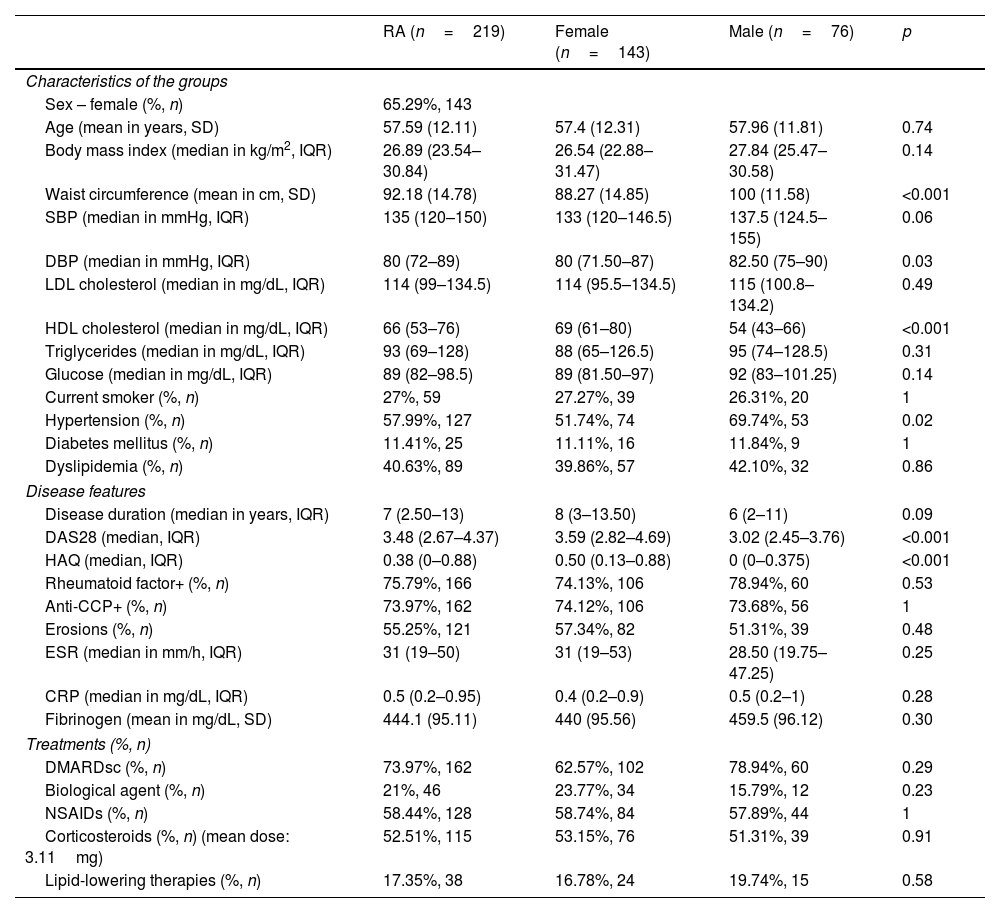
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune and inflammatory disorder that leads to cartilage and bone deterioration. This inflammatory activity causes extra-articular manifestations, including the acceleration of the atherosclerotic process. However, the exact causes of this accelerated process are under investigation. In this study, we compared the advanced lipid profile between patients with RA, patients with metabolic disorders, and controls. We also explored how microRNAs previously associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in RA are linked to these lipid subfractions in RA.
MethodsThe study included 219 patients with RA, 82 with metabolic disorders and 64 controls. Clinical evaluations were performed, and blood samples were collected. Quantification of microRNAs (Let7a, 24, 96, 103, 125a, 125b, 132, 146, 191, 223, 425, 451) and measurement of the advanced lipid profile using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) were carried out. Kruskal–Wallis tests and multivariate linear models were applied.
