In this study, we aimed to investigate the correlation between SUVmax of primary tumor and prognostic factors/molecular subtype in ductal breast cancer patients.
Materials and methodsWe retrospectively reviewed 150 female patients with pathologically proven invasive ductal breast cancer from January 2015 to October 2019 who underwent 18F-FDG PET/CT for initial staging. Histopathological prognostic features of the primary tumor (histological grade, hormone receptor status, Ki-67 index, vb.) were obtained from the tru-cut biopsy report. In 18F-FDG PET/CT studies, the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of the primary breast tumor was calculated and compared with the presence of axillary lymphadenopathy and/or distant metastases, histopathological prognostic factors and molecular subtype.
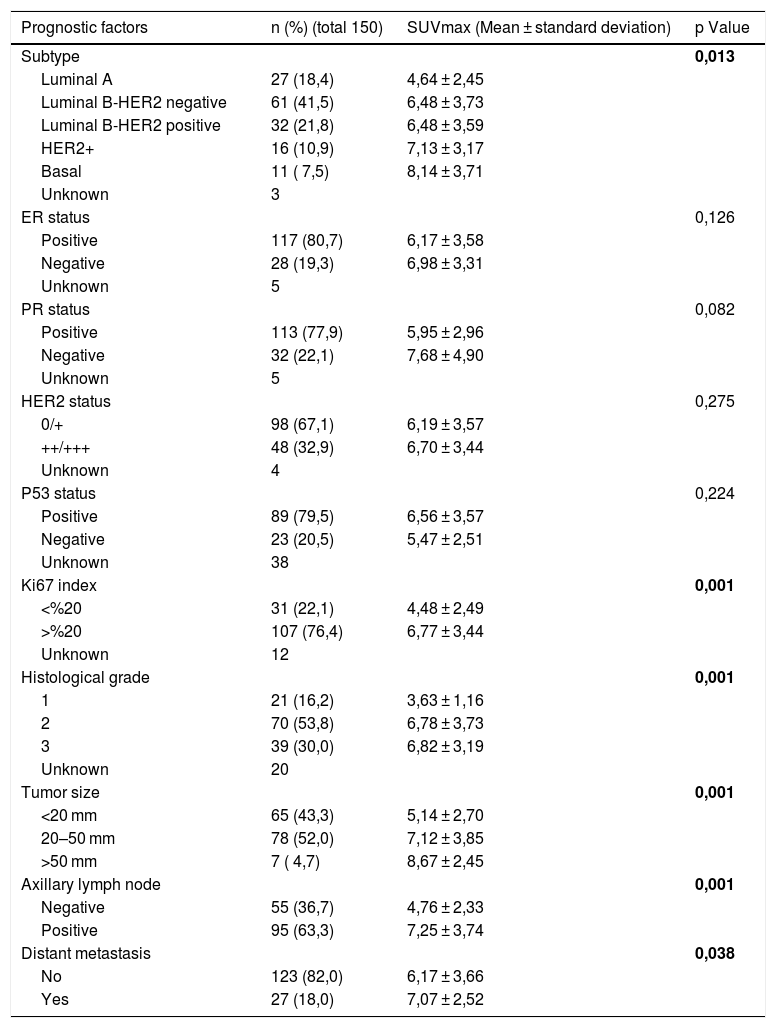
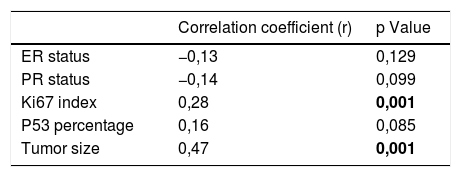
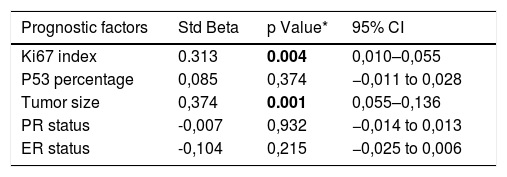
ResultsThe high SUVmax of primary breast tumors is significantly correlated with the clinicopathological factors: high tumor size, high histologic grade, high Ki-67 index, axillary lymph node positivity and distant metastasis. SUVmax value was significantly higher in patients with basal subtype than patients with Luminal A subtype (8,14 ± 3,71 and 4,64 ± 2,45, p = 0,002). Correlation analysis revealed a low correlation between Ki-67 index and SUVmax (r = 0,276, p = 0,001) and moderate correlation between tumor size and SUVmax (r = 0,470, p = 0,001). In multivariate linear regression analysis, Ki-67 index and tumor size had a statistically significant effect on SUVmax values. As these parameters increase, it is seen that it increases SUVmax values (p = 0,004, Std Beta: 0,228, 95% CI:0,010–0,055 and p = 0,001, Std Beta:0,374, 95% CI:0,55–0,136, respectively).
ConclusionHigh SUVmax value is associated with factors suggesting poor prognosis. Pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT can be used as a tool to predict prognosis in breast cancer.
En este estudio, nos propusimos investigar la correlación entre el SUVmax del tumor primario y los factores de pronóstico/subtipo molecular en pacientes con cáncer de mama ductal.
Materiales y métodosRevisamos retrospectivamente a 150 pacientes mujeres con cáncer de mama ductal invasivo patológicamente comprobado desde enero de 2015 hasta octubre de 2019 que se sometieron a una PET/TC 18F-FDG para la estadificación inicial. Las características pronosticas histopatológicas del tumor primario (grado histológico, estado de los receptores hormonales, índice Ki-67, vb.) se obtuvieron del informe de la biopsia tru-cut. En los estudios PET/TC de 18F-FDG se calculó el valor máximo de captación estandarizada (SUVmax) del tumor primario de mama y se comparó con la presencia de linfadenopatías axilares y/o metástasis a distancia, factores pronósticos histopatológicos y subtipo molecular.
ResultadosEl valor elevado de SUVmax de los tumores de mama primarios está significativamente correlacionado con los factores clínico-patológicos: alto tamaño del tumor, alto grado histológico, alto índice Ki-67, positividad de los ganglios linfáticos axilares y metástasis a distancia. El valor SUVmax fue significativamente más alto en los pacientes con subtipo basal que en los pacientes con subtipo Luminal A (8,14 ± 3,71 y 4,64 ± 2,45, p = 0,002). El análisis de correlación reveló una baja correlación entre el índice Ki-67 y el SUVmax (r = 0,276, p = 0,001) y una correlación moderada entre el tamaño del tumor y el SUVmax (r = 0,470, p = 0,001). En el análisis de regresión lineal multivariante , el índice Ki-67 y el tamaño del tumor tuvieron un efecto estadísticamente significativo en los valores del SUVmax. A medida que estos parámetros aumentan, se observa que seincrementan los valores SUVmax (p = 0,004, Std Beta: 0,228, 95% CI:0,010-0,055 y p = 0,001, Std Beta:0,374, 95% CI:0,55-0,136, respectivamente).
ConclusiónEl elevado valor de SUVmax se asocia con factores que sugieren un mal pronóstico. La 18F-FDG PET/TC pretratamiento puede utilizarse como una herramienta para predecir el pronóstico en el cáncer de mama.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)