The active insulin time (AIT) is an adjustable parameter of the MiniMed™ 780G (MM780G) system. We analyze glucose outcomes and patient perception at different AIT settings.
MethodWe conducted a quasi-experimental study on type 1 diabetes mellitus patients treated with MM780G, seen consecutively in our center. AIT was set at 2, 3 and 4h consecutively, during a 2-week period each. Glucose metrics, insulin delivery and a questionnaire about patient perception were evaluated. At the end, results were discussed with the patient and the most appropriate AIT was agreed upon.
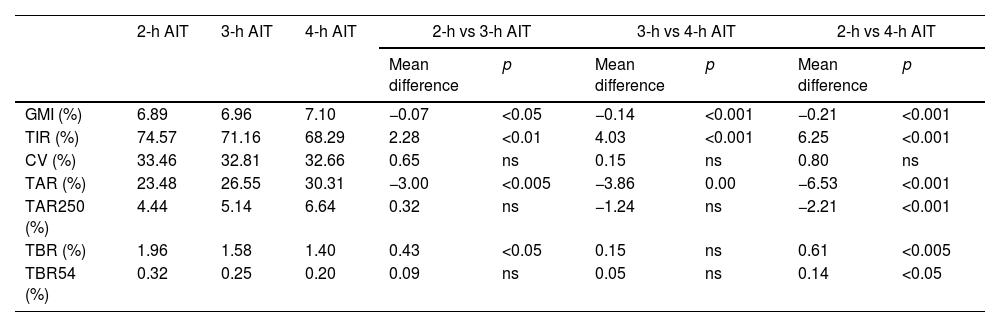
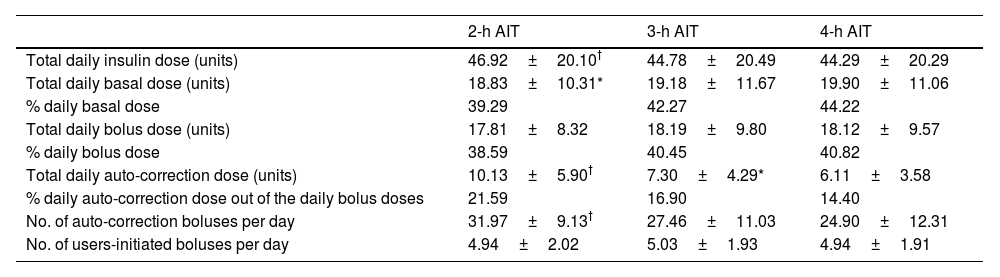
ResultsA total of 58 users were included, aged 18–65 years, 58.6% of whom were women. At baseline, 2-h AIT was set in 6.70% of the patients, >2-h AIT and ≤3-h AIT in 24.67%, >3-h AIT and ≤4-h AIT in 58.62%, and >4-h AIT in 10.34%. Under the 2-h AIT, TIR increased by 2.28% and 6.35% vs 3- and 4-h AIT, respectively. The auto-correction boluses percentage was 21.19% at 2-h AIT, 16.90% at 3-h AIT and 14.40% at 4-h AIT.
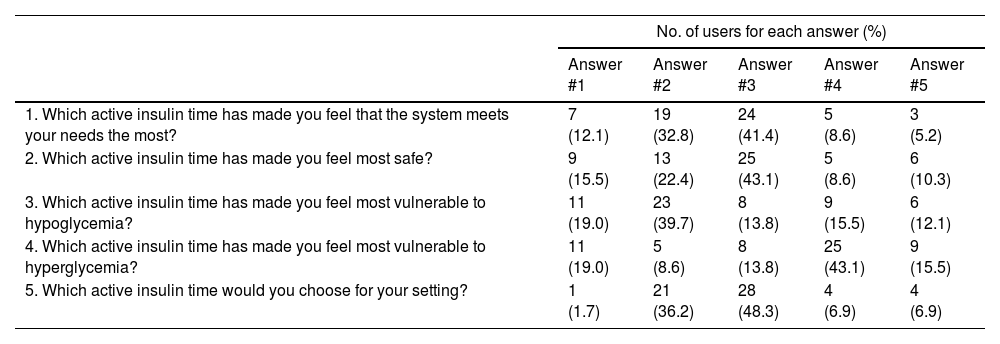
A total of 41.4% of the users considered that 3h was the AIT that most met their needs and 43.1% felt safer and less vulnerable to hypoglycemia at this setting. After trying on different AIT durations, 2h increased from 6.7% of participants to 62%.
ConclusionAt 2-h AIT, the system delivers more auto-correction insulin and improves TIR vs 3- and 4-h AIT. Patients feel safer and less susceptible to hypoglycemia at 3-h AIT, but 2 out of 3 would rather choose the 2-h AIT after knowing glycemic outcomes.
La duración de insulina activa (DIA) es un parámetro ajustable del sistema MiniMed™ 780G (MM780G). El presente estudio analiza los resultados glucémicos y la percepción del paciente con diferentes programaciones de la DIA.
Materiales y métodosEstudio cuasi-experimental sobre pacientes con diabetes tipo 1 tratados con MM780G en nuestro centro. La DIA se estableció en 2, 3 y 4 horas durante un periodo de 2 semanas cada una. Se evaluaron resultados glucémicos, dosificación de insulina y percepción del usuario. Al final del estudio, se acordó con el paciente la DIA más apropiada.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 58 pacientes (18-65 años, 58,6% mujeres). Inicialmente, tenían DIA de 2 horas el 6,70% de los usuarios, > 2 horas y ≤ 3 horas el 24.67%, > 3 y ≤4 horas el 58.62%, y > 4 horas el 10,34%. Con DIA de 2 horas, el TIR aumentó +2,28% y +6.35% frente a 3 y 4 horas. La autocorrección fue 21.19%, 16.90% y 14.40% con 2, 3 y 4 horas respectivamente. El 41,4% de los usuarios consideraba que 3 horas se ajustaba mejor a sus necesidades y el 43,1% se sentía más seguro y menos vulnerable a las hipoglucemias con esta programación. Tras probar diferentes DIA, 2 horas pasó del 6,7% al 62% de los participantes.
ConclusionesLa DIA de 2 horas aumenta la auto-corrección y mejora el TIR, comparado con 3 y 4 horas. Los pacientes se sienten más seguros y menos vulnerables a la hipoglucemia con DIA de 3 horas, pero 2 de cada 3 elegiría 2 horas tras conocer los resultados glucémicos.