To investigate the serum levels of miR-409-3p in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) complicated with coronary heart disease (CHD) and its effect on high glucose (HG)-induced myocardial cell injury.
MethodsA total of 250 patients with T2DM admitted to our hospital from April 2020 through April 2022 were enrolled as the study subjects, and then grouped into T2DM+CHD (group #1) and T2DM (group #2). Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) was used to measure the levels of serum miR-409-3p. The clinical performance of miR-409-3p was evaluated. The human cardiomyocyte AC16 cells were cultured in vitro and treated with HG. MTT assay and flow cytometry were performed to detect cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. Bioinformatic analyses were performed to explore the potential mechanism of miR-409-3p in T2DM complicated with CHD.
ResultsThe expression level of miR-409-3p was increased in the T2DM+CHD group and had a relative high diagnostic value for distinguishing patients with T2DM+CHD from patients with T2DM alone. Correlation analysis showed that serum miR-409-3p was positively associated with the Gensini score and adverse cardiovascular events; miR-409-3p knockdown alleviated HG-induced AC16 cell damage and reduced cell apoptosis. CREB1, BCL2, and SMAD2 were the top 3 hub genes of miR-409-3p.
ConclusionSerum miR-409-3p may serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for predicting T2DM complicated with CHD and forecast adverse events. Targeting miR-409-3p may be a novel therapeutic strategy to intervene in the development of T2DM+CHD.
Investigar los niveles séricos de miR-409-3p en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DMT2) complicada con cardiopatía coronaria (CC) y su efecto sobre la lesión celular miocárdica inducida por glucosa alta (HG).
MétodosUn total de 250 pacientes con DMT2 admitidos en nuestro hospital desde abril de 2020 hasta abril de 2022 se inscribieron como los sujetos del estudio, que se agrupan en DMT2 combinado con el grupo CC y el grupo DMT2. Se aplicó la PCR cuantitativa en tiempo real (RT-qPCR) para medir los niveles de miR-409-3p en suero. Se evaluó el rendimiento clínico de miR-409-3p. Se cultivaron in vitro células de cardiomiocitos humanos AC16 y se trataron con HG. Se realizaron ensayos MTT y citometría de flujo para detectar la viabilidad celular y la apoptosis, respectivamente. Se realizaron análisis bioinformáticos para explorar el mecanismo potencial de miR-409-3p en la DMT2 complicada con cardiopatía coronaria.
ResultadosEl nivel de expresión de miR-409-3p estaba aumentado en el grupo de DMT2+CC y tenía un valor diagnóstico relativamente alto para distinguir a los pacientes con DMT2 y CC de los pacientes con DMT2 sola. El análisis de correlación mostró que miR-409-3p en suero se asociaba positivamente con la puntuación de Gensini y los eventos cardiovasculares adversos. La eliminación de miR-409-3p alivió el daño celular AC16 inducido por HG y redujo la apoptosis celular. CREB1, BCL2 y SMAD2 fueron los 3 genes principales de miR-409-3p.
ConclusionesEl miR-409-3p sérico puede servir como posible biomarcador diagnóstico y pronóstico para predecir la DMT2 complicada con cardiopatía coronaria y pronosticar acontecimientos adversos. Dirigirse a miR-409-3p puede ser una estrategia terapéutica novedosa para intervenir en el desarrollo de la cardiopatía coronaria combinada con la DMT2.
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease with a high incidence rate, and its continuous development can cause vascular endothelial dysfunction, compromising not only the heart but also several organs.1 Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) accounts for appreciatively 90% of all diabetes mellitus patients and mostly occurs in adults and the elderly.2 The long time of high glucose state could damage the vascular barrier, leading to the excessive proliferation of vascular endothelial cells, the weakening of intercellular junction, and the decrease of elasticity, aggravating the vascular lesions in diabetes mellitus patients.3 Coronary heart disease (CHD) is a common complication in patients with T2DM, and most patients with T2DM die of CHD. CHD and T2DM affect one another and form a vicious circle, which in turn aggravates the patient's condition and poses many threats to life safety.4 At present, the pathophysiological mechanism of T2DM+CHD has not yet been fully elucidated. Therefore, finding effective biological indicators to predict the occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events can timely understand the patient's physical and mental health, and improve prognosis.
Related studies manifested the participation of microRNAs (miRs/miRNAs) in the occurrence of T2DM and CHD diseases.5,6 As a group of small noncoding RNA molecules, miRNAs regulate a variety of pathophysiological processes by modulating gene expression at the posttranscriptional level.7,8 The aberrant expression of miR-126, Mir-146a, and miR-193b-3p were reported in T2DM studies.9,10 In studies of T2DM+CHD, many miRNAs have predictive value as biomarkers, such as miR-92a and miR-1306,11,12; miR-409-3p expression was validated to be consistently linked to gestational diabetes mellitus and its targeted genes are associated with metabolic changes in gestational diabetes mellitus.13 In addition, deletion of miR-409-3p improves heart function and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction.14 The relationship between miR-409-3p and T2DM and CHD is still unclear.
