Diabesity is a pathological condition that combines obesity and type 2 diabetes in the same individual. Due to the current rise in both conditions, the prevalence of diabesity is increasing worldwide. Its etiology is known to be multifactorial; therefore, the aim of this study is to understand how diabesity is associated with various sociodemographic variables, healthy habits, and stress.
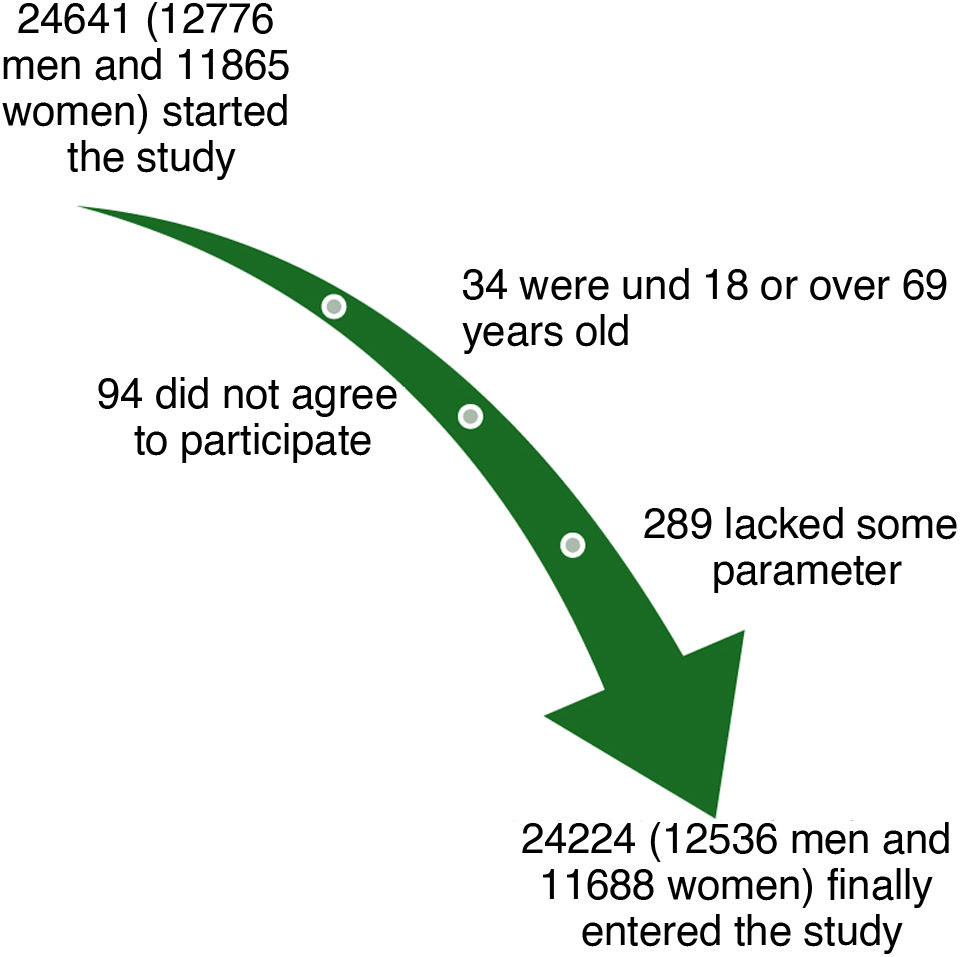
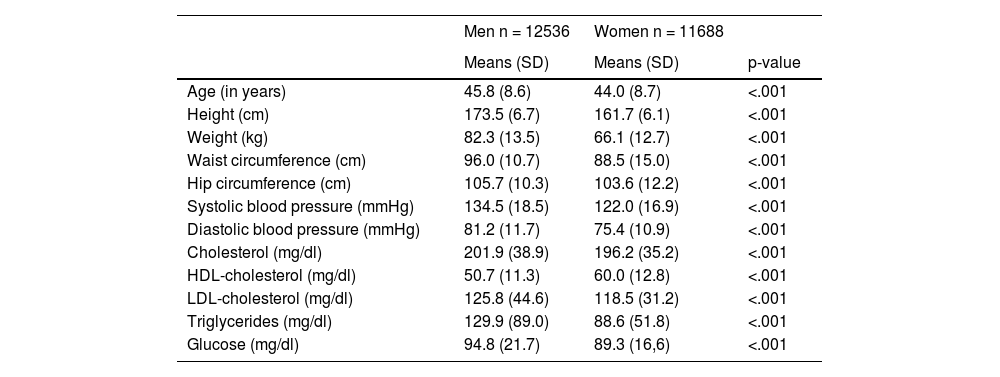
Materials and methodsA descriptive, cross-sectional study was conducted on 24,224 Spanish workers to evaluate the association between diabesity and various factors such as age, gender, socioeconomic status, smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, adherence to the Mediterranean diet, and stress. The criteria used to define diabesity included body mass index (BMI), body fat (BF), and visceral fat (VF).
