This study aimed to investigate the relationship between semiquantitative positron emission tomography (PET) parameters and intratumoral heterogeneity (ITH) on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) imaging and survival data of non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients.
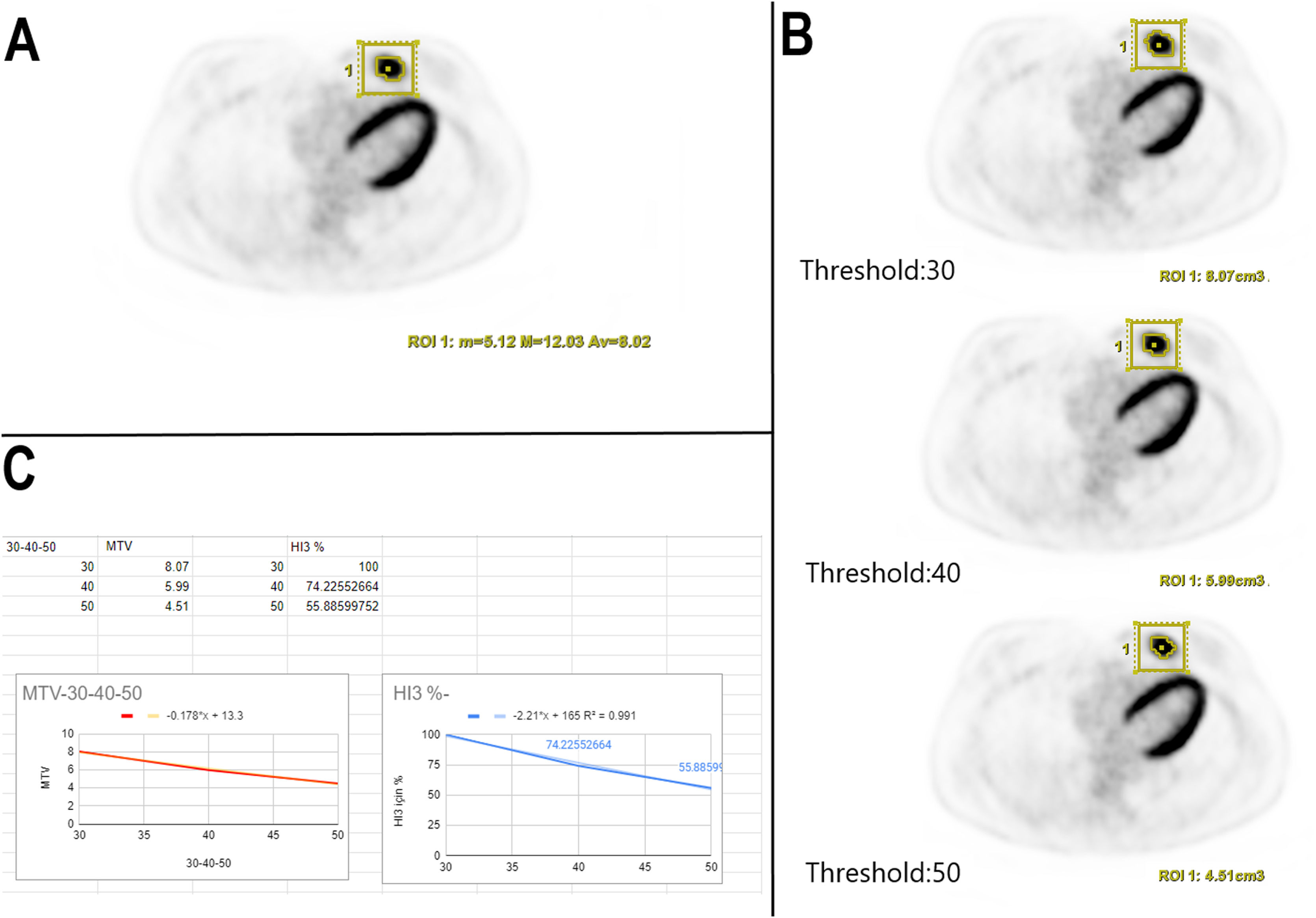
MethodsSixty-two consecutive female patients who underwent pretreatment 18F-FDG PET/CT with non-metastatic TNBC were enrolled. Heterogeneity index (HI) variables derived from the metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and standardized uptake value (SUV) parameters of primary lesions were evaluated. A novel modified method introducing a percentage-based (30–40–50%) MTV slope comparison was proposed. The association between conventional 18F-FDG PET/CT parameters, HI values, and survival results was analyzed retrospectively.
ResultsTumors with higher HI values were associated with shorter survival times. For overall survival (OS), HI2 and HI3 were statistically significant (p=0.009, p=0.016). Regarding radiological progression-free survival (rPFS), HI1 and HI3 were statistically significant (p=0.01, p=0.025). A significant weak correlation between HI1 (p=0.005, ρ=0.34) and a strong correlation was found for HI2 (p<0.0001, ρ=0.89), HI3 and tumor size were not statistically significantly correlated (p=0.063, ρ=0.23). T stage was statistically significantly associated with rPFS and OS ((p=0.038, p=0.003). In contrast, no statistically significant difference was found for the N stage, anatomical, and clinical staging (p>0.05).
ConclusionThis study concluded that ITH predicts survival for non-metastatic TNBC patients. This conclusion was reached with the heterogeneity index variables obtained by different methods. However, our results revealed that HI2 depends on tumor size. Our modified method (HI3) predicts survival independently of tumor size.
Este estudio investigó la relación entre los parámetros semicuantitativos de tomografía por emisión de positrones (PET) y la heterogeneidad intratumoral (HIT) en imágenes de 18F-fluorodesoxiglucosa (18F-FDG PET/TC) y los datos de supervivencia de pacientes con cáncer de mama triple negativo (CMTN) no metastásico.
MétodosSe incluyeron 62 pacientes con CMTN no metastásico que se sometieron a una18F-FDG PET/TC antes del tratamiento. Se evaluaron las variables del índice de heterogeneidad (HI), derivadas del volumen tumoral metabólico (MTV) y los parámetros de valor de captación estandarizada (SUV) de las lesiones primarias. Se propuso un método modificado que introduce comparación de pendiente del MTV basada en porcentajes (30–40–50%). Se analizó retrospectivamente la asociación entre los parámetros convencionales de 18F-FDG PET/TC, los valores de HI y los resultados de supervivencia. Resultados: Los valores altos de HI se asociaron con menor supervivencia. HI2 y HI3 fueron significativos para la supervivencia global (OS) (p=0.009, p=0.016). Para la supervivencia libre de progresión radiológica (rPFS), HI1 y HI3 fueron significativos (p=0.01, p=0.025). HI1 mostró una correlación débil significativa (p=0.005, rho=0.34) y HI2 una fuerte correlación (p<0.0001, rho=0.89) con el tamaño tumoral, mientras que HI3 no fue significativo (p=0.063, rho=0.23). El estadio T se asoció con OS y rPFS (p=0.038, p=0.003). No se encontraron diferencias significativas para el estadio N ni la estadificación anatómica o clínica (p>0.05).
ConclusiónLa HIT predice la supervivencia en CMTN no metastásico. Aunque HI2 depende del tamaño tumoral, el método HI3 predice la supervivencia independientemente de este, ofreciendo un enfoque más preciso.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)