This study measured the serum miR-409-3p expression and explored its predictive value on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with T2DM+CHD. Furthermore, the effects of miR-409-3p on high glucose (HG)-induced myocardial cell injury. The primary study may provide certain references for early intervention and prognosis.
Materials and methodsParticipants and clinical specimensPatients with T2DM (n=250) admitted to our hospital from April 2020 through April 2022 were selected as the study subjects. All patients met the diagnostic criteria of T2DM according to the Chinese Guidelines for T2DM,15 including 135 men and 113 women. The participants showed a 2–10 year history of the disease. CHD was determined by coronary angiography in all patients, and the degree of CHD was evaluated using the Gensini score, which could reflect the severity of coronary artery disease.16 Patients were, then, categorized into 2 groups based on the presence or absence of CHD. There were 118 cases in the T2DM+CHD group, and 132 cases in the T2DM group.
Inclusion criteria: (1) All patients met the diagnostic criteria for T2DM, and those with CHD met the WHO diagnostic criteria for ischemic heart disease and, at least, 1 coronary artery stenosis>50% was confirmed by coronary angiography. (2) Patients with complete clinical data; (3) Patients who understood the study and agreed to sign the informed consent form. Exclusion criteria: (1) Patients with a history of hemorrhagic stroke; (2) Patients with inflammatory and immune diseases; (3) Patients with diabetic nephropathy or diabetic foot complications. This study was conducted after being approved by The People's Hospital of Suzhou National New&high-tech Development Zone Ethics Committee.
Patients were monitored for 1 year. The starting point of observation was the day of discharge and the endpoint was the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events, such as cardiac mortality, cerebral bleeding, cerebral infarction, transient ischemic attack, unstable angina pectoris, recurrent angina, chronic heart failure, and acute myocardial infarction.
Fasting venous blood (6mL) was collected from participants on day 2 after admission. Then, the venous blood was centrifuged at 1000×g for 10min at 4°C, and serum samples were collected and stored at −80°C until use.
Cell culture and treatmentHuman myocardial cell line AC16 cells (Shanghai EK-Bioscience Biotechnology Co. Ltd.) were maintained in a dulbecco's modified eagle medium (DMEM, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, United States) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco) and maintained at 37°C in a 5% incubator. Cells were passaged every 2–3 days and used for subsequent experiments. All AC16 cells were divided into 2 groups, including the normal glucose (NG) group (culture condition: 5.5mmol/L [99mg/dL] glucose concentration) and the high glucose concentration (HG) group (incubation condition: 30mmol/L [540mg/dL] glucose concentration) until about 70–80% confluence.
MiR-409-3p inhibitor (anti-miR) and inhibitor negative control (anti-NC) were obtained from the Guangdong RiboBio (R) company. Transfection was performed using AC16 cells (2×105/mL) with the help of Lipofectamine (R) 3000 (Invitrogen). The AC16 cells were categorized into NG group, HG group, HG+anti-NC group (AC16 cells were treated with HG and transfected with 50nM anti-NC), and HG+anti-miR group (50nM anti-miR).
RT-qPCR for detection of miR-409-3pTotal RNA was extracted from serum specimens of participants or AC16 cells using Trizol reagent and purified with mirVana miRNA Isolation Kit (Thermofisher (R)). The RNA eluate was reverse transcribed into cDNA using the miScript Reverse Transcription Kit (Qiagen (R)). The SYBR Premix Ex Taq II (Takara) was used for the RT-PCR in a R 7300 PCR system (Applied Biosystems R). The 2−ΔΔCt method was used to estimate the relative miR-409-3p levels with U6 as the reference gene.
Cell viability detectionThe transfected cells (5000/well) were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured for 24, 48, and 72h, then the culture medium was changed to medium with MTT (5mg/mL). After 4h of further cultivation, the formazan crystals were dissolved by adding 150μL of DMSO, and then the absorbance value (490nm) of each well was recorded using a microplate reader.
Cell apoptosis detectionCells were collected and washed twice with cold PBS, and resuspended in 100μL binding buffer. Afterwards, the cells were stained with 10μL Annexin V-FITC and 5μL PI for 10min in the dark. Finally, apoptotic cells were analyzed by flow cytometry within 1h and the apoptotic rate was expressed as a percentage of cells.
Differential miR-409-3p targeted mRNAs prediction and enrichment analysisThe targets of miR-409-3p were predicted from miRDB, miRWalk, and ENCORI databases. The enriched KEGG pathway analysis for the interactions between miR-409-3p and mRNAs, as well as GO enrichment was performed using the bioinformatic analysis software DAVID (http://geneontology.org). The target mRNAs of miR-409-3p were overlapped and enrolled in the STRING database (http://string-db.org) for PPI interaction analysis and visualized with the Cytoscape software (top 10 nodes with MCC).
