This study compares the clinical outcomes of Holmium:YAG (Ho:YAG) laser lithotripsy and Thulium Fiber Laser (TFL) lithotripsy in retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) for kidney stones <20 mm.
Materials and methodsPatients who underwent RIRS for renal stones <20 mm between September 2022 and November 2023 were prospectively analyzed. They were randomly assigned to either the TFL or Ho:YAG laser group using a sealed-envelope method. Preoperative demographics, stone characteristics, kidney-ureter-bladder x-ray (KUB), ultrasound and noncontrast computer tomography (NCCT) scan findings were recorded. Operative time, laser usage time, postoperative stone-free rate (SFR), and complications were assessed and statistically analyzed.
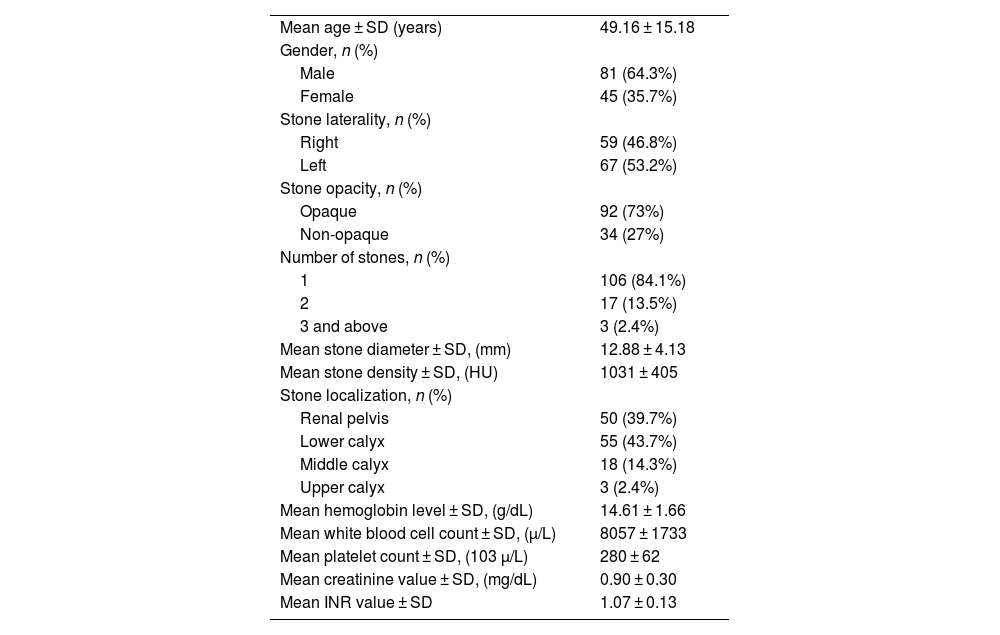
ResultsA total of 126 patients (mean age: 49.16 ± 15.18 years; 64.3% male, 35.7% female) were included. The TFL group (n = 64, 50.8%) had significantly shorter operative and laser usage times than the Ho:YAG laser group (n = 62, 49.2%) (operative time: 45.77 ± 15.67 min vs. 52.79 ± 18.11 min, p = 0.031; laser usage: 29.84 ± 13.32 min vs. 36.39 ± 15.75 min, p = 0.024). No significant SFR difference was found between groups (TFL group: n = 57, 91.8% vs. Ho:YAG laser group: n = 60, 93.8% ; p = 0.488).
ConclusionIn the treatment of kidney stones smaller than 20 mm using laser lithotripsy, both TFL and Ho:YAG laser are effective, safe, and associated with low complication rates. However, the use of TFL significantly reduces operative time and lithotripsy time, potentially improving surgical efficiency. Further studies with larger patient cohorts are necessary to validate these findings and provide additional insights into the advantages and limitations of each laser type.
Comparar los resultados clínicos de la litotricia con láser de holmio:YAG (Ho:YAG) y con láser de fibra de tulio (TFL) en la cirugía retrógrada intrarrenal (CRIR) para el tratamiento de cálculos renales <20 mm.
Materiales y métodosSe analizaron prospectivamente los datos de pacientes sometidos a CRIR por cálculos renales <20 mm entre septiembre de 2022 y noviembre de 2023. Los pacientes fueron asignados aleatoriamente a los grupos TFL o Ho:YAG mediante un método de sobres sellados. Se registraron variables demográficas, características litiásicas y hallazgos preoperatorios en radiografía convencional de riñón-uréter-vejiga (RUV), ecografía y tomografía computarizada sin contraste (TCNC). Se evaluaron el tiempo quirúrgico, el tiempo de activación del láser, la tasa libre de litiasis (TLL) postoperatoria y las complicaciones.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 126 pacientes (edad media: 49,16 ± 15,18 años; 64,3% hombres y 35,7% mujeres). El grupo TFL (n = 64, 50,8%) presentó un tiempo quirúrgico y de uso del láser significativamente menores que el grupo Ho:YAG (n = 62, 49,2%) (tiempo quirúrgico: 45,77 ± 15,67 min vs. 52,79 ± 18,11 min, p = 0,031; tiempo de láser: 29,84 ± 13,32 min vs. 36,39 ± 15,75 min, p = 0,024). No se observaron diferencias significativas en la TLL entre ambos grupos (TFL: n = 57, 91,8% vs. Ho:YAG: n = 60, 93,8%; p = 0,488).
ConclusionesEn el tratamiento de cálculos renales <20 mm mediante litotricia láser, tanto el TFL como el Ho:YAG son técnicas eficaces, seguras y asociadas a bajas tasas de complicaciones. No obstante, el uso del TFL permite una reducción significativa del tiempo quirúrgico y del tiempo de litotricia, lo que podría optimizar la eficiencia del procedimiento. Se requieren estudios adicionales con muestras más amplias para validar estos hallazgos y profundizar en las ventajas y limitaciones de cada tecnología láser.