An 87-year-old woman with a VP shunt to treat normotensive hydrocephalus, was derived to Emergencies because she had a catheter protruding through the rectum. Previously, the doctor's residence decided to pull out the catheter and cut it off. In emergencies, she was asymptomatic with no evidence or palpation of the VP shunt during the physical exam. Blood test only revealed an elevation of RCP (188) with no leukocytosis. Cranial and abdominal CT scan confirmed that the shunt was placed correctly and without signs of perforation.
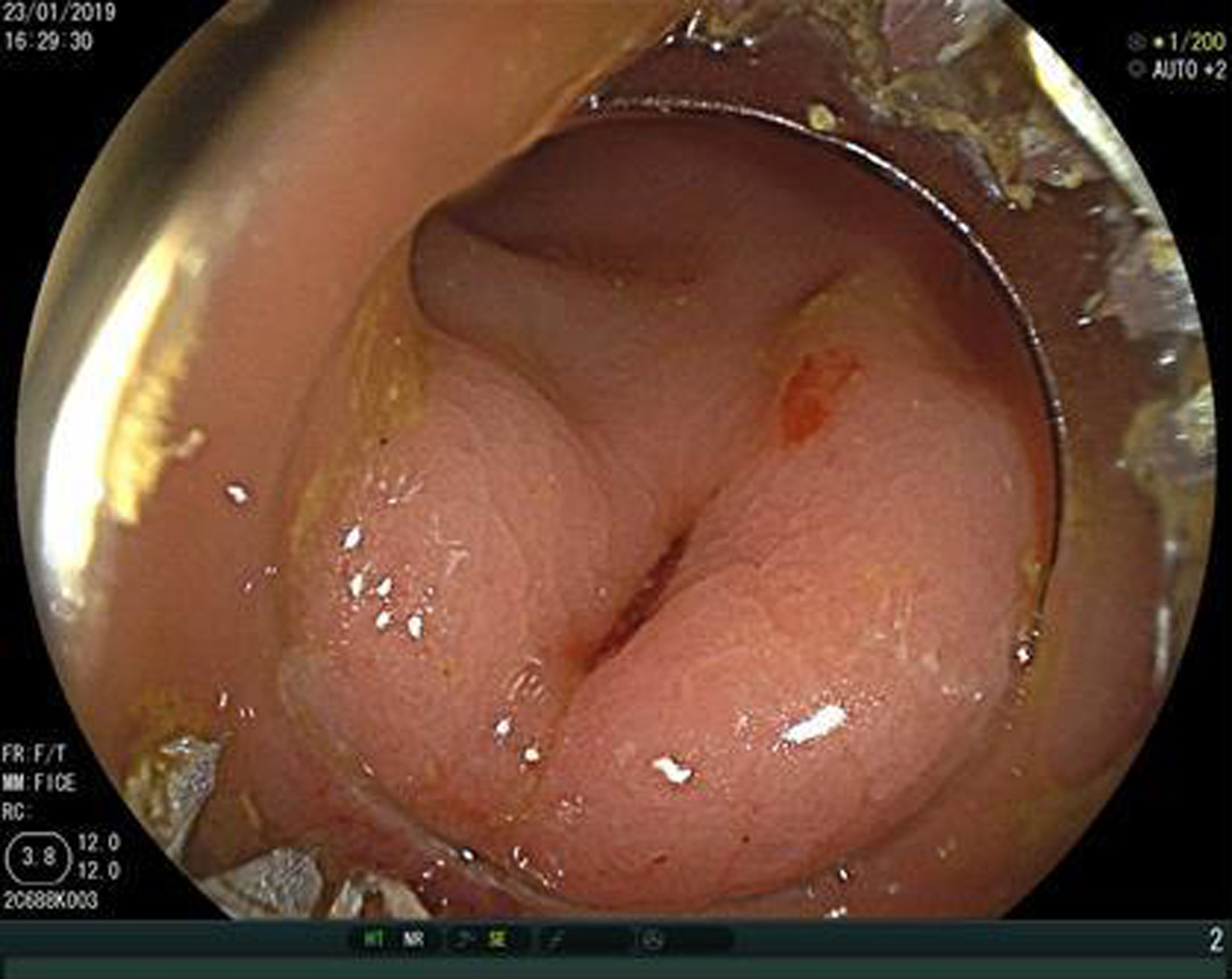
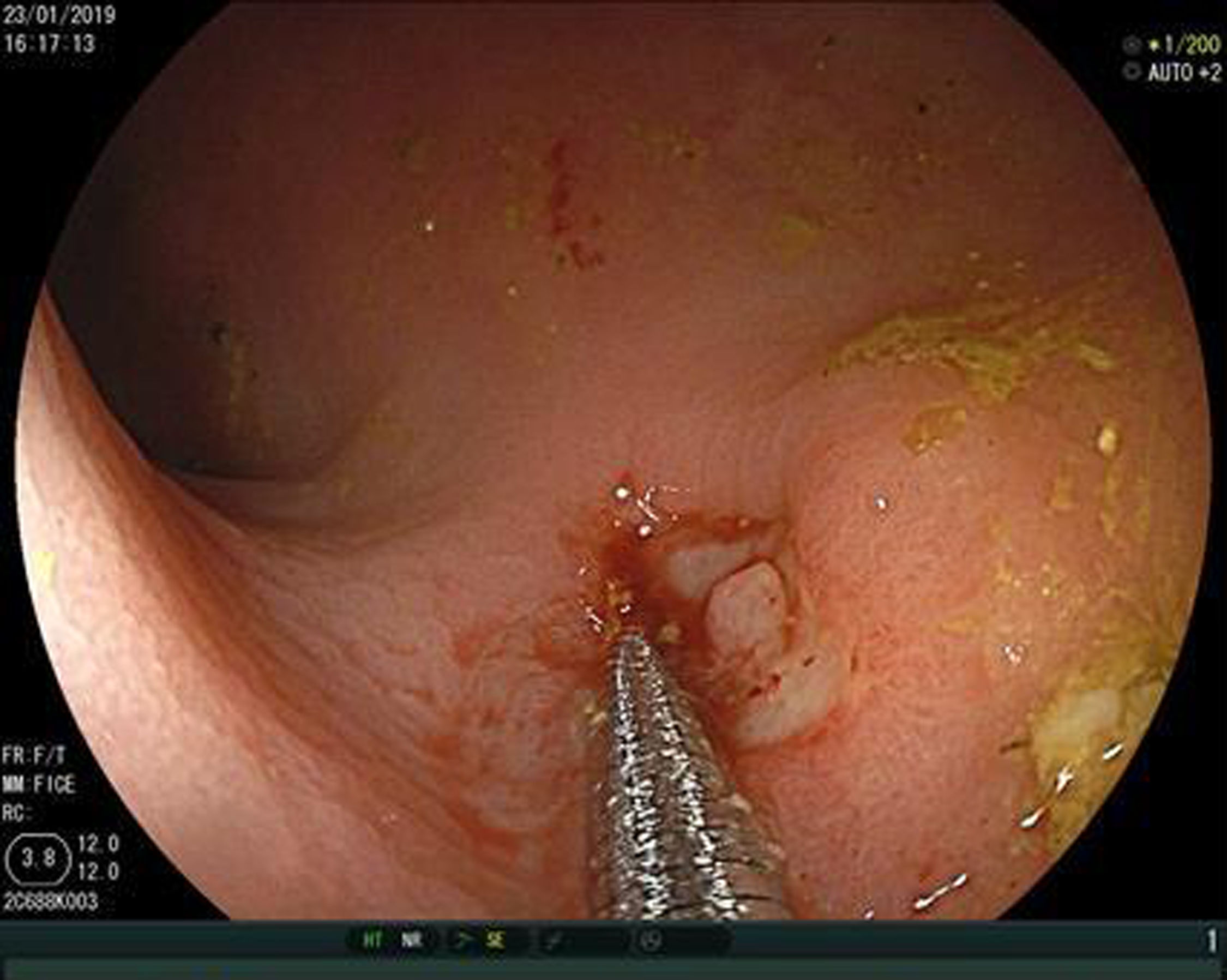
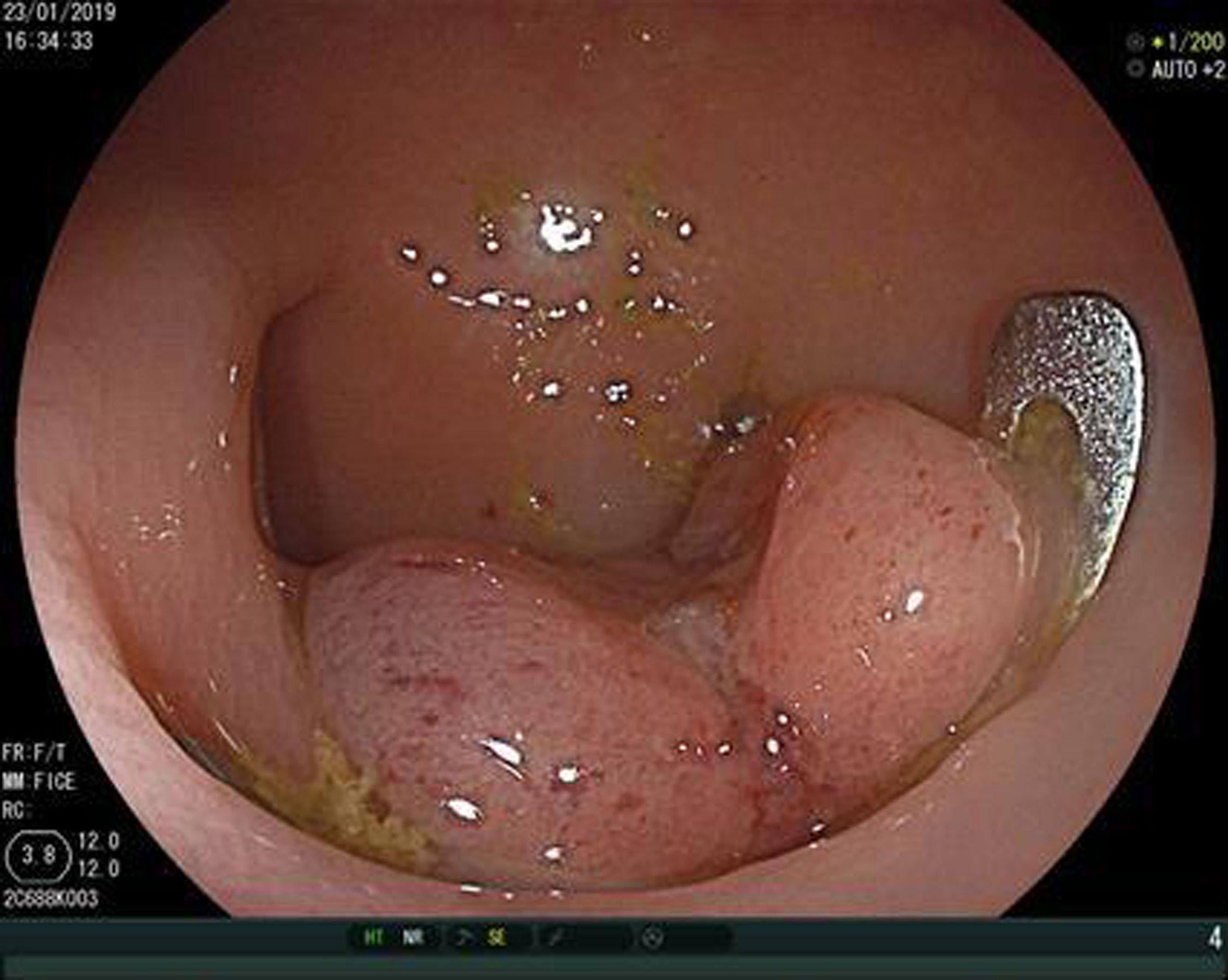
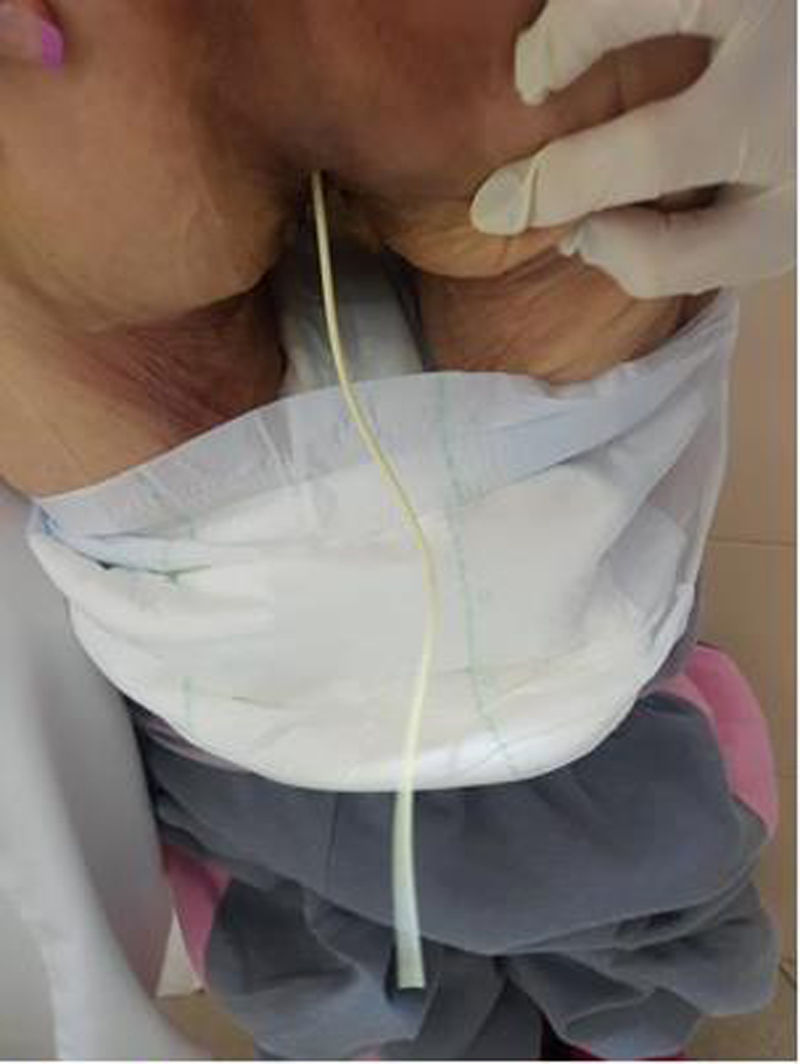
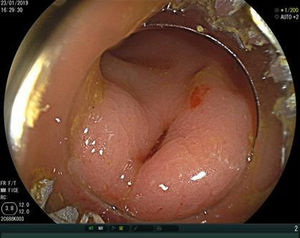
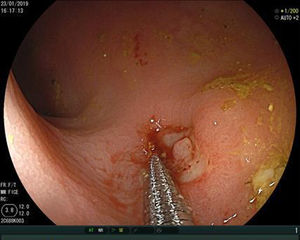
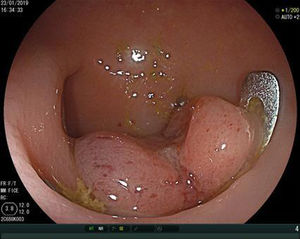
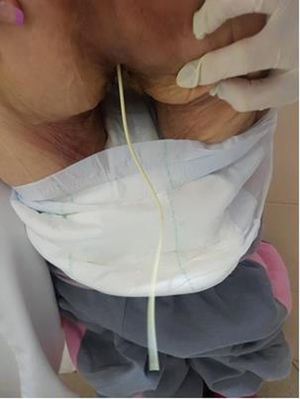
A colonoscopy with CO2 insufflation was performed, without possibility of reaching further than 30cm from the rectal margin due to inappropriate intestinal preparation, and showed no foreign bodies. However, 15mm margin rectal perforation was spotted at 10cm (Figs. 1 and 2) distance from the rectal margin and clipped using OVESCO, which gave excellent result (Fig. 3). Owing to the endoscopy findings, the ventriculoperitoneal shunt was removed. The patient stayed under surveillance for 24h and continued asymptomatic. She was finally discharged. The next day the patient came again exteriorising the rest of the catheter and it was removed manually with no complications (Fig. 4).
Iatrogenic rectal perforation of a VP is a rare adverse event.1–3 It must be suspected in patients that carry this catheter with abdominal pain.1–7 In few cases, surgery can be avoided with endoscopy management.