Statistical analysisSPSS (version 26) and GraphPad Prism (version 9.0) software were used for statistical analysis. Measurement data were expressed mean±SD. The Student's t-test and the one-way ANOVA test were used for comparison between 2 groups and among multiple groups, respectively. The clinical significance of miR-409-3p was assessed using the Receiver operative curve and Kaplan–Meier curve. P values<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
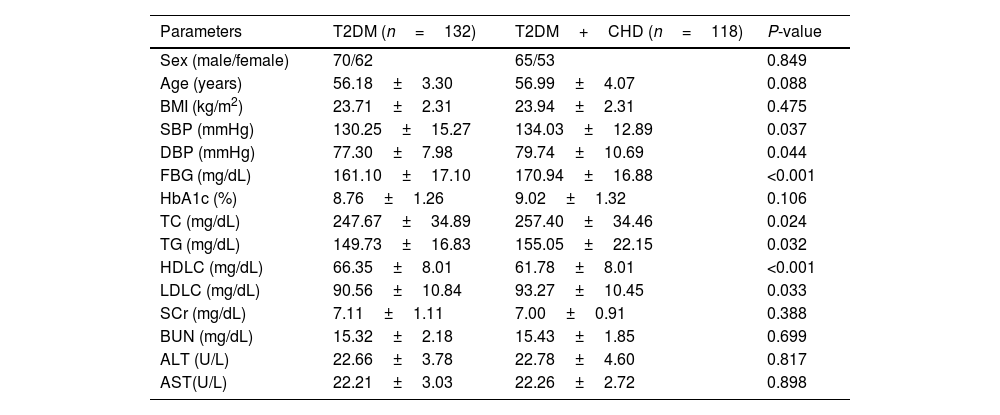
ResultsComparison of clinical characteristics of the study populationTable 1 illustrates the clinical parameters of the T2DM group and T2DM+CHD group. There were no significant differences regarding sex, age, body mass index (BMI), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (ALT), and aspartate transaminase (AST) between the study population. Compared with the T2DM group, the levels of SBP, DBP, FBG, TC, TG, LDLC increased, while the HDLC levels decreased in the T2DM+CHD group (Table 1).
Clinical characteristics of the study population.
| Parameters | T2DM (n=132) | T2DM+CHD (n=118) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 70/62 | 65/53 | 0.849 |
| Age (years) | 56.18±3.30 | 56.99±4.07 | 0.088 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.71±2.31 | 23.94±2.31 | 0.475 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 130.25±15.27 | 134.03±12.89 | 0.037 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 77.30±7.98 | 79.74±10.69 | 0.044 |
| FBG (mg/dL) | 161.10±17.10 | 170.94±16.88 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 8.76±1.26 | 9.02±1.32 | 0.106 |
| TC (mg/dL) | 247.67±34.89 | 257.40±34.46 | 0.024 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 149.73±16.83 | 155.05±22.15 | 0.032 |
