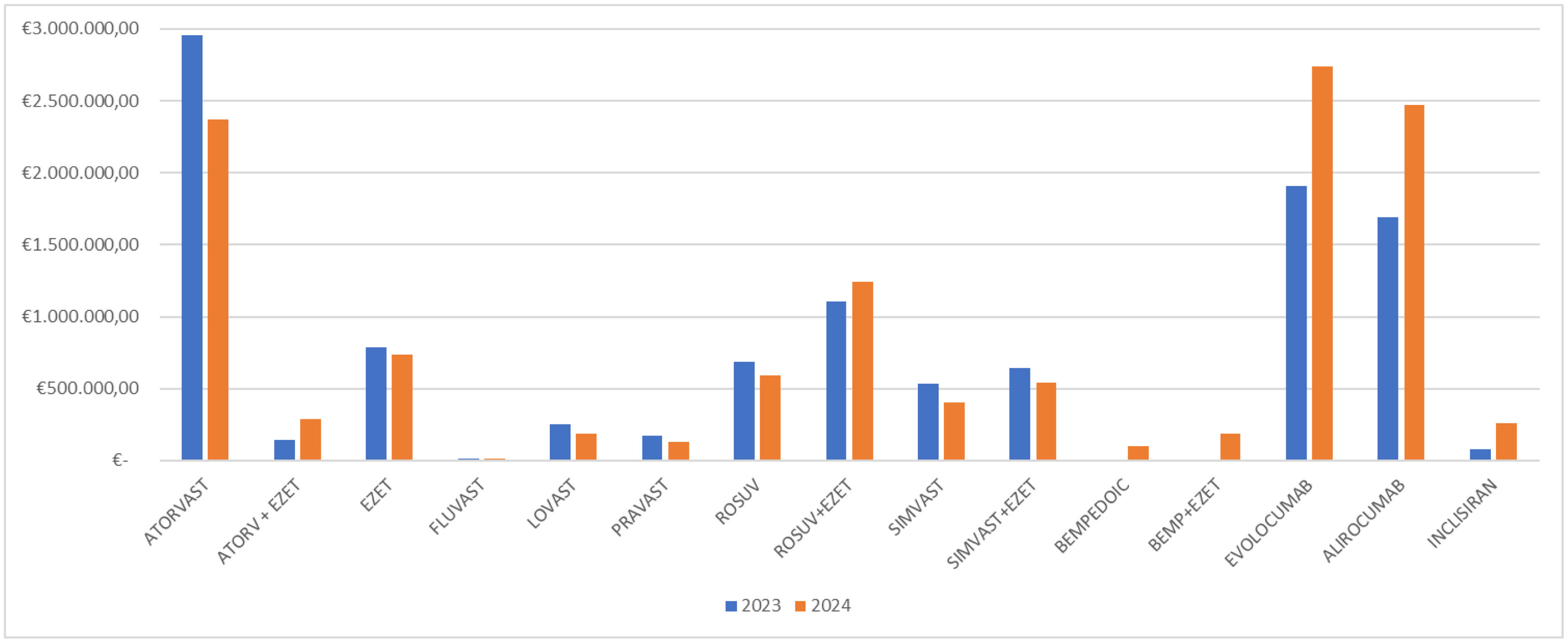
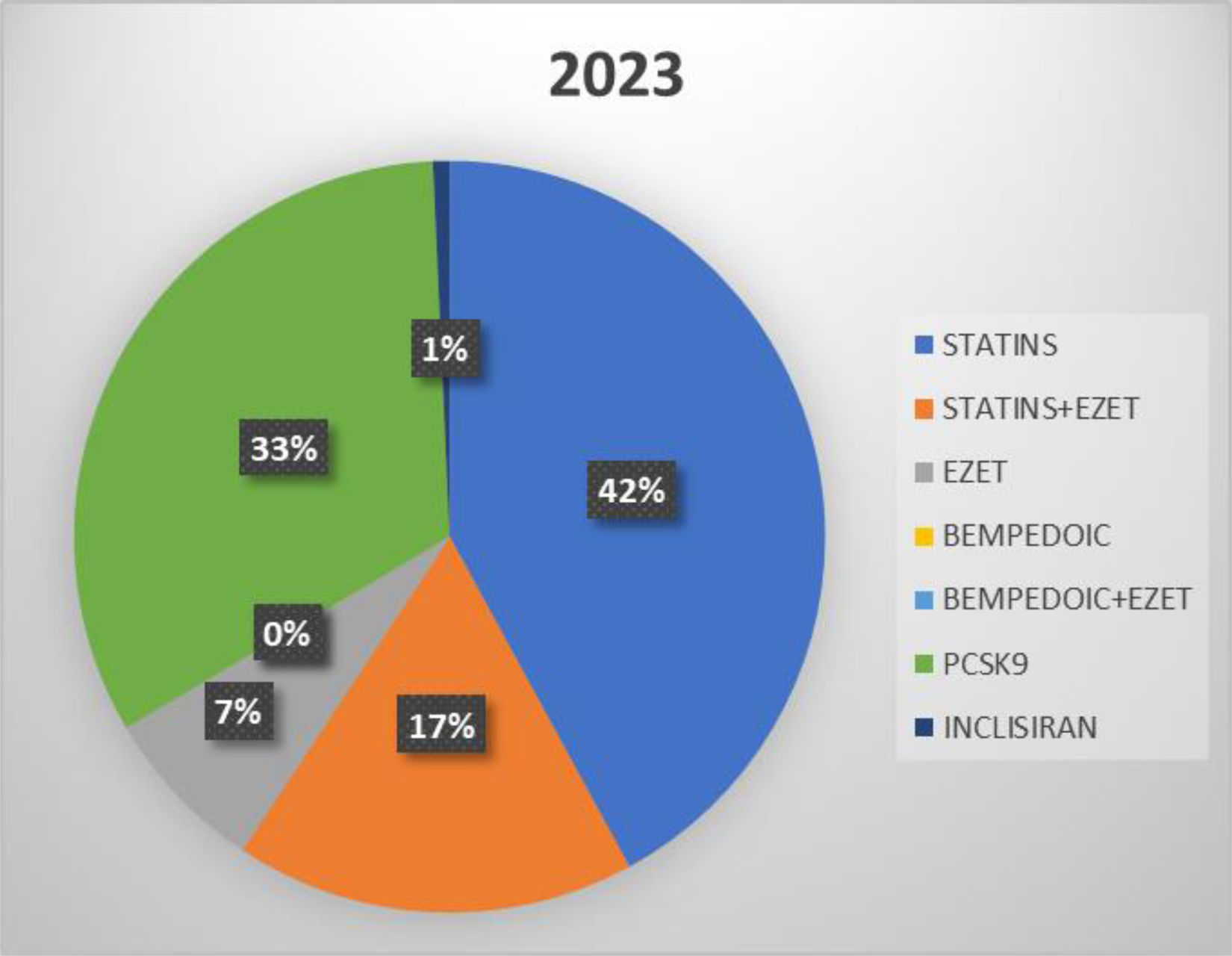
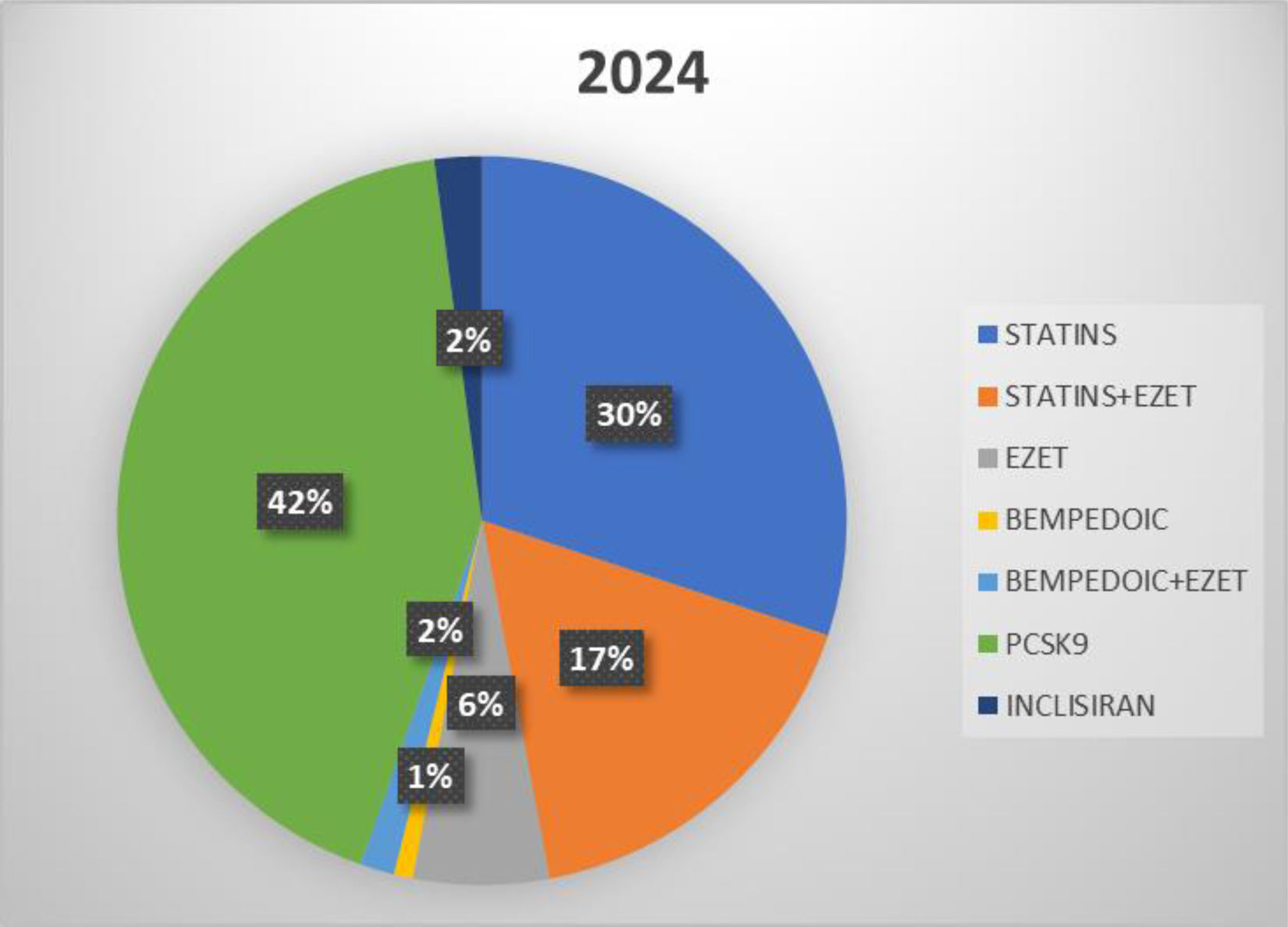
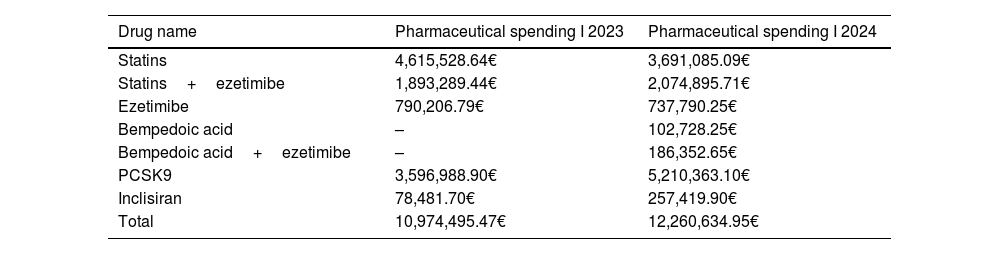
ResultsFindings indicate a declining trend in the use of traditional statin monotherapy, accompanied by an increase in the uptake of newer and combination therapies. Statin use declined significantly, from 42% in the first half of 2023 to 30% in the corresponding period of 2024. The use of combination therapy involving statins and ezetimibe remained stable at 17% across both timeframes. In contrast, PCSK9 inhibitors showed a notable rise in use, increasing from 33% to 40% between the two periods. The utilization of bempedoic acid, whether as monotherapy or combined with ezetimibe, remained marginal, consistently below 2%.
ConclusionThe therapeutic landscape for dyslipidemia has evolved substantially in recent years with the introduction of multiple novel agents. Among these, bempedoic acid, characterized by a more favorable cost profile, may serve as a valuable adjunct to statins and ezetimibe, potentially enhancing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse effects—thus delaying or avoiding the need for more costly injectable treatments such as evolocumab, alirocumab, and