This study investigates the concordance of bioelectrical impedance vector analysis (BIVA) measurements in both hemisomes in patients receiving fluid therapy, since clinical practice suggests performing them in the hemisoma contralateral to that of its administration to avoid interferences.
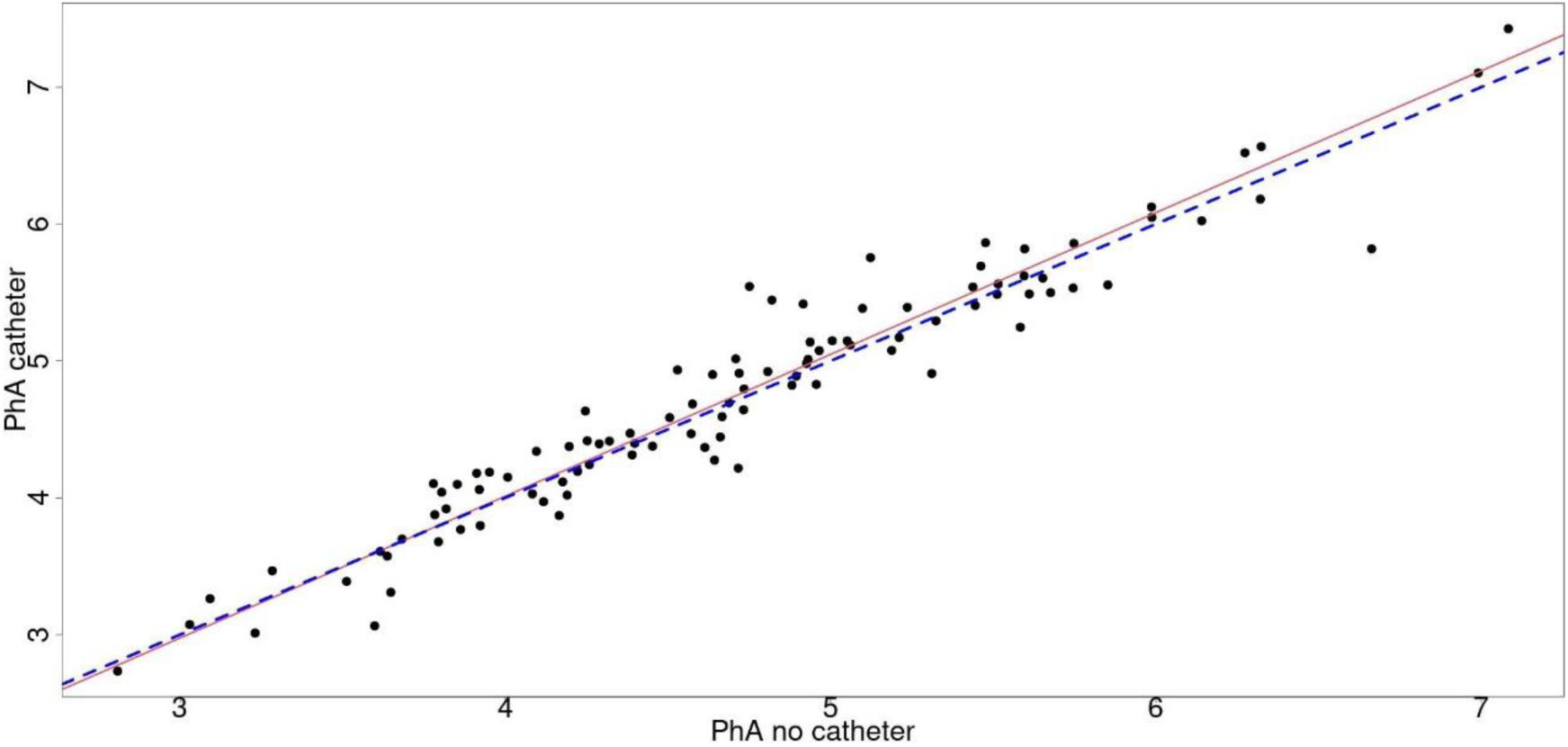
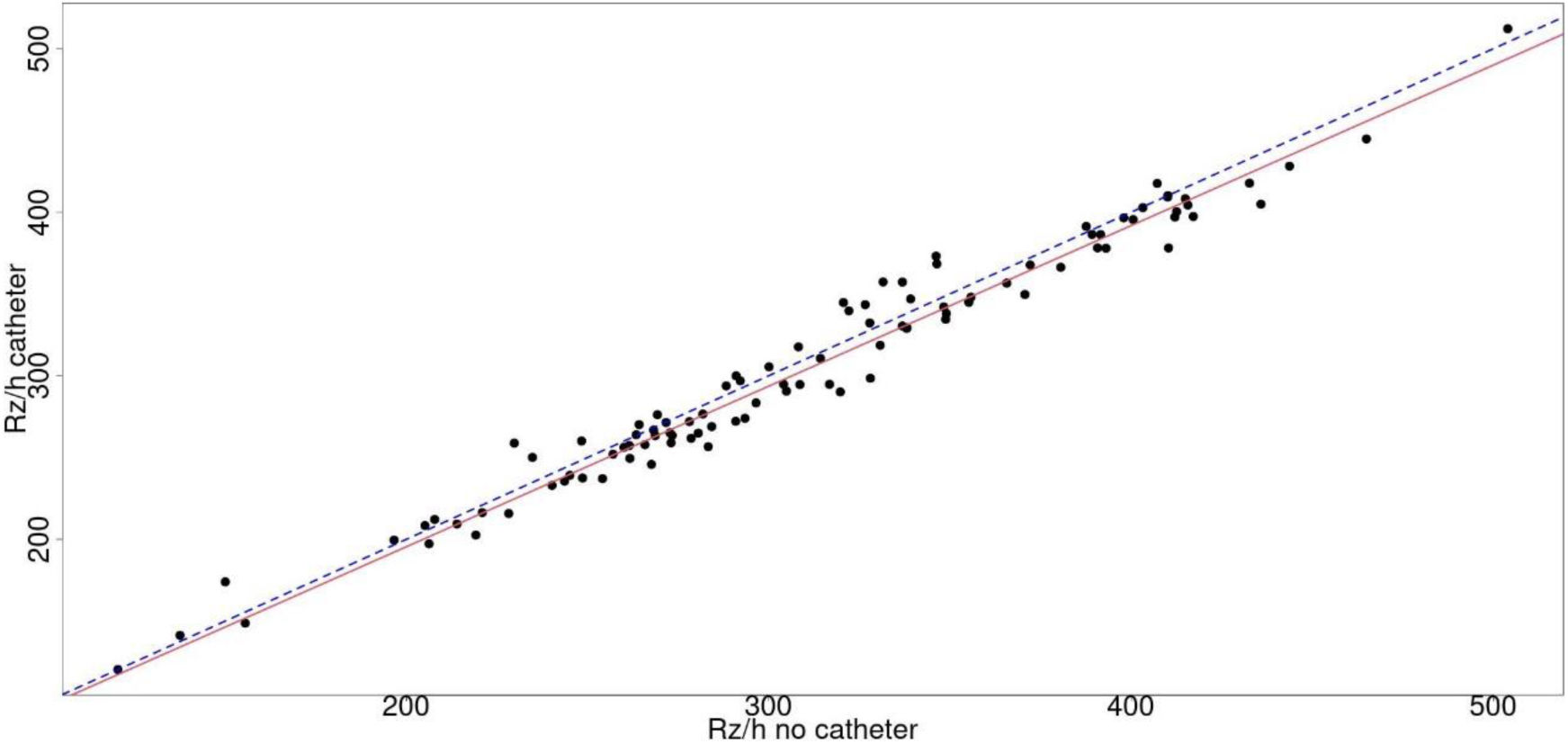
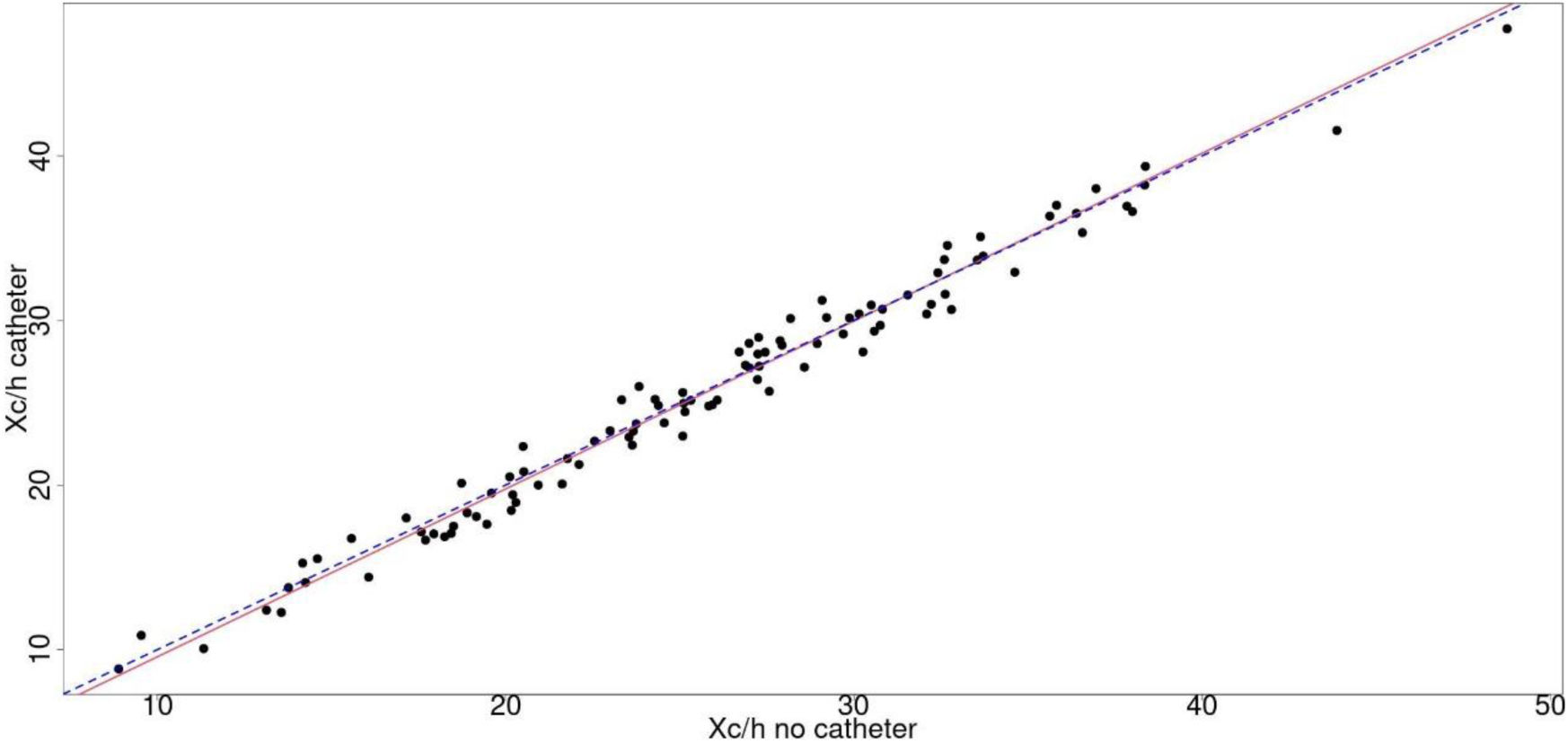
The primary objective of this study was to evaluate the concordance of phase angle (PhA), resistance and reactance, both standardized by height (Rz/h, Xc/h) between the hemisoma where the patient is receiving iv fluids and the other one.