| HDLC (mg/dL) | 66.35±8.01 | 61.78±8.01 | <0.001 |
| LDLC (mg/dL) | 90.56±10.84 | 93.27±10.45 | 0.033 |
| SCr (mg/dL) | 7.11±1.11 | 7.00±0.91 | 0.388 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 15.32±2.18 | 15.43±1.85 | 0.699 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.66±3.78 | 22.78±4.60 | 0.817 |
| AST(U/L) | 22.21±3.03 | 22.26±2.72 | 0.898 |
Body mass index (BMI), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (ALT), and aspartate transaminase (AST), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC).
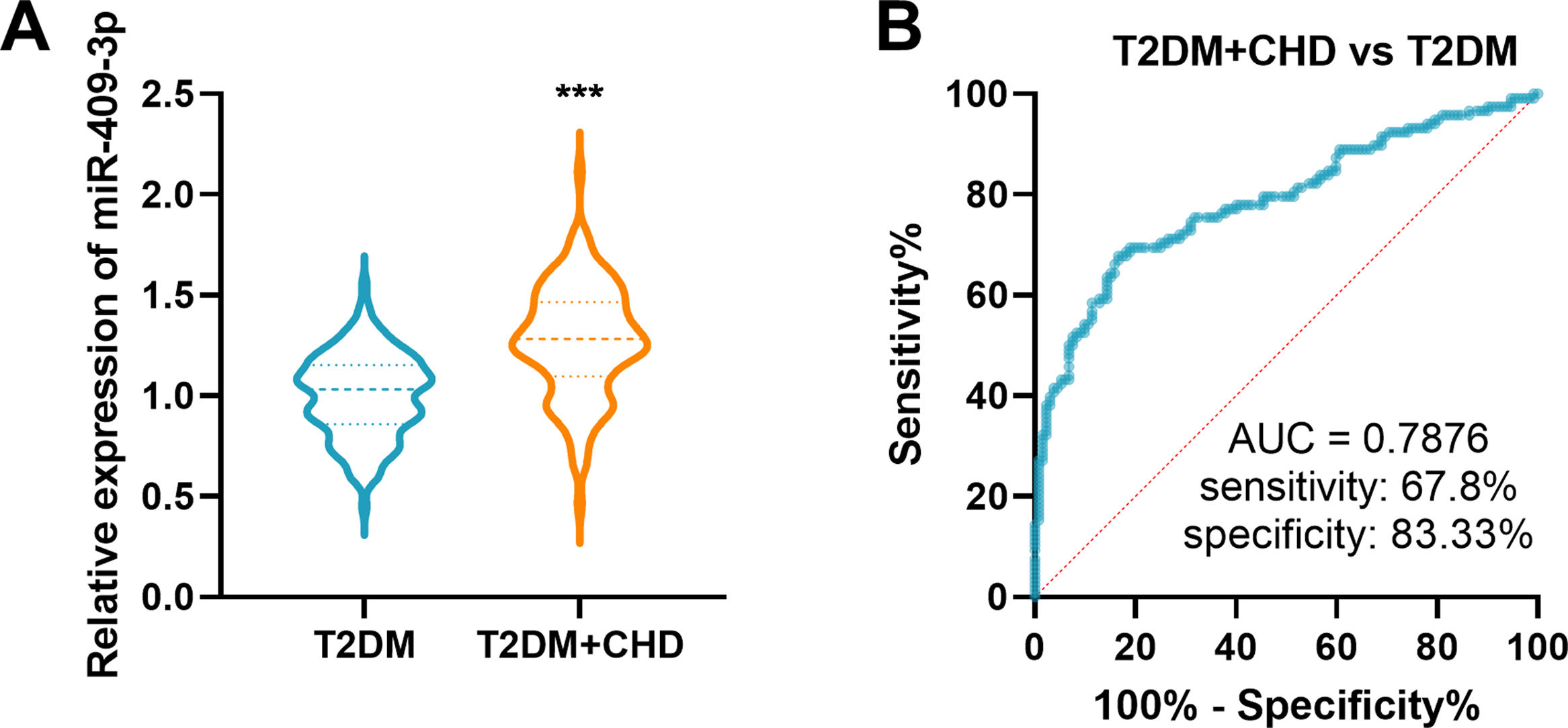
Compared to T2DM group, the T2DM+CHD group showed an increased miR-409-3p expression with a 1.3-fold increase (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, the ROC curve illustrated serum miR-409-3p has a high predictive value (AUC=0.7876) in distinguishing T2DM+CHD from T2DM patients (Fig. 1B) with a 67.8% sensitivity rate and a 83.33% specificity rate.
Levels and diagnostic value of serum miR-409-3p in study population. (A) Serum miR-409-3p levels were enhanced in patients with T2DM+CHD vs patients with T2DM alone. ***P<0.001. (B) Serum miR-409-3p has potential diagnostic performance in distinguishing T2DM+CHD patients from T2DM patients alone. AUC=0.7876.
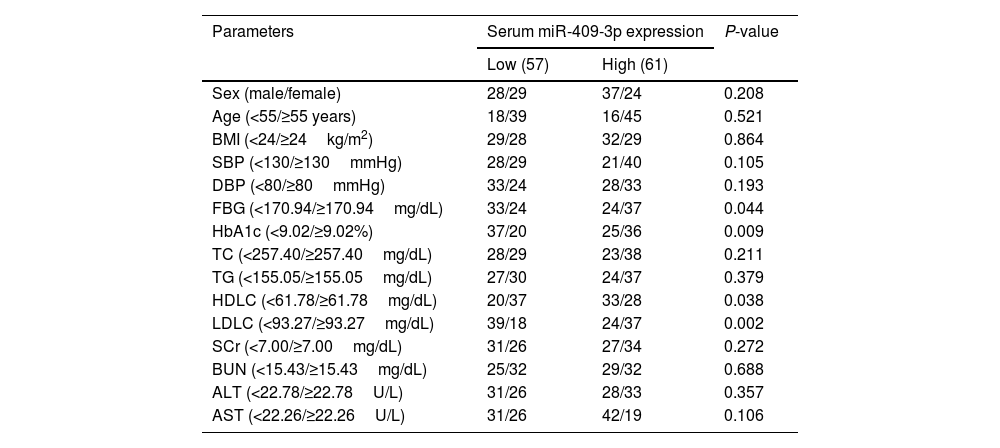
To probe the effects of miR-409-3p in T2DM+CHD patients, T2DM+CHD group patients were categorized into 2 groups based on the serum miR-409-3p levels in these patients and listed in Table 2. Table 2 shows that high miR-409-3p expression was correlated with FBG, HbA1c, HDLC, and LDLC whereas, no significant correlation was observed between miR-409-3p expression and other clinical parameters, including sex, age, BMI, SBP, DBP, TC, TG, SCr, BUN, ALT, and AST.
