Abstracts Asociación Mexicana de Hepatología (AMH) 2024
More infoHepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Viral hepatitis, alcohol, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are important risk factors. To describe the clinical characteristics, staging, treatment, and outcomes of patients with HCC at a third-level hospital.
Materials and PatientsA retrospective, descriptive study was carried out from January 2021 to April 2024, in which 76 patients from the liver clinic consultation were included. Clinical characteristics, biochemical characteristics, staging and treatment were collected.
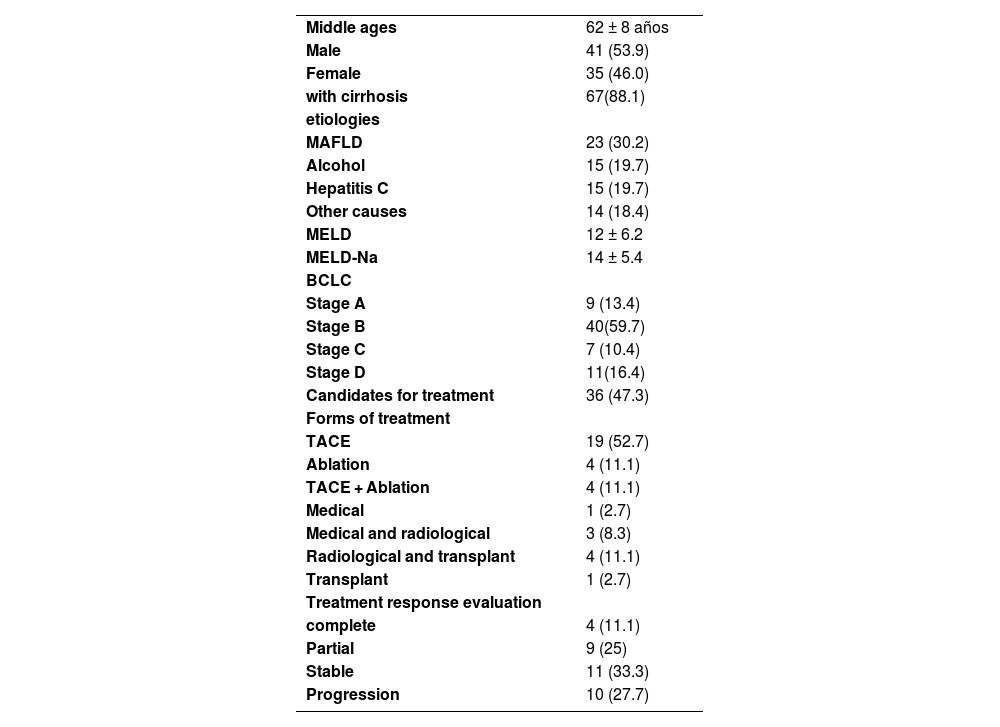
ResultsThe study included 76 patients, mean age 62 ±8(53.9% men); 88.1% of patients with cirrhosis; with the following etiologies: 30.2% due to MAFLD, 19.7% due to alcohol, 19.7% due to Hepatitis C and 18.4% due to other causes, With MELD 12 ±6.22, MELD Na 14.1± 5.4, 67 patients were classified in BCLC, of which 13.4% are in stage A, 59.7% B, 10.4% C, and 16.4% D. 36 patients were candidates for treatment distributing in 52.7% Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE), 11.1% ablation, 11.1% TACE and ablation:; 2.7% Medical (Lenvatinib), 8.3% medical and radiological (Nivolumab/Lenvatinib with TACE/Ablation), 11.1% radiological (TACE) and transplant and 2.7% transplant. Treatment response evaluation according to mRESIST criteria: 11.1% complete response, 25% partial response, 33.3% stable disease and 27.7% progression. The 3-month mortality rate was 8.3%.
ConclusionsIn our population group, mostly men, the most common etiology is MAFLD, two-thirds in intermediate stage, 47% were candidates for treatment, predominating the use of TACE. One-third remained with stable disease and 11.1% had a complete response. Mortality at 3 months was low.
Ethical statement: The authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Declaration of interests: None.
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Characteristics of patients with HCC n = 76
BCLC, Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; HCC, Hepatocellular carcinoma; MAFLD, Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; MELD, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease; MELD-Na, Model for End-Stage Liver Disease-Sodium; TACE, Transarterial chemoembolization.