MethodsClinical, prospective and descriptive study, which included 100 hospitalized patients with total parenteral nutrition (TPN) or other intravenous fluid therapy. BIVA measurements were taken in both hemisomes and analyzed by means of Bland–Altman plots, Passing–Block test and conditional method agreement trees (COAT).
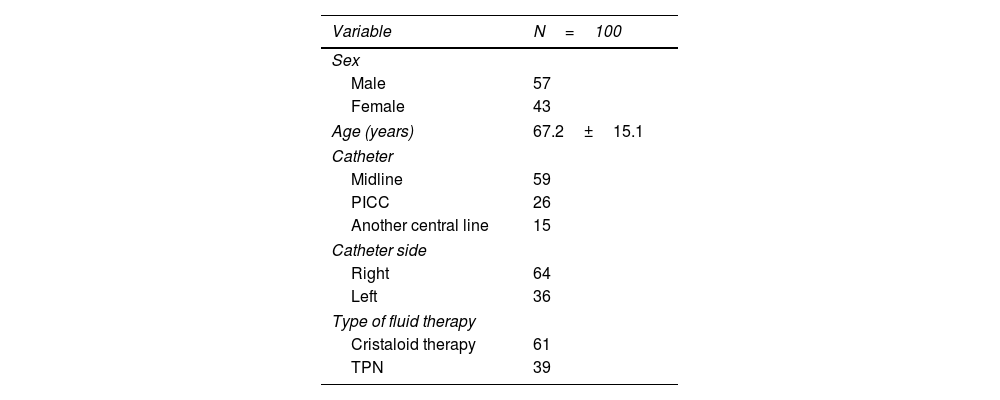
Results100 patients were included (57 men and 43 women), with an average age of 67.2±15.1 years. Univariate analysis using the Bland–Altman plot showed no concordance of PhA, Rz/h and Xc/h between both hemisomes in patients who received fluid therapy, but Passing–Block test showed no systematic or proportional differences between hemisomas and multivariate COAT analysis did not show that the specified covariates affected concordance.
ConclusionsNo systematic or proportional differences between hemisomas in resistance and reactance has been demonstrated, suggesting the possibility of being able to perform the measurement independently of the side of fluid administration.
Este estudio investiga la concordancia de las mediciones del análisis de vector de impedancia bioeléctrica (BIVA) en ambos hemisomas en pacientes que reciben fluidoterapia, ya que la práctica clínica sugiere realizarlas en el hemisoma contralateral al de su administración para evitar interferencias.
El objetivo principal de este estudio fue evaluar la concordancia del ángulo de fase (PhA), resistencia y reactancia, ambas estandarizadas por altura (Rz/h, Xc/h) entre el hemisoma en el que el paciente está recibiendo fluidos intravenosos y el contralateral.
MétodosEstudio clínico, prospectivo y descriptivo, que incluyó 100 pacientes hospitalizados con nutrición parenteral total (NPT) u otra fluidoterapia intravenosa. Las mediciones de BIVA se realizaron en ambos hemisomas y se analizaron mediante gráficos de Bland-Altman, prueba de Passing Block y árboles de acuerdo de métodos condicionales (COAT).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 100 pacientes (57 hombres y 43 mujeres), con una edad media de 67,2±15,1 años. El análisis univariante mediante el gráfico de Bland-Altman no mostró concordancia de PhA, Rz/h y Xc/h entre ambos hemisomas en pacientes que recibieron fluidoterapia, el test Passing Block no mostró diferencias sistemáticas o proporcionales entre hemisomas y el análisis multivariante COAT no mostró que las covariables especificadas afectaran a la concordancia.
ConclusionesNo se han demostrado diferencias sistemáticas o proporcionales entre hemisomas en resistencia y reactancia, lo que sugiere la posibilidad de poder realizar la medición independientemente del lado de administración de fluidos.