Correlation between serum miR-409-3p expression and clinical data of T2DM+CHD patients.
| Parameters | Serum miR-409-3p expression | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (57) | High (61) | ||
| Sex (male/female) | 28/29 | 37/24 | 0.208 |
| Age (<55/≥55 years) | 18/39 | 16/45 | 0.521 |
| BMI (<24/≥24kg/m2) | 29/28 | 32/29 | 0.864 |
| SBP (<130/≥130mmHg) | 28/29 | 21/40 | 0.105 |
| DBP (<80/≥80mmHg) | 33/24 | 28/33 | 0.193 |
| FBG (<170.94/≥170.94mg/dL) | 33/24 | 24/37 | 0.044 |
| HbA1c (<9.02/≥9.02%) | 37/20 | 25/36 | 0.009 |
| TC (<257.40/≥257.40mg/dL) | 28/29 | 23/38 | 0.211 |
| TG (<155.05/≥155.05mg/dL) | 27/30 | 24/37 | 0.379 |
| HDLC (<61.78/≥61.78mg/dL) | 20/37 | 33/28 | 0.038 |
| LDLC (<93.27/≥93.27mg/dL) | 39/18 | 24/37 | 0.002 |
| SCr (<7.00/≥7.00mg/dL) | 31/26 | 27/34 | 0.272 |
| BUN (<15.43/≥15.43mg/dL) | 25/32 | 29/32 | 0.688 |
| ALT (<22.78/≥22.78U/L) | 31/26 | 28/33 | 0.357 |
| AST (<22.26/≥22.26U/L) | 31/26 | 42/19 | 0.106 |
Body mass index (BMI), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), glutamic pyruvic transaminase (ALT), and aspartate transaminase (AST), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting blood glucose (FBG), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLC), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLC).
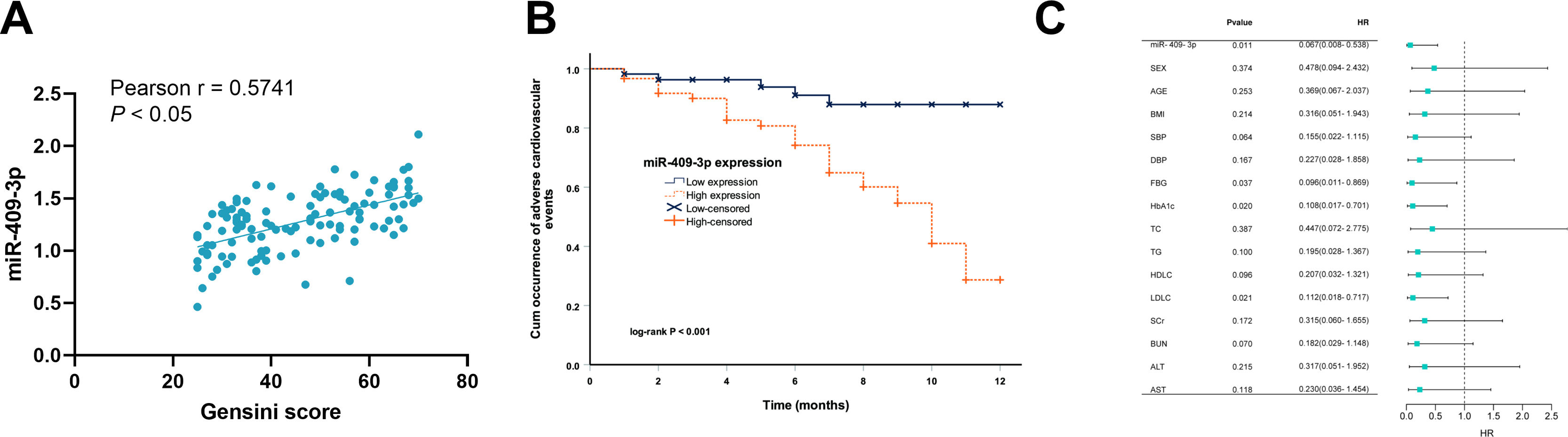
Pearson analysis shows that miR-409-3p levels were positively correlated with the Gensini score (r=0.5741, P<0.05, Fig. 2A). The Gensini score is associated with the severity of coronary heart disease, thus, the prognostic performance of serum miR-409-3p in T2DM+CHD patients was probed. Among the 118 cases of T2DM+CHD patients, 34 patients had adverse cardiovascular events. The Kaplan–Meier curve revealed that patients who had high miR-409-3p levels were more likely to experience adverse events and had poor prognosis (Fig. 2B). Multiple logistic analysis indicated that miR-409-3p was a risk factor associated with the severity of T2DM+CHD patients (Fig. 2C).
Serum miR-409-3p was associated with the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. (A) A positive correlation was seen between serum miR-409-3p and the Gensini score. Pearson r=0.5741, P <0.05. (B) High miR-409-3p expression was associated with adverse cardiovascular events. Log-rank test P<0.001. (C) Serum miR-409-3p expression was one of the risk factors for the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. P=0.015.
