The aim of this study was to screening PTSD among flood victims in Indonesia.
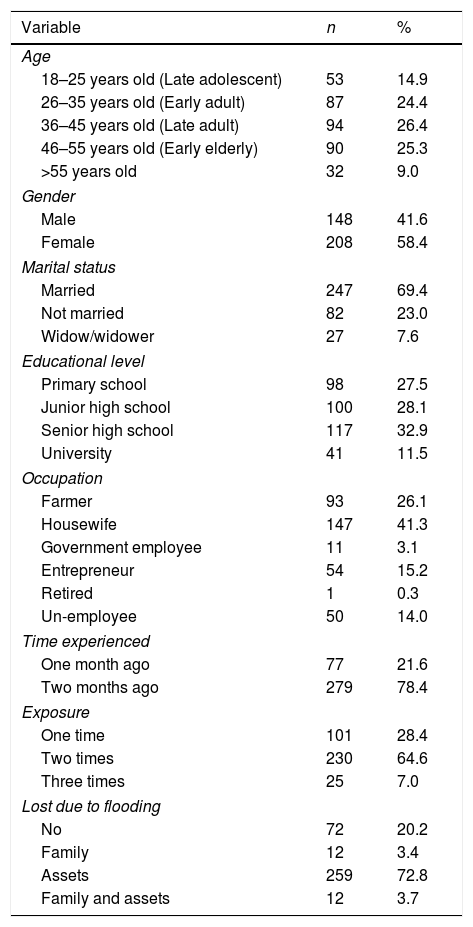
MethodQuantitative non-experimental research method with a descriptive cross-sectional study. There were 356 flooding victims who participated in this study using purposive sampling techniques. The questionnaire used was PCL 5 DSM-V to determine the incidence of PTSD.
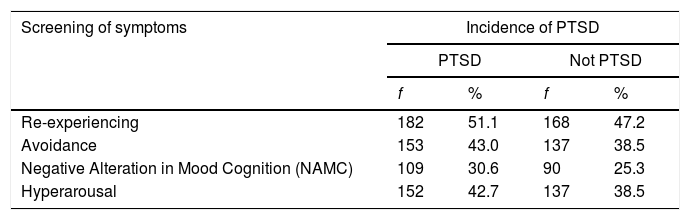
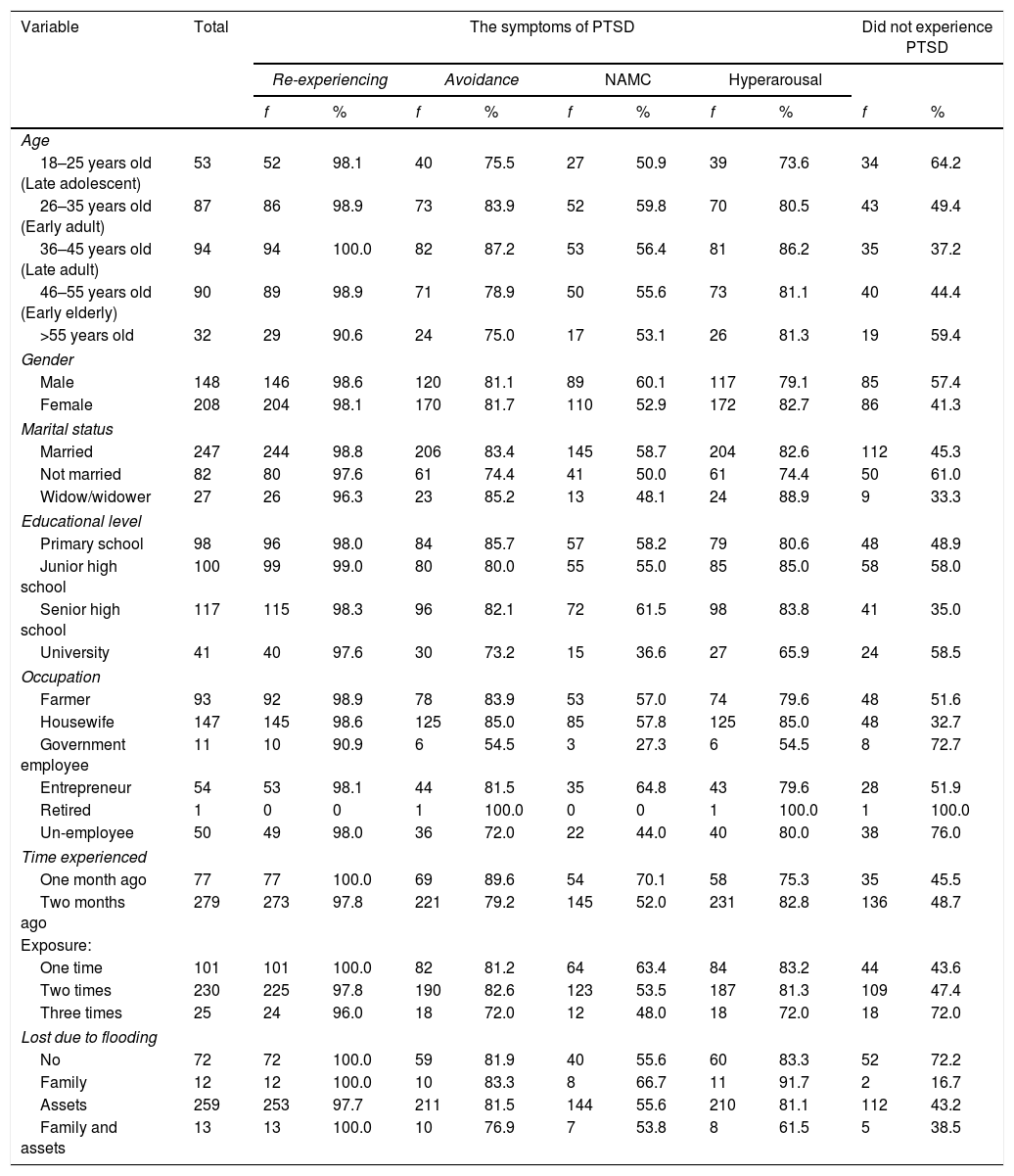
ResultsThe results of the study reported that 52% experiencing PTSD, and 48% did not experience PTSD. The majority of symptoms of PTSD were re-experiencing (98.3%).
ConclusionsIt can be concluded that the incidence of PTSD could arise at any age, gender, level of education and occupation by experiencing symptoms of re-experiencing, avoidance, negative alteration in mood cognition and hyperarousal. Hence, this study suggested improving intervention to decrease symptoms of PTSD.