This study investigated the association between genetic polymorphisms in the TLR4 (rs4986790 and rs4986791) and IL6 (rs1800795) genes with obesity in a Venezuelan population.
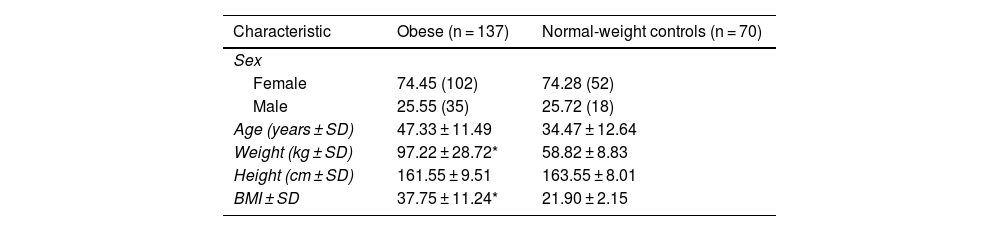
MethodsWe conducted a retrospective case-control study with 207 unrelated Venezuelans (137 obese, 70 normal weight). Blood samples were obtained to measure glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL, insulin, and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR ≥ 2.6) and genotype the TLR4 (rs4986790 and rs4986791) and IL6 (rs1800795) polymorphisms using PCR-SSP. Statistical tests: Student's t-test, Pearson correlation coefficient, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95%CI were used.
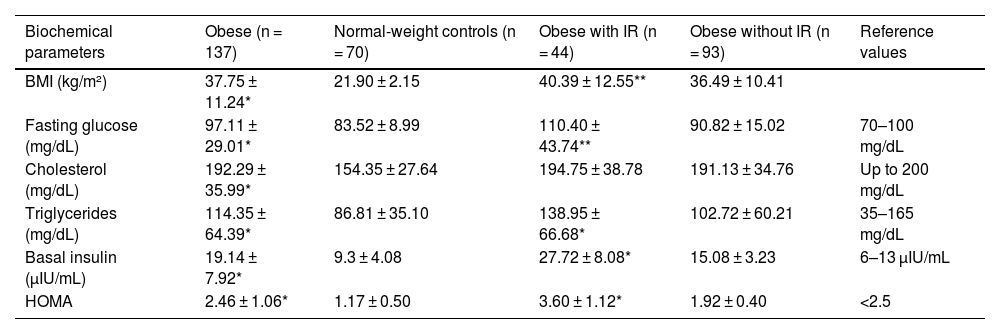
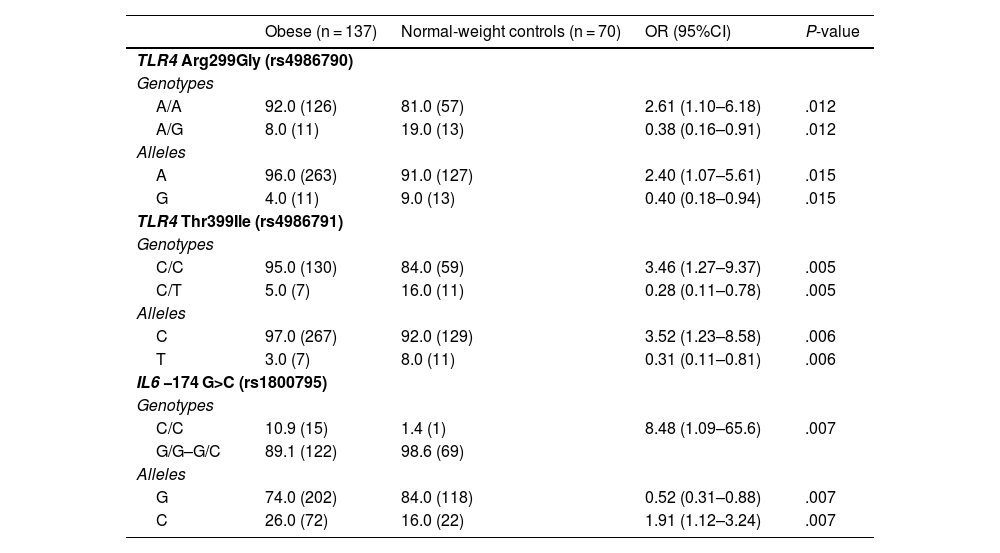
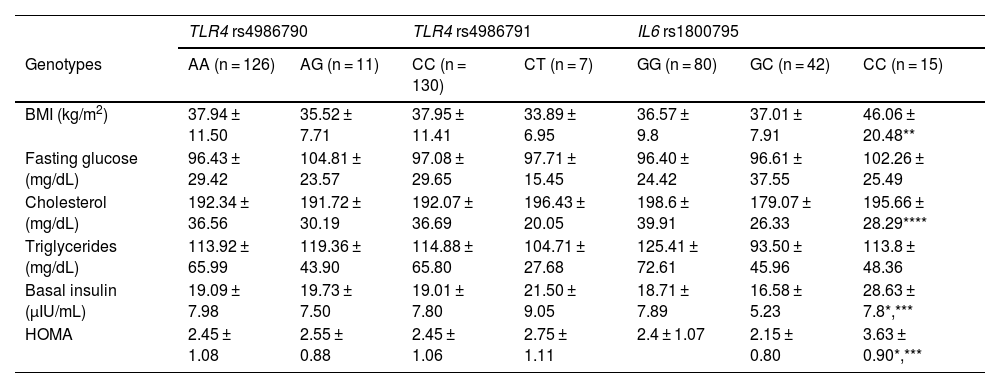
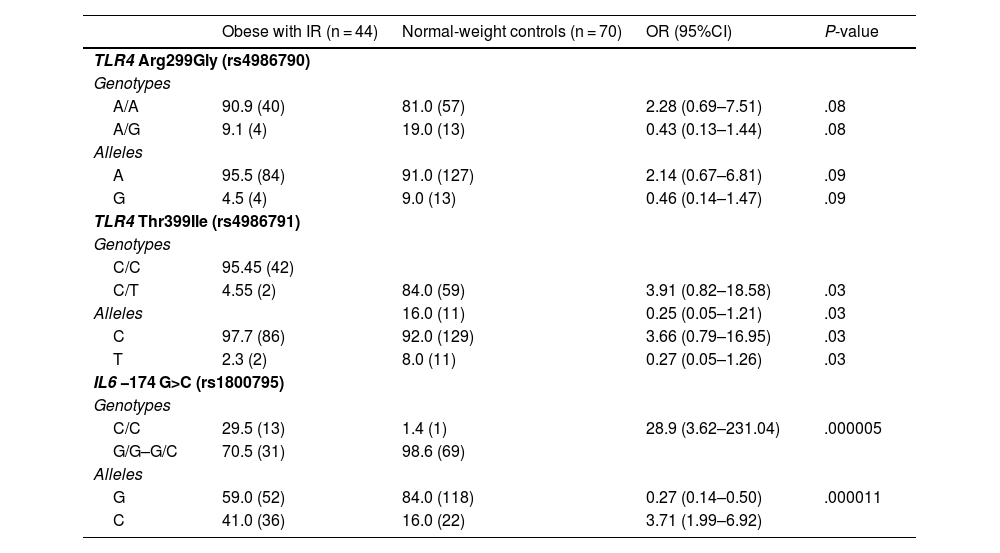
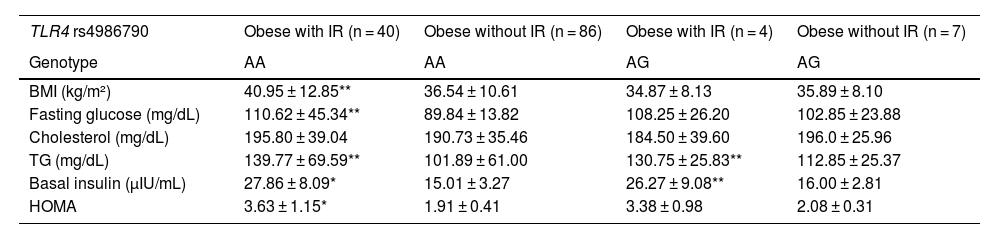
ResultsThe relationship between obesity and insulin resistance (IR) was confirmed. Heterozygous genotypes A/G (TLR4 rs4986790, P = .012) and C/T (TLR4 rs4986791, P = .005) were more frequent in normal-weight individuals, while homozygous genotypes A/A (TLR4 rs4986790, P = .012) and C/C (TLR4 rs4986791, P = .005) were more frequent in obese individuals. The C allele and CC genotype of IL6 rs1800795 (P = .007) were associated with obesity. The IL6 C/C genotype was associated with higher insulin and HOMA in obese individuals. In obese individuals with IR, the CC genotype (TLR4 rs4986791, P = .03) was more common, as opposted to CT, which was less common (P = .03). The C/C genotype of IL6 rs1800795 was more frequent in obese individuals with IR (P < .0001). Obese individuals with IR and the AA genotype of TLR4 rs4986790 had higher BMI, HOMA-IR, and glucose.