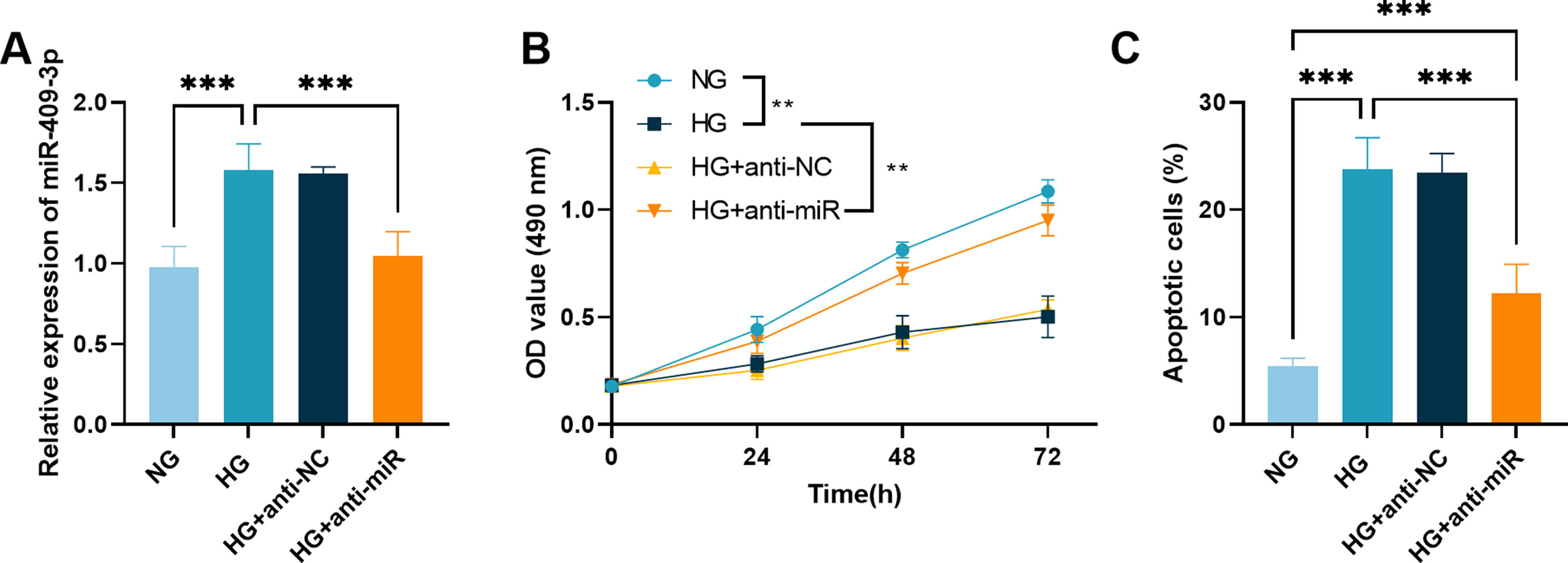
Compared with the NG group, miR-409-3p expression was enhanced in HG-induced AC16 cells. MiR-409-3p inhibitor repressed the increased miR-409-3p levels in HG-induced AC16 cells (Fig. 3A). The proliferation activity of AC16 cells in the HG group decreased at 24, 48, and 72h time points the vs the NG group. The proliferative activity of AC16 cells was increased in HG+anti-miR group vs the HG group (Fig. 3B). The apoptosis of AC16 cells was increased after HG treatment vs the NG group, while the raised apoptosis rate was diminished after restraint of miR-409-3p expression in HG+anti-miR group vs the HG group (Fig. 3C).
Effects of miR-409-3p knockdown on HG-induced proliferative properties and apoptotic abilities. (A) The transfection efficiency was measured in AC16 cells. ***P<0.001. (B) Knockdown of miR-409-3p elevated the proliferative activity of HG-treated AC16 cells. **P<0.01. (C) Silencing of miR-409-3p protected AC16 from antagonizing HG-induced apoptosis. ***P<0.001.
