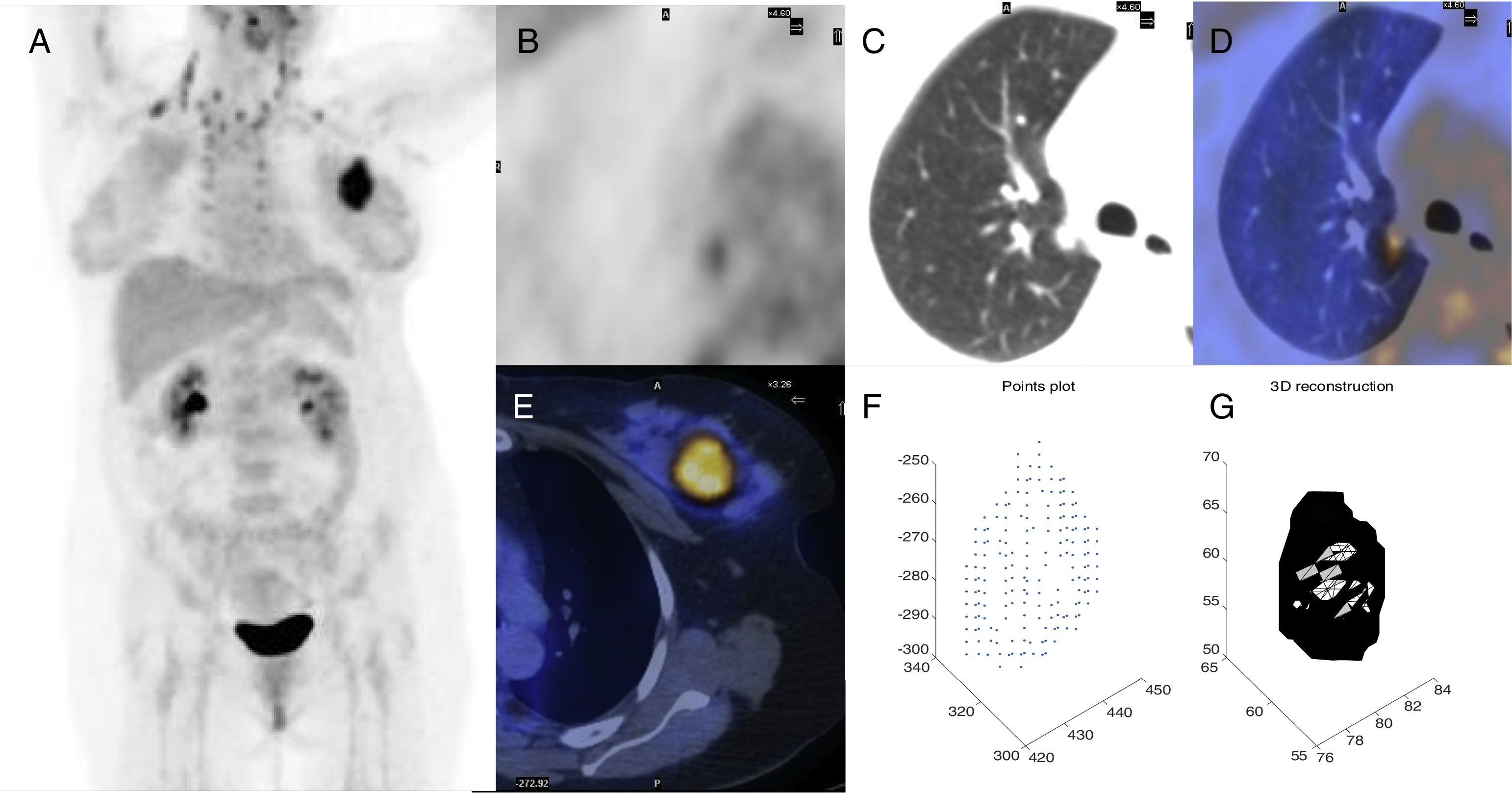
To investigate the usefulness of metabolic variables using 18F-FDG PET/CT in the prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NC) response and the prognosis in locally advanced breast cancer (LABC).