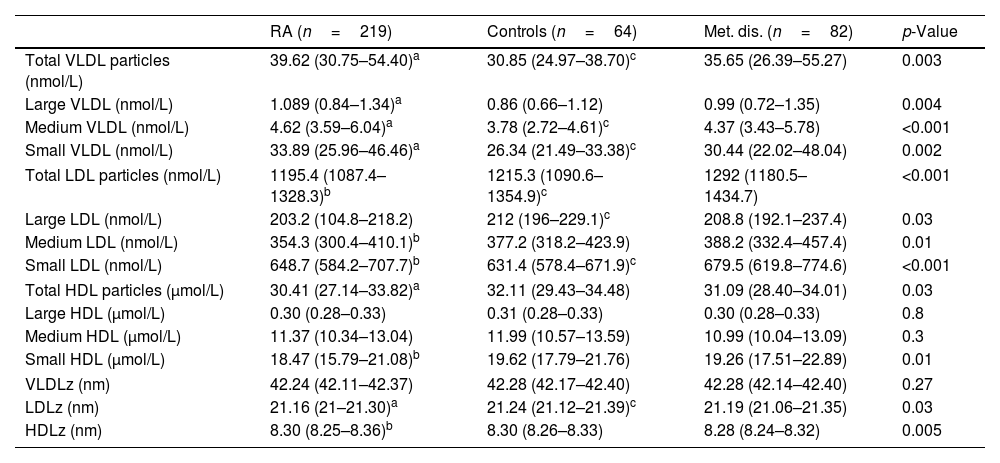
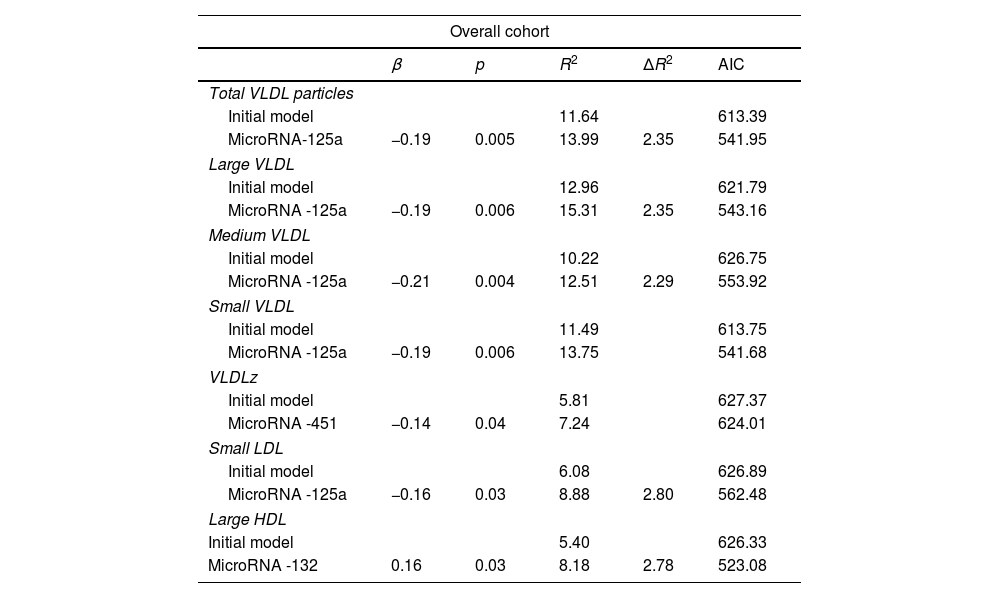
ResultsPatients with RA exhibited elevated total, large, medium, and small VLDL particles compared to controls. Their LDL subfractions were decreased compared to patients with metabolic disorders, with differences with controls. Patients with RA had fewer and smaller HDL particles than both groups. MicroRNA-125a was associated with VLDL subfractions and small LDL particles. Other microRNAs (96, 132, 191, 451) showed associations with certain LDL subfractions.
ConclusionsIn patients with RA, elevated levels of VLDL particles have been observed, while LDL levels remain similar to controls. The notable association of microRNA-125a with the metabolism of both VLDL and LDL in RA patients suggests its involvement in lipid regulation. This could point to microRNA-125a as a promising therapeutic target to address the increased cardiovascular risks of RA.
La artritis reumatoide (AR) es un trastorno autoinmunitario e inflamatorio que provoca el deterioro de cartílagos y huesos. Esta actividad inflamatoria causa manifestaciones extraarticulares, como la aceleración del proceso aterosclerótico. Sin embargo, las causas exactas de este proceso acelerado aún se están investigando. En este estudio, comparamos el perfil lipídico avanzado entre pacientes con AR, pacientes con trastornos metabólicos y controles. También exploramos cómo micro-ARN previamente asociados con aterosclerosis subclínica en AR están asociados a estas subfracciones lipídicas en AR.
MétodosEl estudio incluyó a 219 pacientes con AR, 82 con trastornos metabólicos y 64 controles. Se realizaron evaluaciones clínicas y se recogieron muestras de sangre. Se cuantificaron micro-ARN (Let7a, 24, 96, 103, 125a, 125b, 132, 146, 191, 223, 425, 451) y se midió el perfil lipídico avanzado utilizando resonancia magnética nuclear. Se aplicaron pruebas de Kruskal-Wallis y modelos lineales multivariados.
ResultadosLos pacientes con AR exhibieron partículas VLDL elevadas (totales, grandes, medianas y pequeñas) en comparación con los controles. Sus subfracciones LDL eran menores comparadas con las de los pacientes metabólicos, sin diferencias respecto a los controles. Los pacientes con AR tenían menos partículas de HDL y de menor tamaño en comparación con los otros grupos. El micro-ARN-125a se asoció con las subfracciones VLDL y partículas pequeñas de LDL. Otros micro-ARN (96, 132, 191, 451) también mostraron asociaciones con subfracciones LDL.
ConclusionesEn pacientes con AR se observaron niveles elevados de partículas VLDL, mientras que los niveles de LDL permanecen similares a los controles. La notable asociación del micro-ARN-125a con el metabolismo tanto de VLDL como de LDL en pacientes con AR evidencia su participación en la regulación lipídica. Esto podría señalar al micro-ARN-125a como un objetivo terapéutico prometedor para abordar los riesgos cardiovasculares aumentados de la AR.