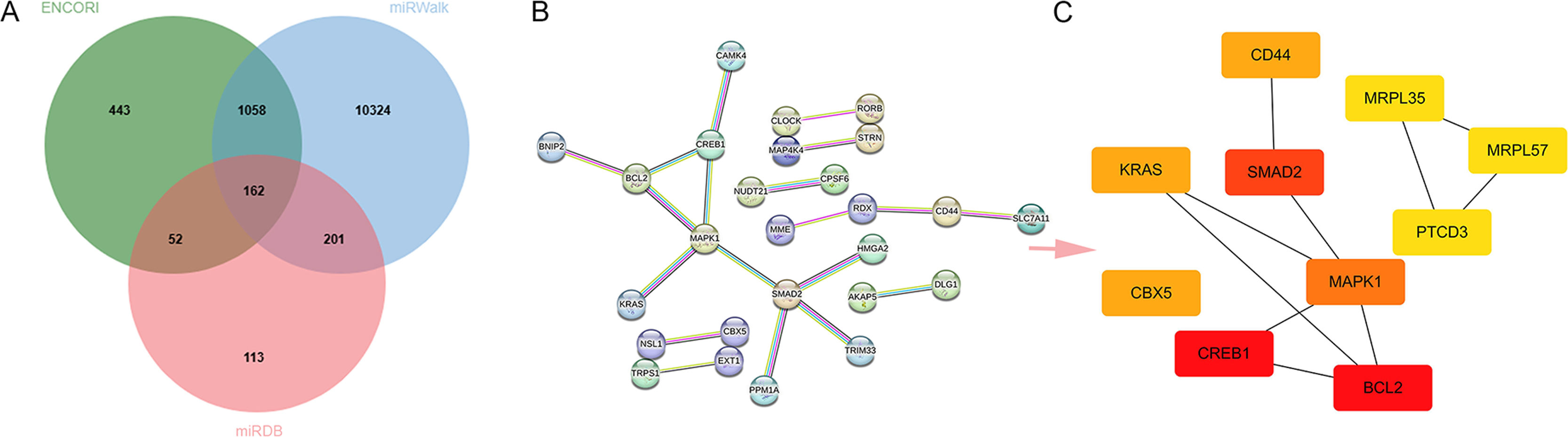
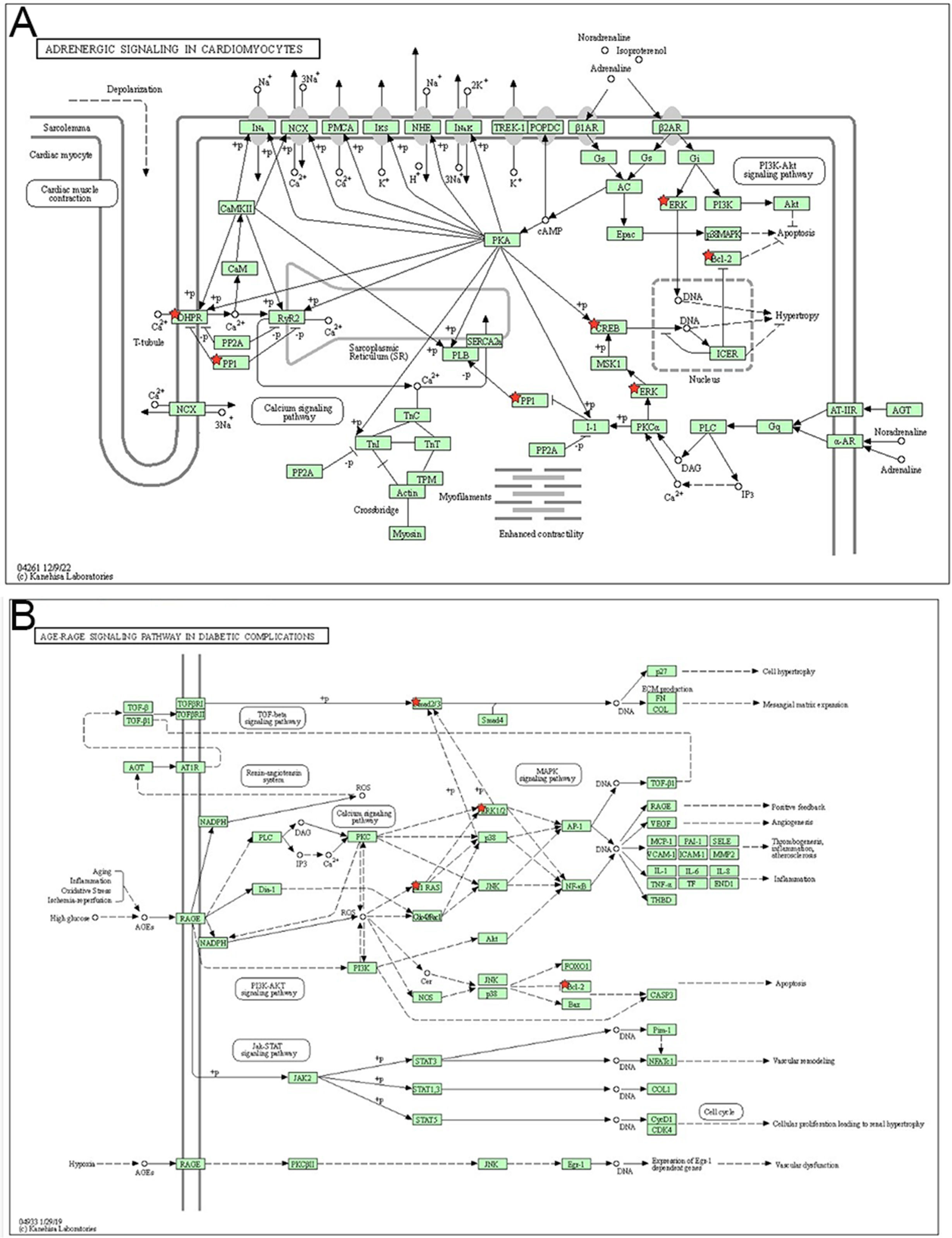
To explore the plausible mechanism of miR-409-3p in the process of T2DM+CHD, online bioinformatic databases (ENCORI, miRWalk, and miRDB) were used to screen and overlap possible targets (Fig. 4A). The overlapped 162 targets were enrolled into enrichment pathway analysis using the online database DAVID. The GO and KEGG pathway enrichment data are listed in the Supplementary Table 1. The enriched KEGG pathways of the DAVID databased displayed in the KEGG pathway database showed that the targets of miR-409-3p were enriched in many signaling pathways, especially adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes and age-rage signaling pathway in diabetic complications (Supplementary Fig. 1A and B). The 162 targets of miR-409-3p were enrolled in a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network using STRING (settings: interaction score with highest confidence 0.900 and hide disconnected nodes in the network) (Fig. 4B). Afterwards, the top 10 hub genes were visualized using Cytoscape software and the result showed that CREB1, BCL2, SMAD2, MAPK1, CD44, KRAS, CBX5, MRPL35, MRPL57, and PTCD3 played crucial roles in maintaining stability in the network, especially CREB1, BCL2, and SMAD2 (Fig. 4C).
