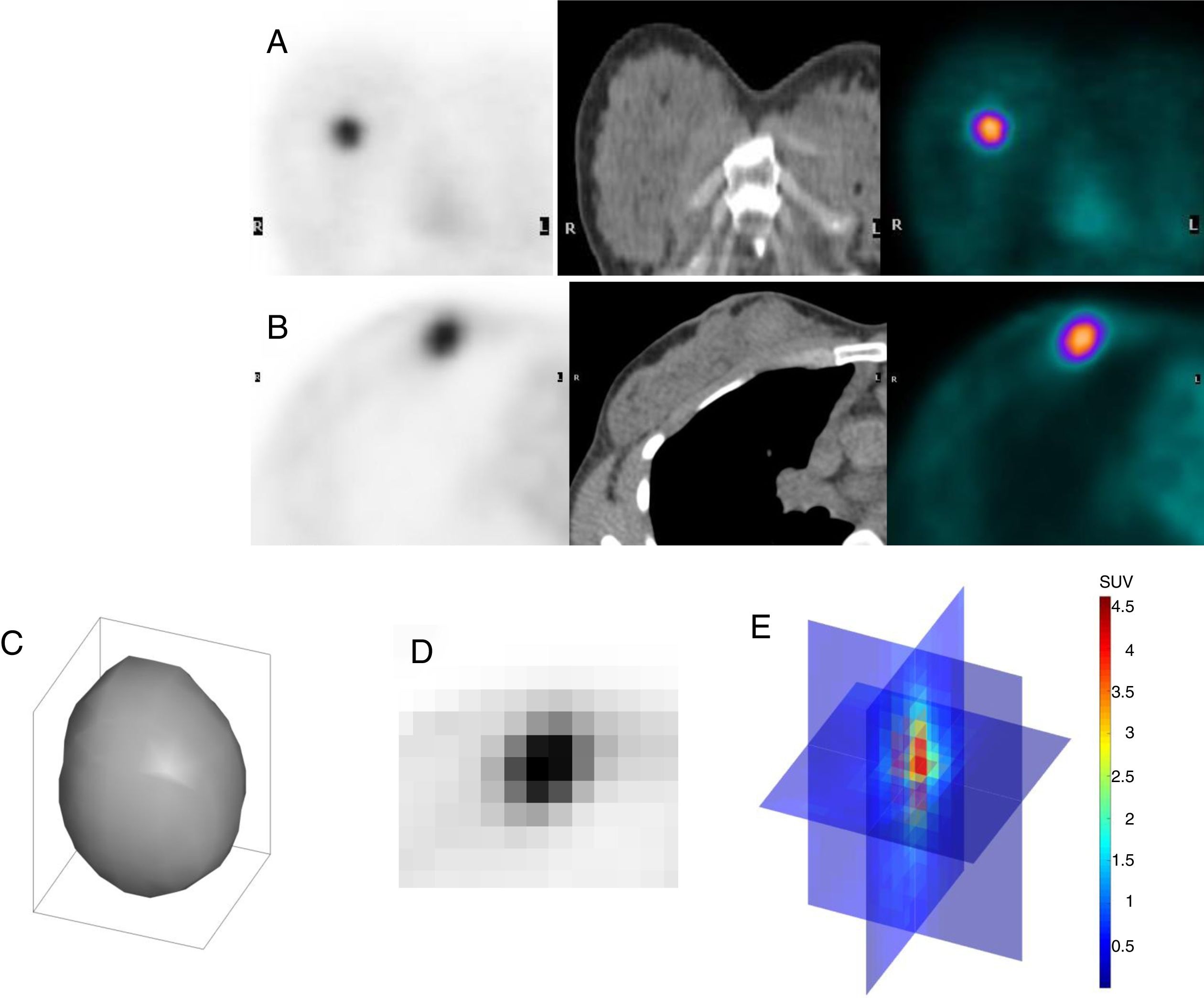
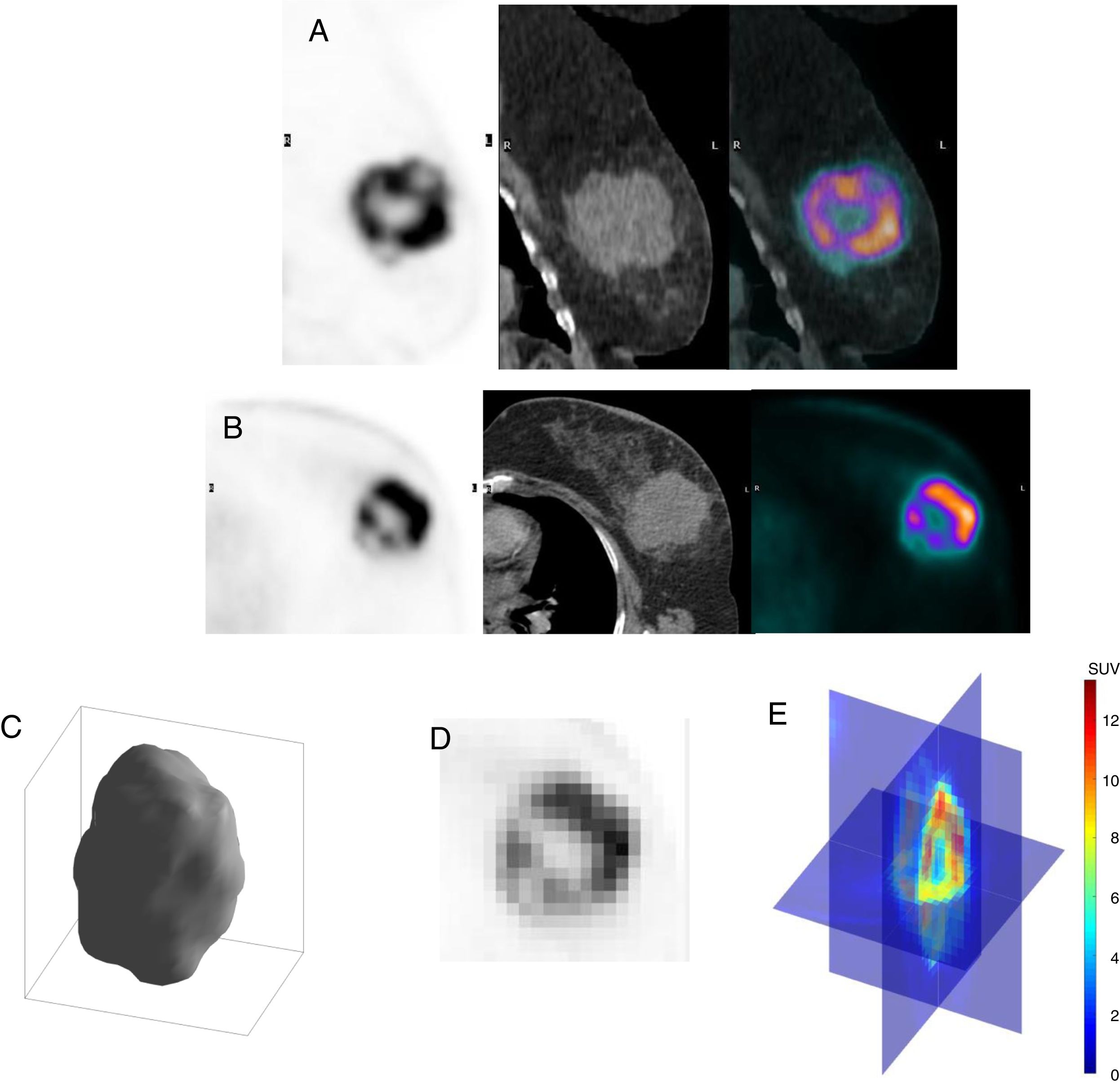
To analyze the relationship between measurements of global heterogeneity, obtained from 18F-FDG PET/CT, with biological variables and their predictive and prognostic role in patients with locally advanced breast cancer (LABC).
