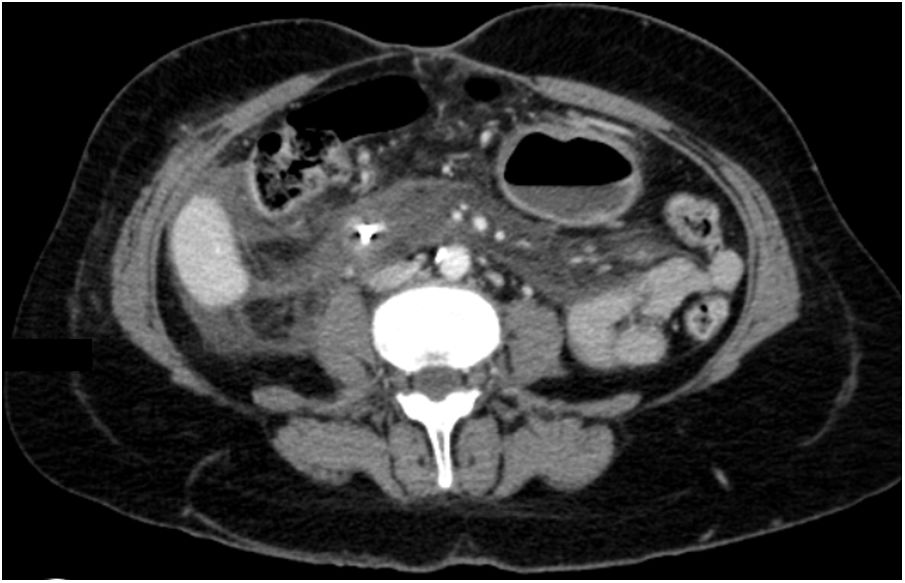
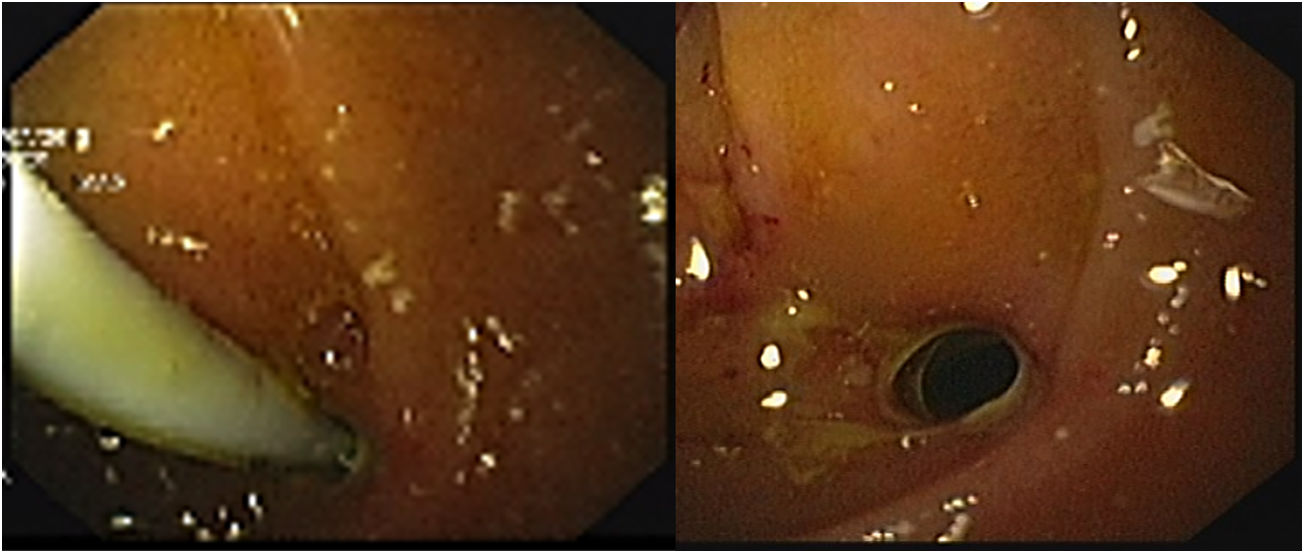
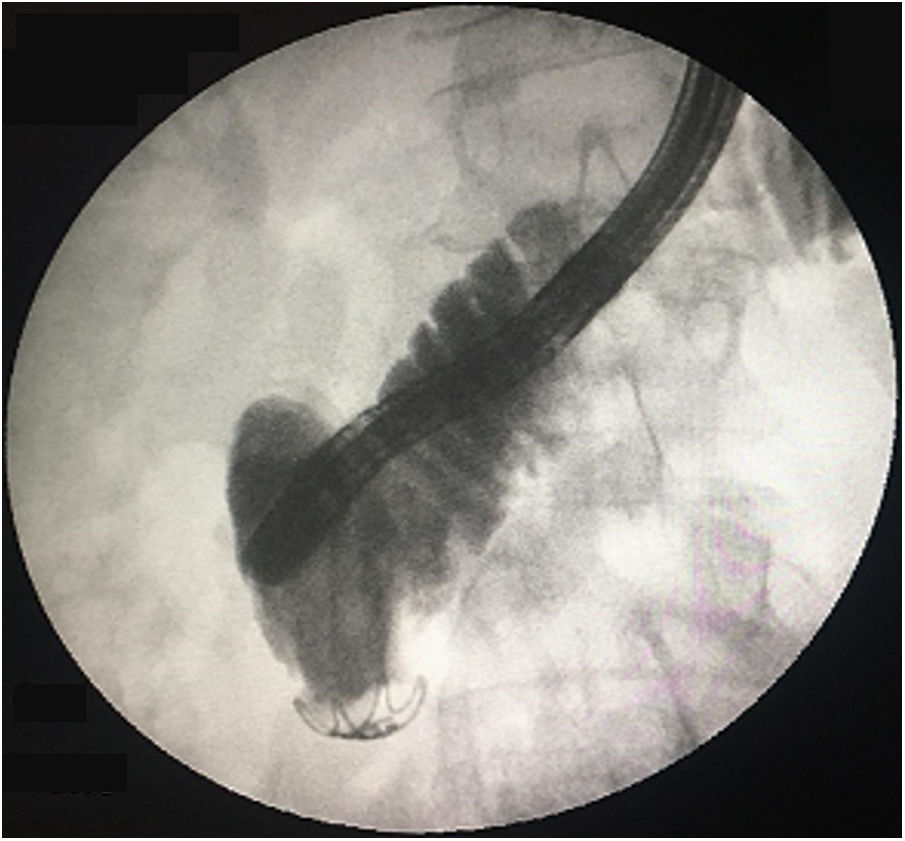
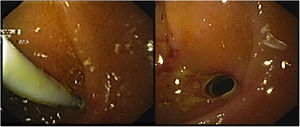
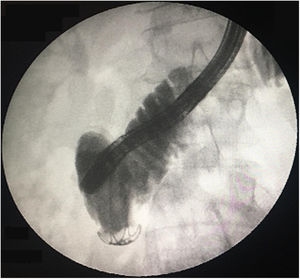
A 52-year-old woman underwent elective endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for treatment of an infra-hilar main bile duct (MBD) stenosis and fistula from the left hepatic duct due to a cholecystectomy performed one month prior. After dilatation with a 10Fr Savary bougie, a plastic stent (10Fr, 9cm) was placed across the stenotic segment with the proximal tip in the right hepatic duct. Eight hours later, the patient was admitted with abdominal pain and vomiting. Physical examination was positive for a painful abdomen with no tenderness. Blood tests revealed: C-reactive protein – 44.6mg/dl and procalcitonin – 4.66ng/ml. Urgent abdominal computed tomography showed pneumoretroperitoneum, the proximal end of the stent at the distal MBD and the distal end in the retroperitoneum, with presence of fluid and extra-luminal gas (Fig. 1). Urgent esophagogastroduodenoscopy confirmed stent migration to the second portion of duodenum and penetration through the duodenal wall. The plastic stent was removed using rat-tooth forceps, revealing a fistula orifice measuring 3mm in the duodenal wall (Fig. 2a and b). The perforation was closed with an over-the-scope-clip (OTSC) and the final opacification showed no extravasation of contrast (Fig. 3). However, there was a late failure of OTSC with need of surgical drainage of retroperitoneal abscesses and fistula close. Plastic stent migration with duodenal perforation is a rare but serious condition (3–5%), occurring usually within 2 weeks after the procedure.1 To our knowledge only 2 cases of duodenal closure using an OTSC were described.2,3
All authors contributed equally to this report.
Conflicts of interest and source fundingNone declared.