inclisiran. Ongoing monitoring of prescribing trends and expenditure is crucial to ensuring the sustainability of healthcare systems, facilitating the adoption of innovative and effective treatments while preventing unnecessary resource allocation.
La hipercolesterolemia es un importante factor de riesgo en el desarrollo de enfermedades cardiovasculares. Las estatinas han sido el tratamiento principal para reducir el colesterol LDL durante años; sin embargo, los acontecimientos adversos relacionados con su uso han llevado al desarrollo de terapias alternativas, como la ezetimiba, el ácido bempedoico y los inhibidores de PCSK9, incluidos alirocumab, evolocumab e inclisiran.
MétodosEl estudio tiene como objetivo comparar el consumo y los costes de los fármacos hipolipemiantes en el primer semestre de 2023 y 2024 para evaluar el impacto económico de las nuevas terapias en el manejo de la dislipidemia y la adherencia a las guías. Los datos se recogieron en farmacias comunitarias privadas, así como en farmacias hospitalarias y de distrito. El consumo de medicamentos se midió utilizando el sistema de clasificación ATC y la dosis diaria definida (DDD).
ResultadosEl estudio reveló una tendencia a la reducción del uso de la monoterapia tradicional con estatinas y un aumento de las terapias más recientes y combinadas. Las estatinas mostraron una reducción significativa, pasando del 42% en el primer semestre de 2023 al 30% en el primer semestre de 2024. Las terapias combinadas, como las estatinas con ezetimiba, no mostraron ningún cambio de tendencia, manteniendo una cuota del 17% en ambos periodos. Las nuevas terapias, como los inhibidores de PCSK9, mostraron un aumento del 33% en el primer semestre de 2023 al 40% en el primer semestre de 2024, mientras que el ácido bempedoico, ya sea en monoterapia o en combinación con ezetimiba, se mantuvo por debajo del 2%.
ConclusionesEn los últimos años, el tratamiento de la dislipidemia ha visto la introducción de muchas alternativas terapéuticas. El ácido bempedoico, de reciente introducción y menor coste, utilizado como terapia coadyuvante con estatinas y ezetimiba, podría reducir los efectos secundarios y mejorar la eficacia terapéutica sin recurrir inmediatamente a fármacos inyectables de mayor coste como evolocumab, alirocumab e inclisiran. El seguimiento de las tendencias de prescripción y los costes es esencial para mantener la sostenibilidad del sistema sanitario, permitiendo invertir en innovación y terapias eficaces sin despilfarros.