ConclusionThese findings suggest that genetic variations in the TLR4 and IL6 genes may predispose to obesity and its metabolic complications in the Venezuelan population.
Este estudio investigó la asociación entre los polimorfismos genéticos del gen TLR4 (rs4986790 y rs4986791) y del gen IL6 (rs1800795) con la obesidad en una población venezolana.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio retrospectivo de casos y controles con 207 venezolanos no relacionados (137 obesos, 70 normopeso). Se obtuvieron muestras de sangre para medir glucosa, colesterol, triglicéridos, HDL, insulina y resistencia a la insulina (HOMA-IR ≥ 2,6), y para genotipificar los polimorfismos TLR4 (rs4986790 y rs4986791) e IL6 (rs1800795) mediante PCR-SSP. Se utilizaron pruebas estadísticas: t de Student, correlación de Pearson, Chi-cuadrado, odds ratio (OR) con IC del 95%.
ResultadosSe confirmó la relación entre obesidad y resistencia a la insulina (RI). Los genotipos heterocigotos A/G (TLR4 rs4986790, p = 0,012) y C/T (TLR4 rs4986791, p = 0,005) fueron más frecuentes en normopeso, y los homocigotos A/A (TLR4 rs4986790, p = 0,012) y C/C (TLR4 rs4986791, p = 0,005) en obesos. El alelo C y genotipo CC de IL6 rs1800795 (p = 0,007) se asociaron con obesidad. El genotipo IL6 C/C se asoció con mayor insulina y HOMA en obesos. En obesos con RI, el genotipo CC (TLR4 rs4986791, p = 0,03) fue más común, y CT menos común (p = 0,03). El genotipo C/C de IL6 rs1800795 fue más frecuente en obesos con RI (p < 0,0001). Obesos con RI y genotipo AA de TLR4 rs4986790 presentaron mayor IMC, HOMA-IR y glucosa.
ConclusiónEstos hallazgos sugieren que la variación genética en los genes TLR4 e IL6 podría contribuir a la predisposición a la obesidad y sus complicaciones metabólicas en la población venezolana.