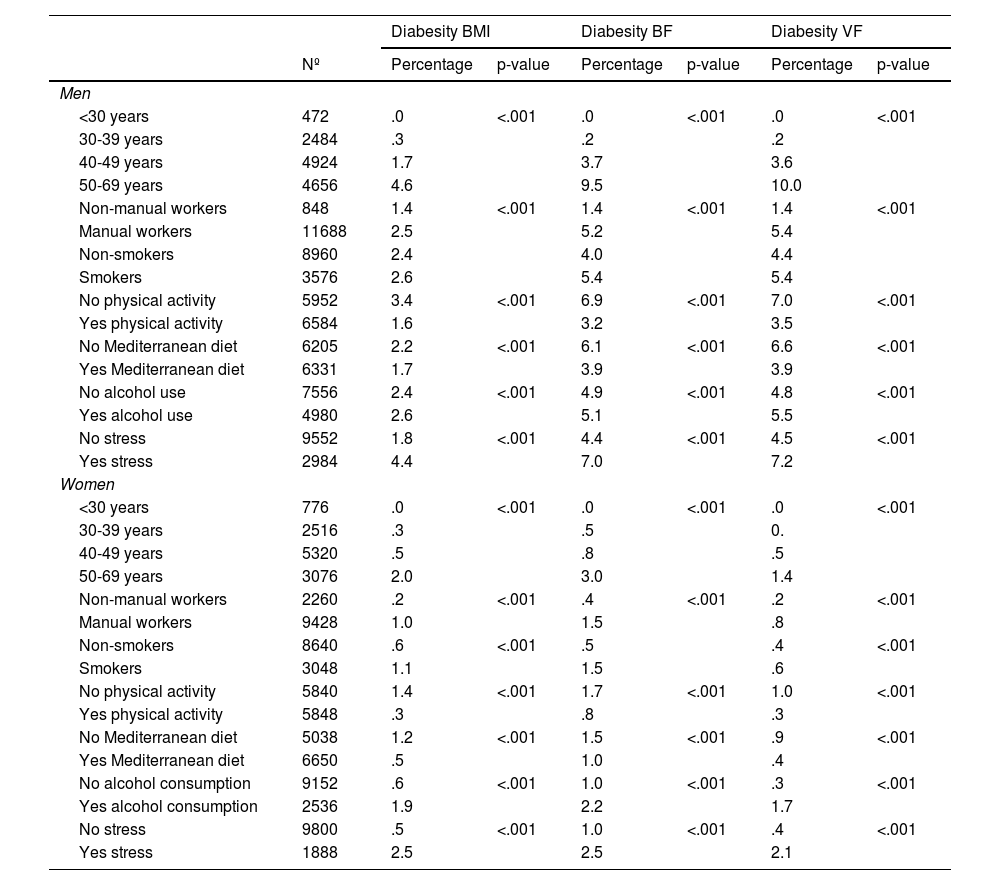
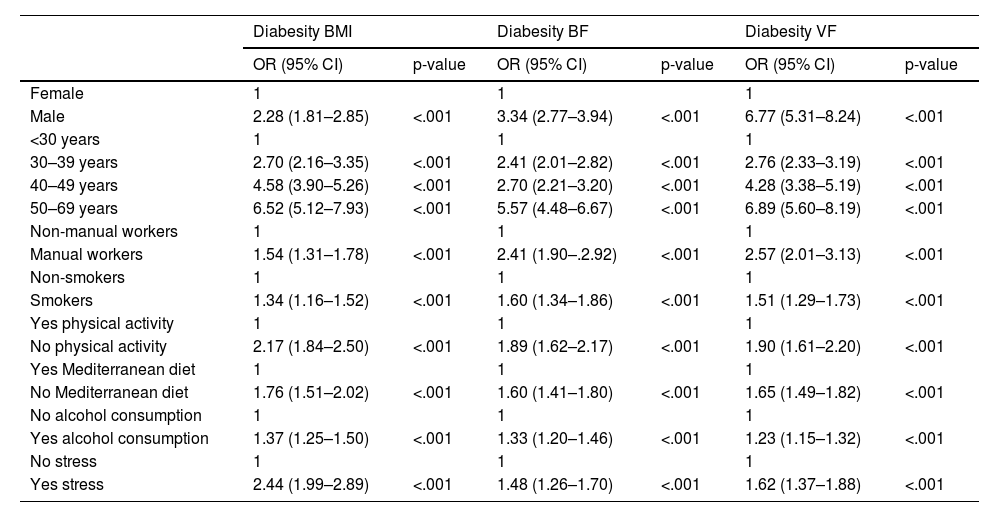
ResultsAll the aforementioned variables were found to be associated with diabesity. The highest odds ratios (OR) were observed for age, with values ranging from 5.57 (95% CI: 4.48–6.67) when BF was used as the diabesity criterion to 6.89 (95% CI: 5.60–8.19) when VF was the criterion. Similarly, elevated ORs were observed for male gender, with ORs of 6.77 (95% CI: 5.31–8.24) for VF and 3.34 (95% CI: 2.77–3.94) for BF.
ConclusionsIn our study, the profile of a person at highest risk of diabesity is a man over 50 years old from a lower socioeconomic status, who is a smoker, regular alcohol consumer, sedentary, with low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, and experiencing high stress levels.
La diabesidad es un cuadro patológico que aúna en un mismo individuo obesidad y diabetes tipo 2. Debido al incremento actual de ambas patologías la diabesidad está incrementando su prevalencia en todo el mundo. Es conocido que su etiología es multifactorial, por ello el objetivo de este estudio es conocer cómo se asocia la diabesidad con diferentes variables sociodemográficas, hábitos saludables y estrés.
Material y métodosSe realiza un estudio descriptivo y transversal en 24224 trabajadores españoles en los que se valora la asociación entre diabesidad y diferentes variables como edad, género, estatus socioeconómico, tabaco, alcohol, ejercicio físico, dieta mediterránea y estrés. Los criterios para determinar diabesidad incluyen índice de masa corporal, grasa corporal (GC) y grasa visceral (GV).
ResultadosTodas las variables antes mencionadas muestran asociación con la diabesidad, encontrando que las odss ratio (OR) más elevadas corresponden a la edad con valores que oscilan entre 5,57 (IC 95% 4,48-6,67) si el criterio de diabesidad es GC y 6,89 (IC 95% 5,60-8,19) si el criterio es GV. Las OR también son elevadas para el género masculino con OR de 6,77 (IC 95% 5,31-8,24) si el criterio es GV y 3,34 (IC 95% 2,77-3,94) si el criterio es la GC.
ConclusionesEl perfil de persona con más riesgo de presentar diabesidad en nuestro estudio corresponde a un varón mayor de 50 años, perteneciente al estatus socioeconómico más desfavorecido, fumador, consumidor habitual de alcohol, sedentario, con baja adherencia a la dieta mediterránea y con alto nivel de estrés.