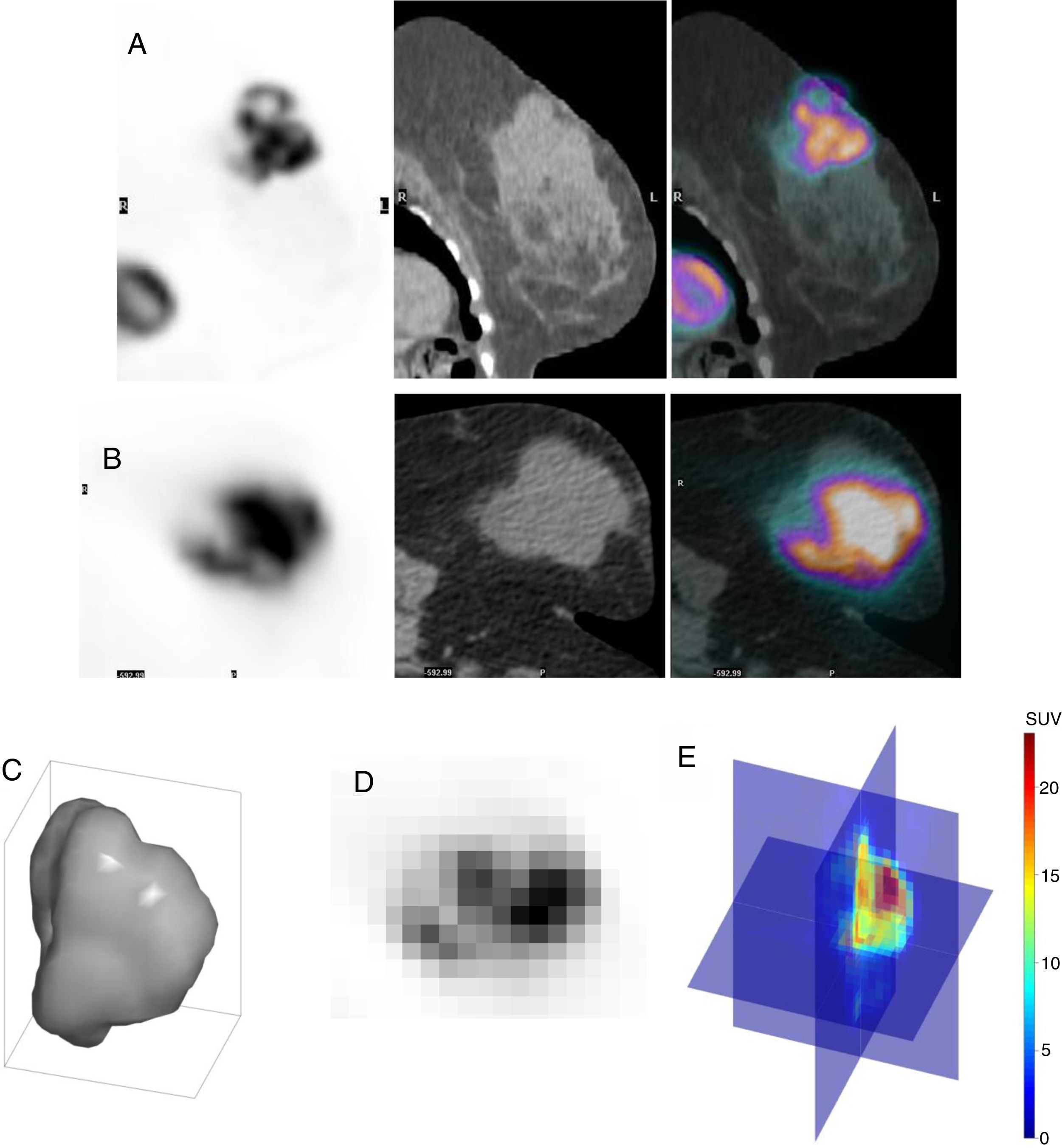
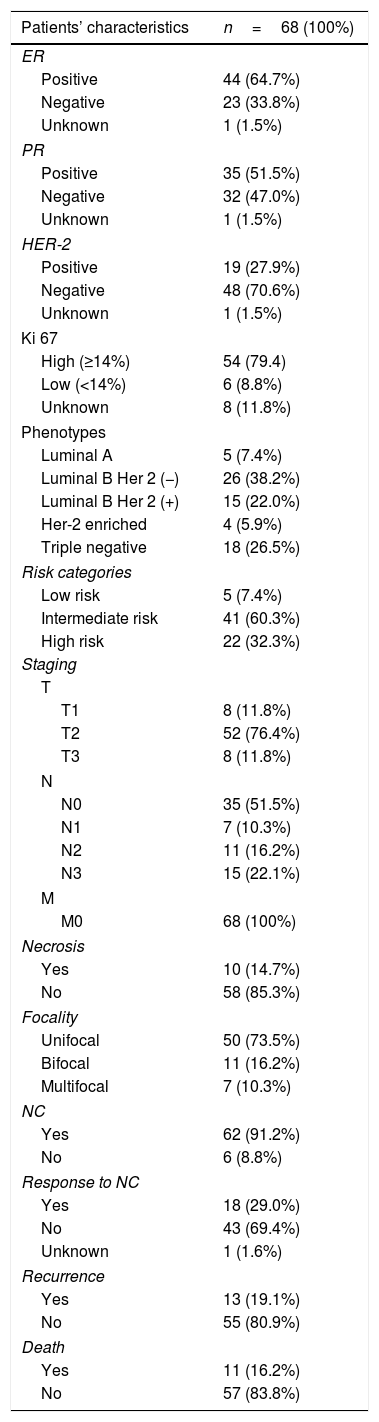
Material and methods68 patients from a multicenter and prospective study, with LABC and a baseline 18F-FDG PET/CT were included. Immunohistochemical profile [estrogen receptors (ER) and progesterone receptors (PR), expression of the HER-2 oncogene, Ki-67 proliferation index and tumor histological grade], response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NC), overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were obtained as clinical variables. Three-dimensional segmentation of the lesions, providing SUV, volumetric [metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and total lesion glycolysis (TLG)] and global heterogeneity variables [coefficient of variation (COV) and SUVmean/SUVmax ratio], as well as sphericity was