Materials and methodsProspective study including 67 patients with LABC, NC indication and a baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT. After breast tumor segmentation, SUV variables (SUVmax, SUVmean and SUVpeak) and volume-based variables, such as metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and total lesion glycolysis (TLG), were obtained. Tumors were grouped into molecular phenotypes, and classified as responders or non-responders after completion of NC. Disease-free status (DFs), disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS) were assessed. A univariate and multivariate analysis was performed to study the potential of all variables to predict DFs, DFS, and OS.
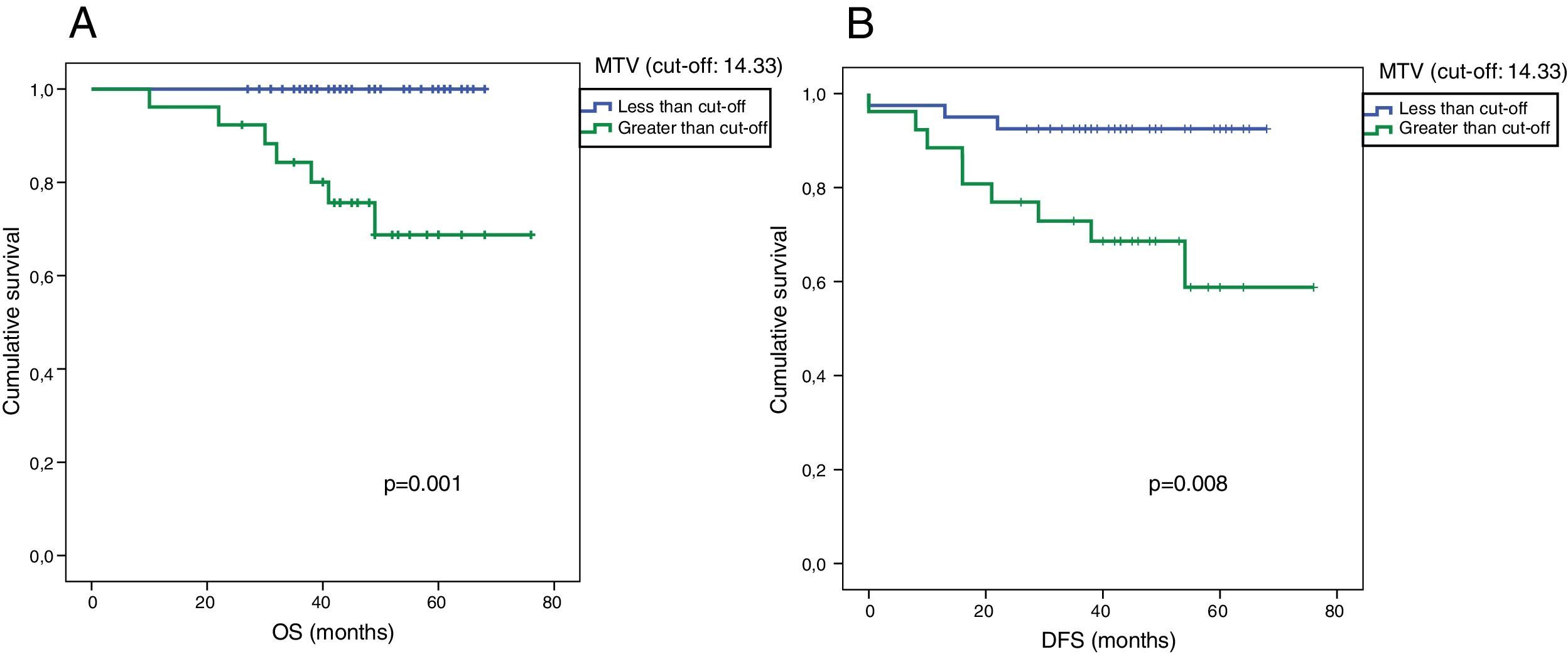
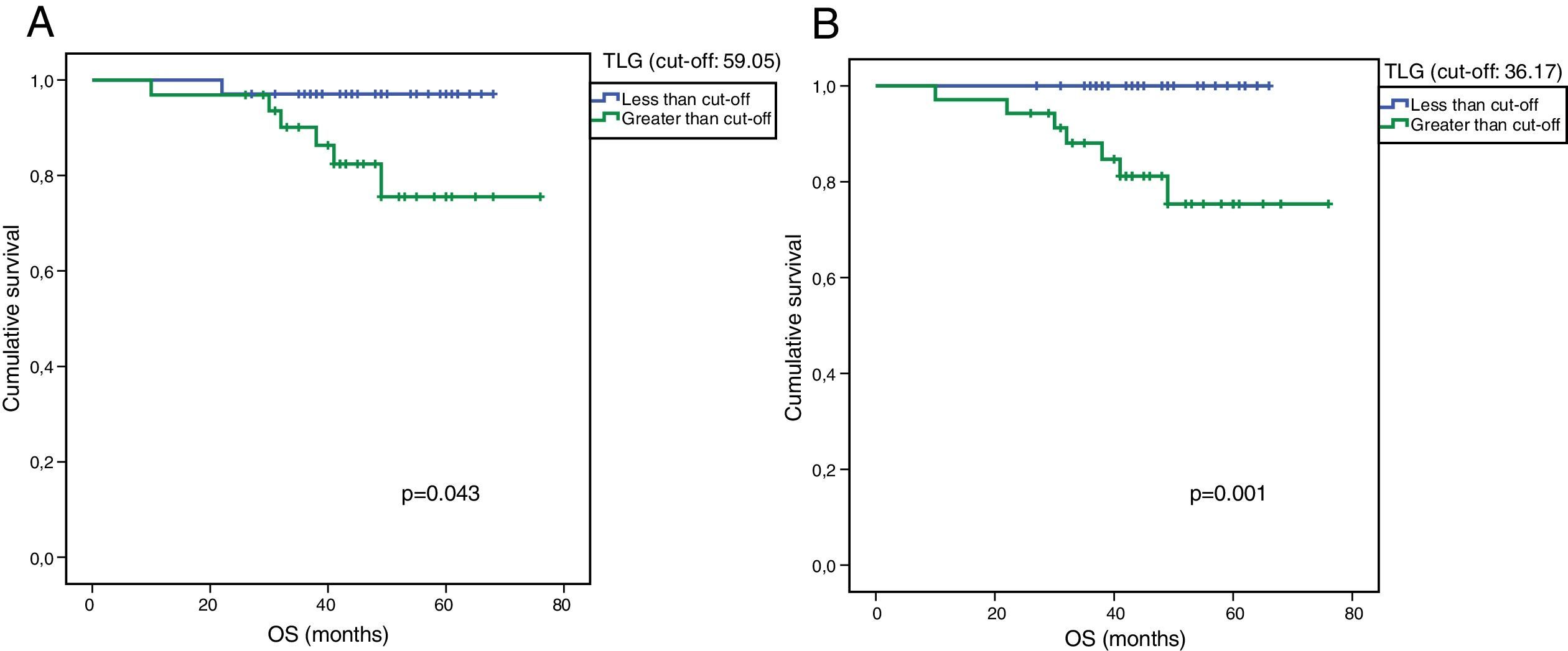
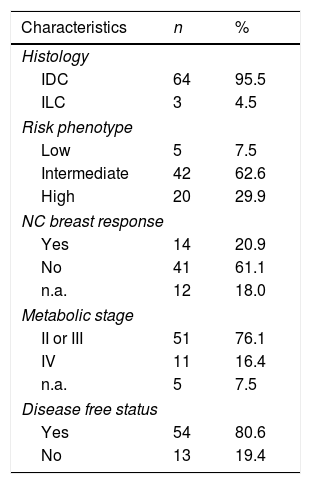
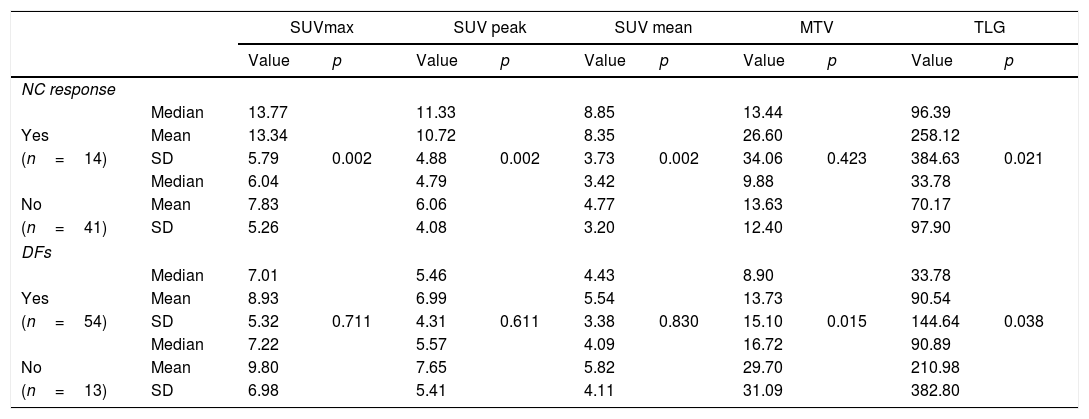
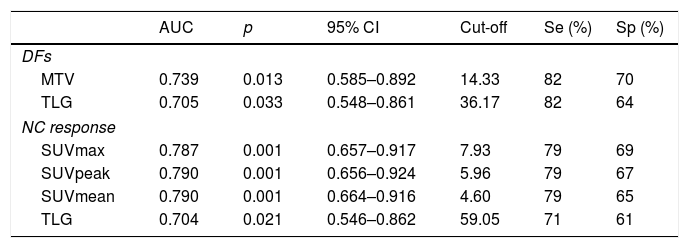
ResultsFourteen patients were classified as responders. Median±SD of DFS and OS was 43±15 and 46±13 months, respectively. SUV and TLG showed a significant correlation (p<0.005) with the histological response, with higher values in responders compared to non-responders. MTV and TLG showed a significant association with DFs (p=0.015 and p=0.038 respectively). Median, mean and SD of MTV and TLG for patients with DFs were: 8.90, 13.73, 15.10 and 33.78, and 