DiscussionPatients with T2DM+CHD often exhibit a damaged cardiac system due to vascular lesions, yet the early symptoms are not obvious, and as disease progresses, atherosclerosis and angina pectoris can show.17 Early prediction of the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with T2DM+CHD may stop the progression of the disease in time and improve the prognosis of the patients with targeted therapy. The results of this study showed that the levels of serum miR-409-3p in T2DM complicated with CHD were higher than those from patients with T2DM alone and had potential diagnostic performance. The serum miR-409-3p was related to the severity of the disease (Gensini score) in patients with T2DM complicated with CHD. Functional findings indicated that the inhibition of miR-409-3p elevated the proliferative activity of HG-treated AC16 cells and protected AC16 from antagonizing HG-induced apoptosis. Bioinformatic analysis revealed the top 10 hub genes of miR-409-3p, especially including CREB1, BCL2, and SMAD2.
The vital role of miR-409-3p was revealed in inflammation, apoptosis, and proliferation in many diseases.18,19 For instance, miR-409-3p was identified as an anti-angiogenic miRNA that could modulate insulin resistance.20 miR-409-3p expression was enhanced in acute coronary syndrome and deficiency of its expression could improve myocardial neovascularization by regulating DNAJB9/p38 MAPK signaling.14 In this study, miR-409-3p was upregulated in patients with T2DM complicated with CHD vs patients with T2DM alone, which replied that miR-409-3p may participate in the severity processes of T2DM. T2DM patients were defined according to Chinese Guidelines, which were not significantly different from ADA guidelines and more suitable for the Chinese population. Additionally, serum miR-409-3p has a relatively high diagnostic performance in differentiating patients with T2DM-complicated CHD from patients with T2DM alone. Using serum miR-409-3p expression in patients with T2DM complicated CHD, the clinical analysis indicated that miR-409 expression was correlated with FBG, HbA1c, HDLC, and LDLC, but not with TG and TC, which may be biased by the limited samples or influenced by other clinical factors. As most studies reported, FBG, HbA1c, HDLC, and LDLC are cardiovascular risk factors.21,22 These data revealed that miR-409-3p could also be correlated with the processes of T2DM complicated with CHD. Besides, the combination of clinical cardiovascular risk factors and miR-409-3p may improve the sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis for T2DM complicated with CHD. In addition, serum miR-409-3p could predict the severity of the disease (Gensini score) in patients with T2DM complicated with CHD. High miR-409-3p expression was prone to adverse cardiovascular events, which suggests that serum miR-409-3p has prognostic value in patients with T2DM complicated with CHD. Multiple logistic analyses revealed that miR-409-3p expression was a risk factor associated with the severity of T2DM+CHD patients. However, the clinical role of miR-409-3p needs further validation in a large cohort of samples.
Functional findings indicated that the silencing of miR-409-3p strengthened the proliferative abilities of HG-treated AC16 cells and protected AC16 from antagonizing HG-induced apoptosis. A previous study indicated that silencing miR-409-3p repressed cardiac fibroblast proliferation and fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation by regulating Gpd1.23 The above findings suggest that miR-409-3p is a potential target for intervention in cardiomyocyte injury in high glucose in patients with T2DM complicated with CHD. Bioinformatic analysis overlapped the targets of miR-409-3p and found the top 10 targets, including CREB1, BCL2, and SMAD2, which are crucial factors in adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes and age-rage signaling pathway in diabetic complications. CREB1, BCL2, and SAMD2 are involved in various signaling and take part in the progression of diseases.24–26 These data suggest that miR-409-3p may be involved in the progression of T2DM+CHD by binding to CREB1, BCL2, or SMAD2.
In conclusion, serum miR-409-3p may serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for predicting T2DM complicated with CHD and forecasting adverse events; miR-409-3p knockdown may antagonize HG-induced damage in human cardiomyocytes. Therefore, targeting miR-409-3p may be a novel therapeutic strategy to intervene in the progression of T2DM+CHD. The detailed mechanism of miR-409-3p needs to be further explored.
FundingNone declared.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.