performed. The correlation between the results obtained with the immunohistochemical profile, the response to NC and survival was also analyzed.
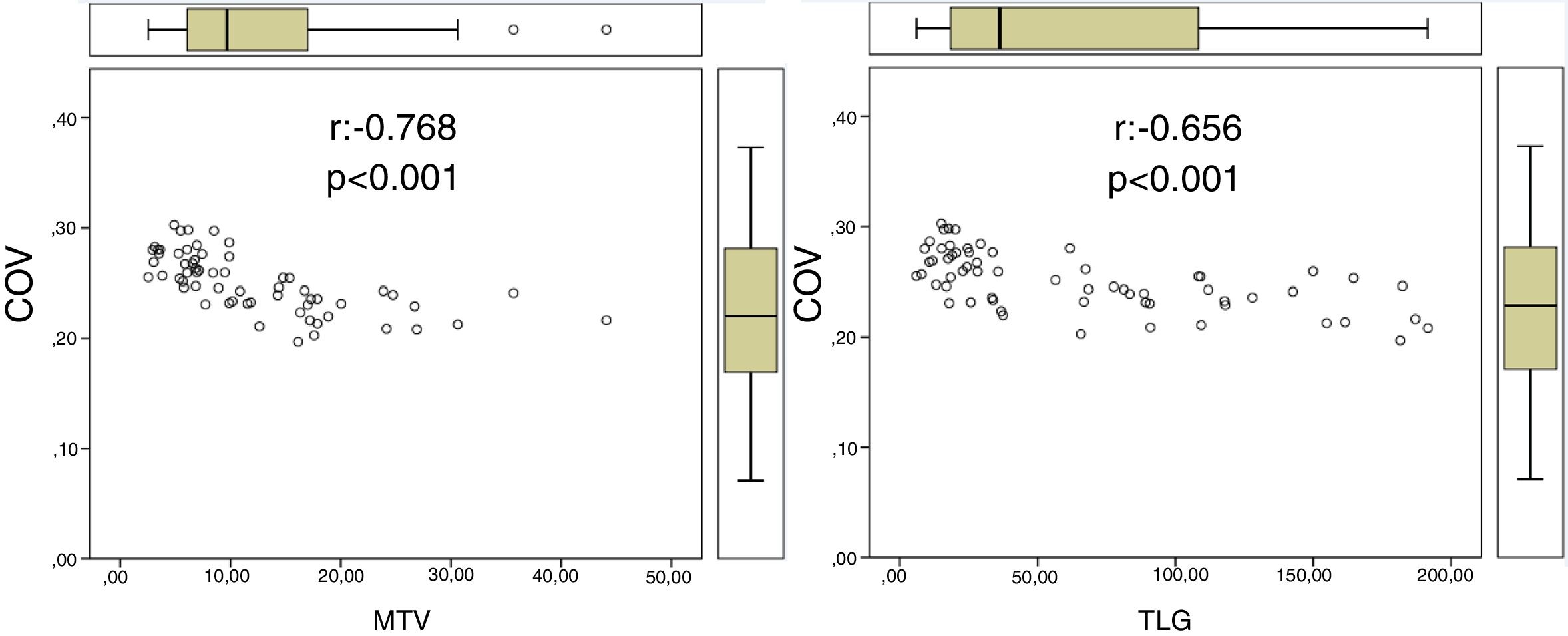
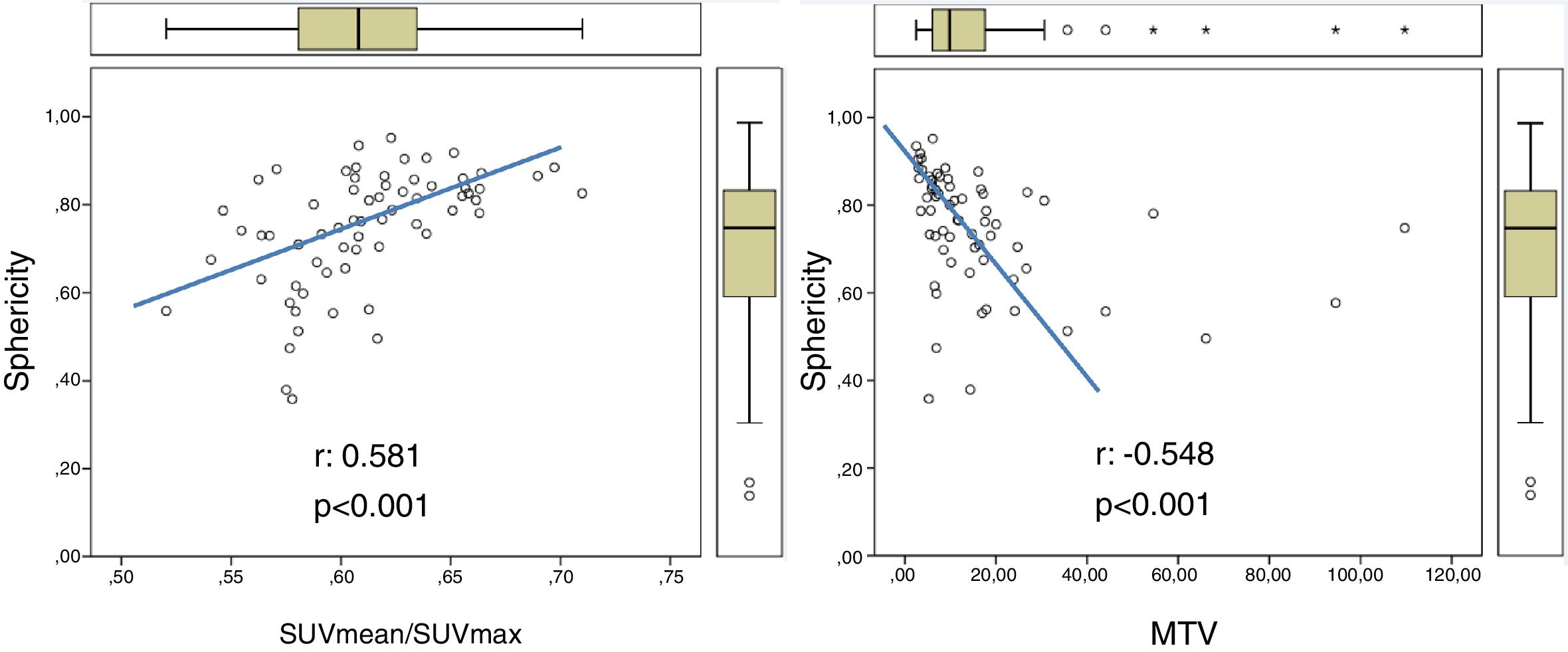
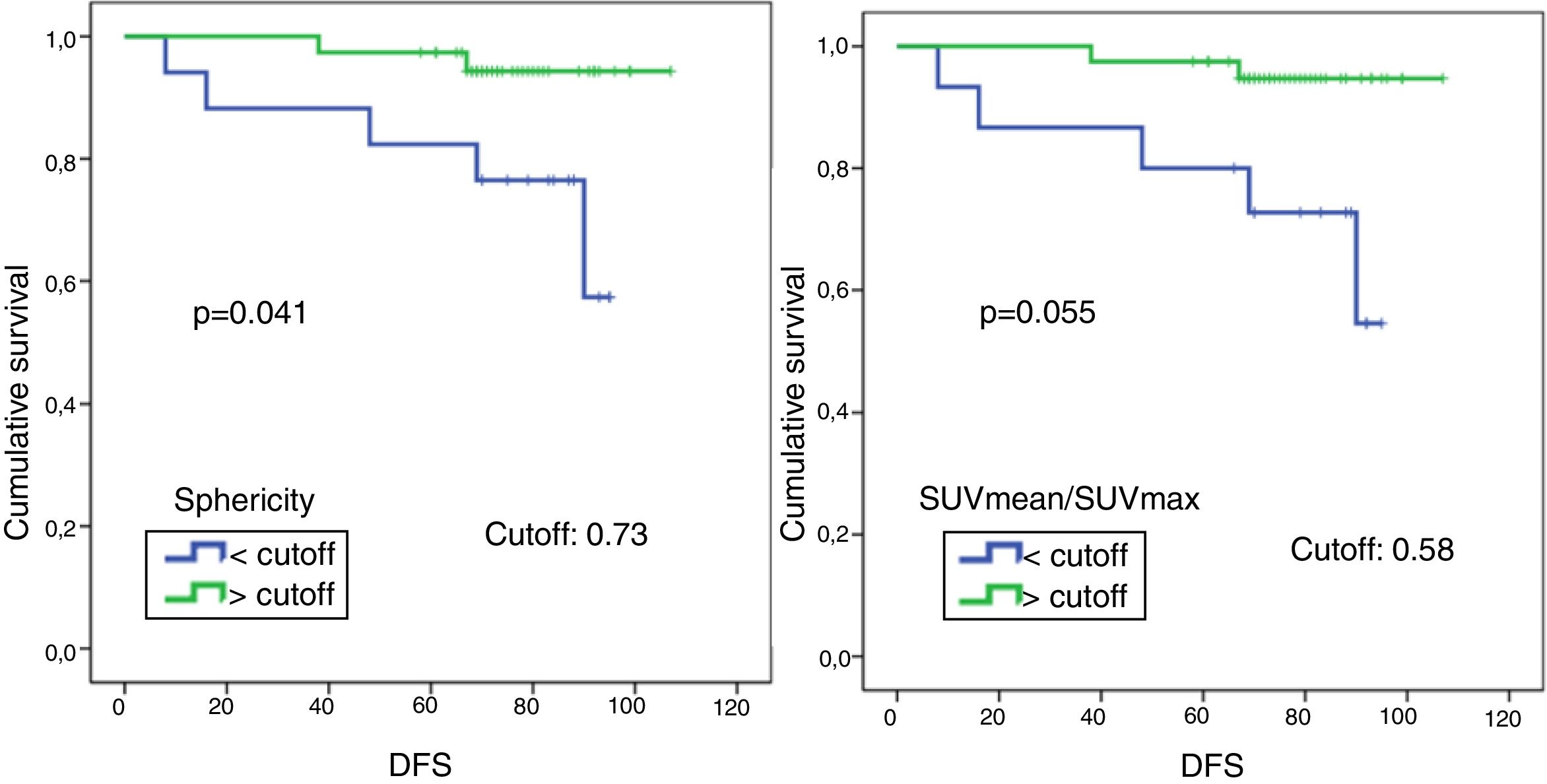
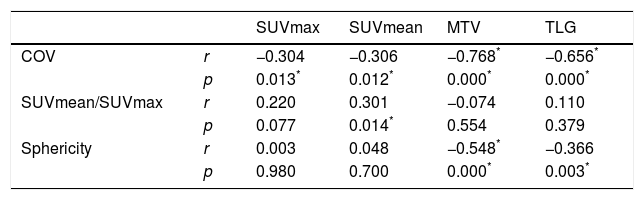
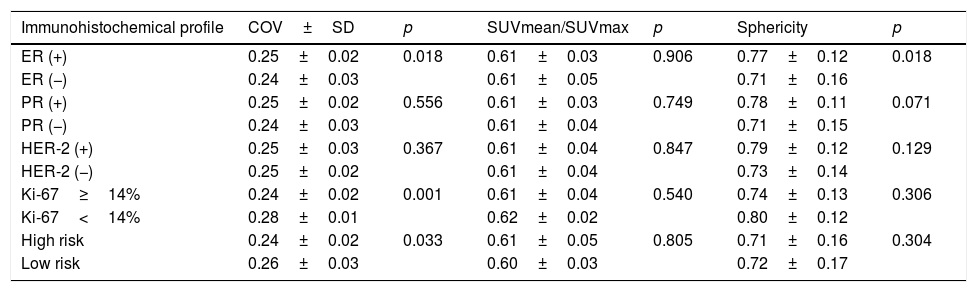
ResultsOf the patients included, 62 received NC. Only 18 responded. 13 patients relapsed and 11 died during follow-up. ER negative tumors had a lower COV (p=0.018) as well as those with high Ki-67 (p=0.001) and high risk phenotype (p=0.033) compared to the rest. No PET variable showed association with the response to NC nor OS. There was an inverse relationship between sphericity with DFS (p=0.041), so, for every tenth that sphericity increases, the risk of recurrence decreases by 37%.