90.54 and 144.64, respectively. Median, mean and SD of MTV and TLG for patients with non-DFs were: 16.72, 29.70 and 31.09 and 90.89, 210.98 and 382.80, respectively. No significant relationships were observed with SUV variables and DFs. Volume-based variables were significantly associated with OS and DFS, although in multivariate analysis only MTV was related to OS. No SUV variables showed an association with the prognosis.
ConclusionVolume-based metabolic variables obtained with 18F-FDG PET/CT, unlike SUV based variables, were good predictors of both neoadjuvant chemotherapy response and prognosis.
Investigar la utilidad de las variables metabólicas obtenidas en la 18F-FDG PET/TC en la predicción de la respuesta a quimioterapia neoadyuvante (QN) y el pronóstico en cáncer de mama locamente avanzado (CMLA).
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo que incluye 67 pacientes con CMLA, indicación de QN y 18F-FDG PET/TC basal. Se obtuvieron variables SUV (SUVmax, SUVmedio y SUVpico) y volumétricas, tales como el volumen tumoral metabólico (VTM) y la glicólisis total lesional (GTL). Los tumores se agruparon en fenotipos moleculares y fueron clasificadas como respondedores y no respondedores tras la finalización de la QN. Se obtuvo el estado libre de enfermedad (ELE), supervivencia libre de enfermedad (SLE) y supervivencia global (SG). Se realizó análisis univariante y multivariante para estudiar el potencial de todas las variables en la predicción de la ELE, SLE y SG.
