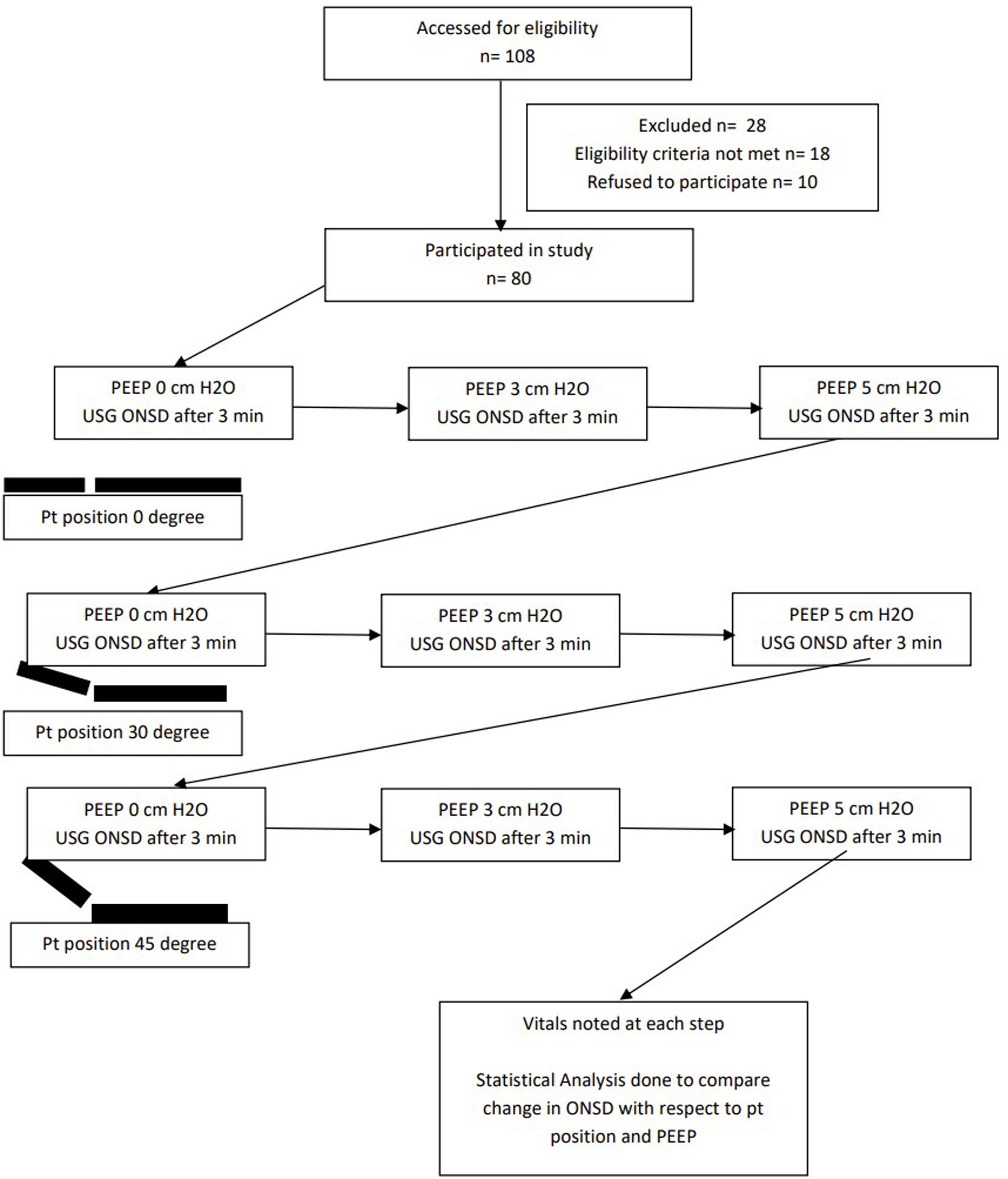
This study aims to assess the effect of different PEEP levels and patient positioning on optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) as a surrogate marker for intracranial pressure (ICP) in patients with severe TBI on mechanical ventilation.
DesignA prospective interventional study assessing the effects of PEEP and patient positioning on ONSD in ventilated TBI patients.
SettingThe aim of this study was to explore how alterations in the PEEP and patient position influence the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD), which is a marker of the ICP. Eighty patients on ventilators with TBIs were placed in three different positions with the bed's head end at 0°, 30°, and 45° angles.
InterventionsThe ONSD was assessed using an ultrasound probe at PEEP of 0, 3, and 5cm H2O in all three positions.
Variables of interestONSD, ICP and PEEP.
ResultsThe study findings indicate that no statistically significant alteration in the ONSD observed at different PEEP levels or various patient positions. Although there was an increase in the ONSD when the PEEP was increased from 0 to 5cm H2O, this increase did not reach statistical significance. Notably, the most notable changes in ONSD were observed at the 30-degree patient position when the PEEP increased from 0 to 5cm H2O (6.12±0.38 vs. 6.23±0.40), with a p value of 0.07, indicating a trend toward significance.
ConclusionThe study results suggest that the application of PEEP up to 5cm H2O did not lead to significant changes in the ONSD, suggesting a degree of safety in its application for patients with TBI.
En los traumatismos craneoencefálicos graves, la presión positiva al final de la espiración (PEEP) elevada puede provocar un aumento de la presión intracraneal (PIC) y una disminución de la presión de perfusión cerebral (PPC), lo que conduce a un mal pronóstico y a resultados adversos para el paciente.
DiseñoEstudio observacional.
EscenarioEl objetivo de este estudio fue explorar cómo las alteraciones de la PEEP y la posición del paciente influyen en el diámetro de la vaina del nervio óptico (ONSD), que es un marcador de la PIC. Se colocó a ochenta pacientes con TCE conectados a respiradores en 3 posiciones diferentes, con la cabecera de la cama en ángulos de 0, 30 y 45°.
IntervencionesLa ONSD se evaluó utilizando una sonda de ultrasonidos con una PEEP de 0, 3 y 5cmH2O en las 3 posiciones.
Variables de interésONSD, PIC y PEEP.
ResultadosLos hallazgos del estudio indican que no se observaron alteraciones estadísticamente significativas en la ONSD con diferentes niveles de PEEP o en varias posiciones del paciente. Aunque se observó un aumento del ONSD cuando se aumentó la PEEP de 0 a 5cmH2O, este aumento no alcanzó la significación estadística. Cabe destacar que los cambios más notables en el ONSD se observaron en la posición del paciente de 30° cuando la PEEP aumentó de 0 a 5cmH2O (6,12±0,38 frente a 6,23±0,40), con un valor p de 0,07, lo que indica una tendencia hacia la significación.
ConclusiónLos resultados del estudio sugieren que la aplicación de PEEP hasta 5cmH2O no produjo cambios significativos en el ONSD, lo que sugiere un grado de seguridad en su aplicación para los pacientes con TCE.
Artículo
Socios de la Asociación de Medicina Crítica y Cuidado Intensivo
Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la AMCI, clique aquí