ConclusionsBreast tumors in our LABC dataset behaved as homogeneous and spherical lesions. Larger volumes were associated with a lower sphericity. Global heterogeneity variables and sphericity do not seem to have a predictive role in response to NC nor in OS. More spherical tumors with less variation in gray intensity between voxels showed a lower risk of recurrence.
Determinar la relación de las medidas de heterogeneidad global y la esfericidad tumoral obtenidas en 18F-FDG PET/TC con variables biológicas, así como su papel predictivo y pronóstico en pacientes con cáncer de mama localmente avanzado (CMLA).
Material y métodosSe incluyeron 68 pacientes con CMLA, con indicación de tratamiento neoadyuvante (TNA) y18F-FDG PET/TC basal procedentes de un estudio prospectivo multicéntrico en curso. Se determinó el perfil inmunohistoquímico [receptores de estrógenos (RE) y de progesterona (RP), expresión del oncogén HER-2, índice de proliferación Ki-67 y grado histológico tumoral], la respuesta al TNA, la supervivencia global (SG) y la supervivencia libre de enfermedad (SLE). Se realizó la segmentación tridimensional de las lesiones, obteniendo variables SUV, volumétricas y de heterogeneidad global, así como la esfericidad. También se analizó la correlación entre los resultados obtenidos con el perfil inmunohistoquímico, la respuesta a la TNA y la supervivencia.
ResultadosDe las pacientes incluidas, 62 recibieron TNA, respondiendo a éste sólo 18. 13 pacientes recidivaron y 11 fallecieron durante el seguimiento. Los tumores que no expresaron RE tuvieron un COV inferior (p=0.018), así como los de Ki-67 alto (p=0.001) y los de fenotipo de alto riesgo (p=0.033) frente al resto. Ninguna variable PET mostró asociación con la respuesta al TNA ni con la SG. La esfericidad y el índice SUVmedio/SUVmax se relacionaron con la SLE de forma inversa (p=0.041 y p=0.055, respectivamente) de modo que, por cada décima que aumenta la esfericidad, el riesgo de recurrencia disminuye en un 37%.
ConclusionesLos tumores de mama localmente avanzados incluidos en nuestra muestra se comportaron como lesiones homogéneas y esféricas. Los de mayor volumen se asociaron con menor esfericidad. Las variables de heterogeneidad global y la esfericidad no parecen tener un papel predictivo en respuesta a la TNA ni en la SG. Los tumores más esféricos y con menos variación en la intensidad de gris entre los voxels mostraron un menor riesgo de recurrencia.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)