ResultadosCatorce pacientes se clasificaron como respondedoras. La media ±DE de la SLE y la SG fue de 43±15 y 46±13 meses, respectivamente. El SUV y la GTL mostraron una relación significativa (p<0,005) con la respuesta histológica, con mayores valores en las pacientes respondedoras con respecto a las no-respondedoras. El VTM y la GTL mostraron asociación con el ELE (p=0,015 y p=0,038, respectivamente). La mediana, media y DS del VTM y la GTL para pacientes en ELE fue de 8,90, 13,73, 15,10 y del 33,78, 90,54 y 144,64, respectivamente. La mediana, media y DS del VTM y la GTL para pacientes en no ELE fueron de: 16,72, 29,70 y 31,09 y de 90,89, 210,98 y 382,80, respectivamente. No se encontró relación con las variables de SUV y el ELE. Las variables volumétricas se asociaron de forma significativa con la SG y con la SLE, aunque en el análisis multivariante solo el VTM se relacionó con la SG. Ninguna variable de SUV mostró asociación con el pronóstico.
ConclusiónLas variables metabólicas obtenidas con la 18F-FDG PET/TC, de forma distinta a las variables de SUV, fueron buenos predictores tanto de la respuesta al tratamiento quimioterápico neoadyuvante y el pronóstico.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)