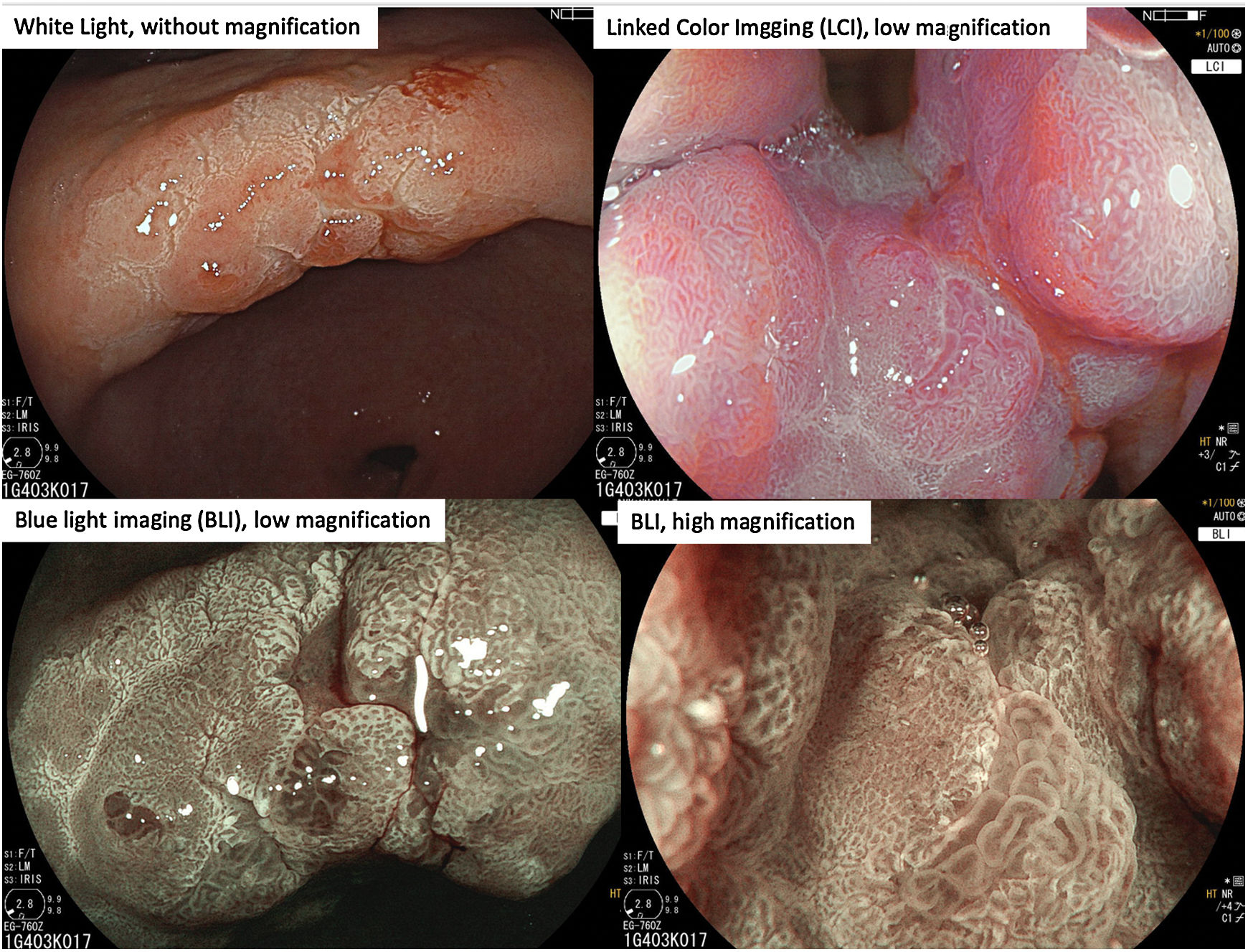
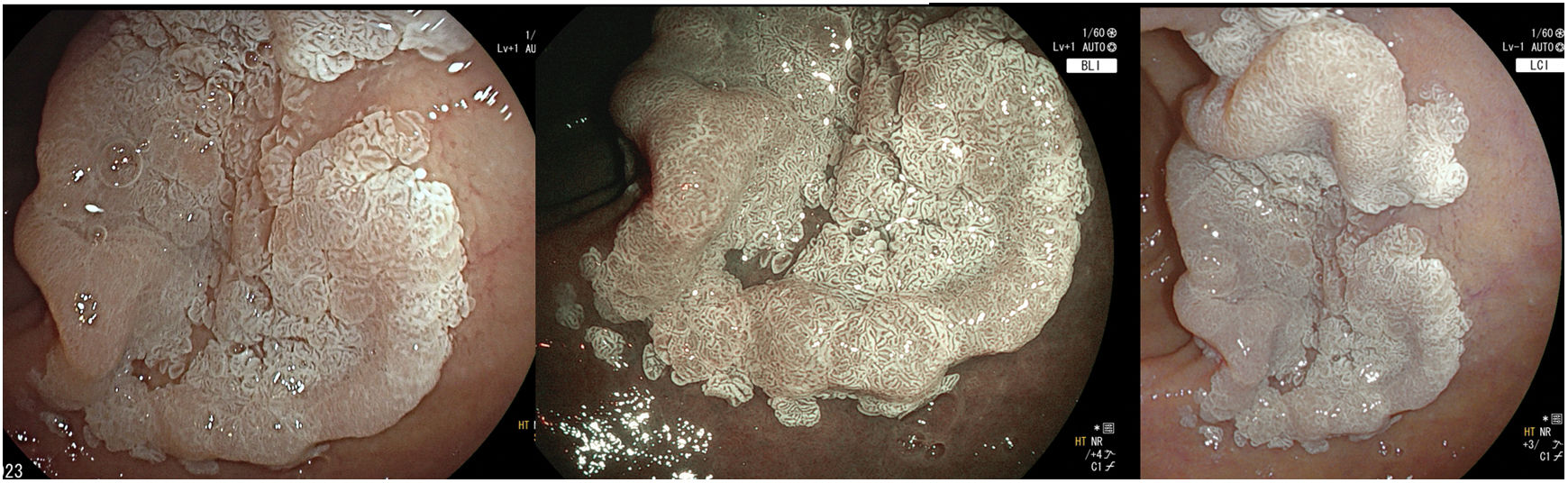
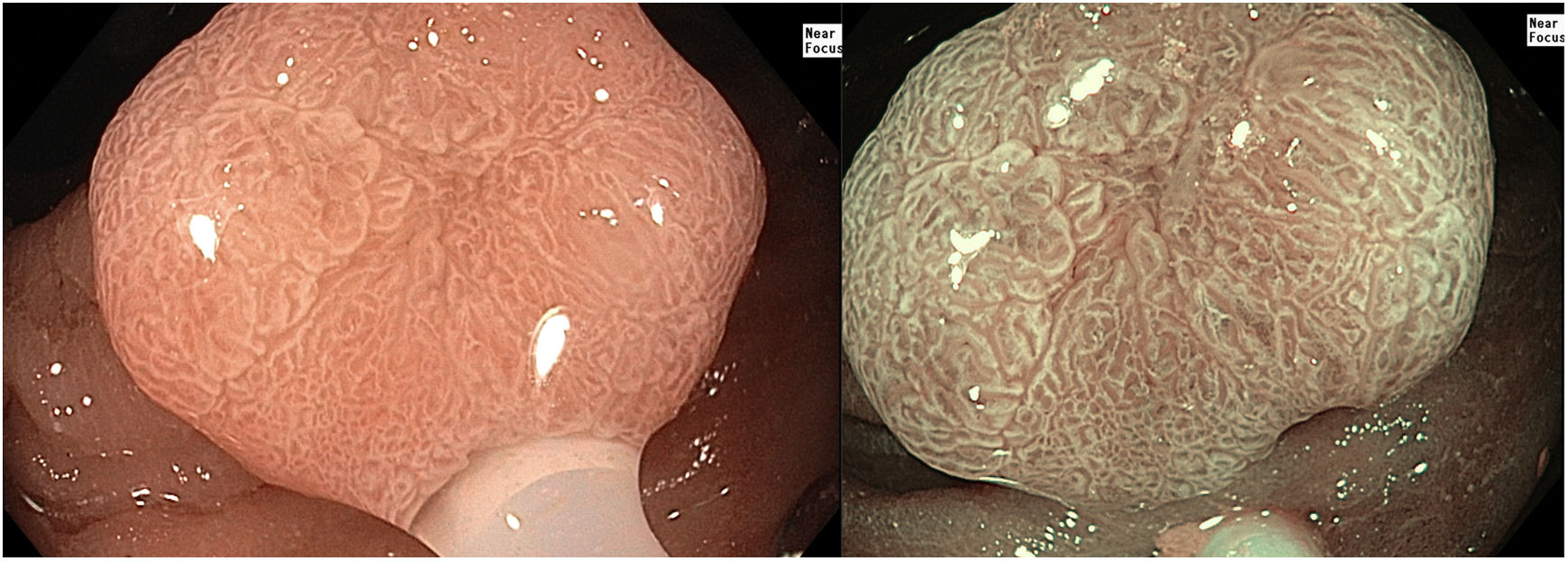
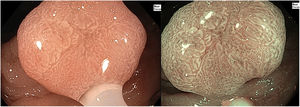
The white opaque substance (WOS) described by Yao et al. in 20081 is a phenomenon that may be present in gastric epithelial neoplasia and gastric intestinal metaplasia (Fig. 1). But it also could be seen in other gastrointestinal lesions, such as esophageal adenocarcinoma, duodenal (Fig. 2) and colorectal adenomas (Fig. 3).
WOS is visualized using either normal white light or “blue light” (like NBI, BLI or I-Scan OE), and indicates the accumulation of lipid micro-droplets in the superficial (intraepithelial and subepithelial) part of epithelial neoplasias due to an impaired mitochondrial oxidation, lipoprotein excretion and lipid degradation. The lipid drops have a higher reflective index than organelles and organic components of the tissue, so the light is strongly scattered and reflected, being recognized as white coloration by the human eye.