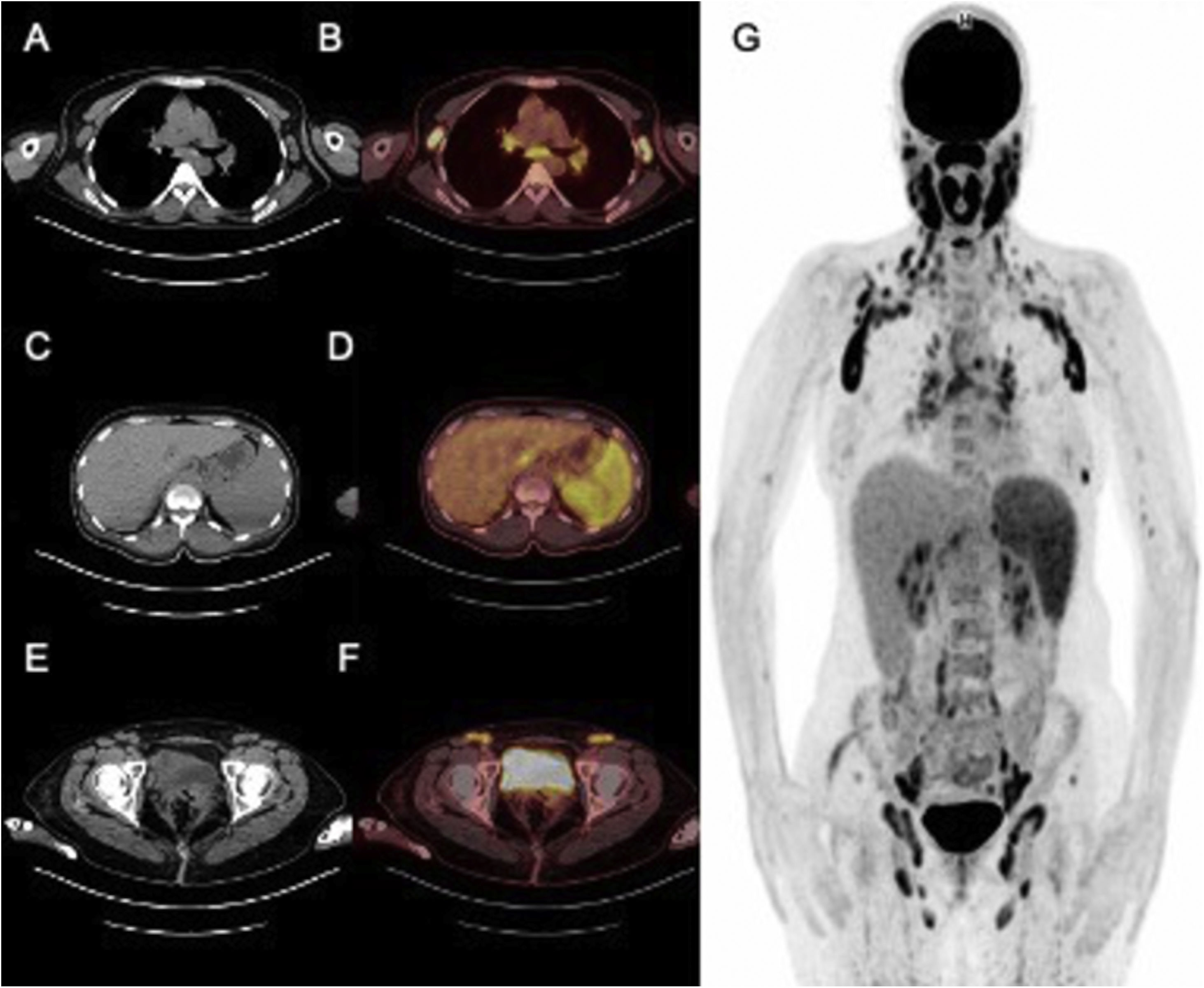
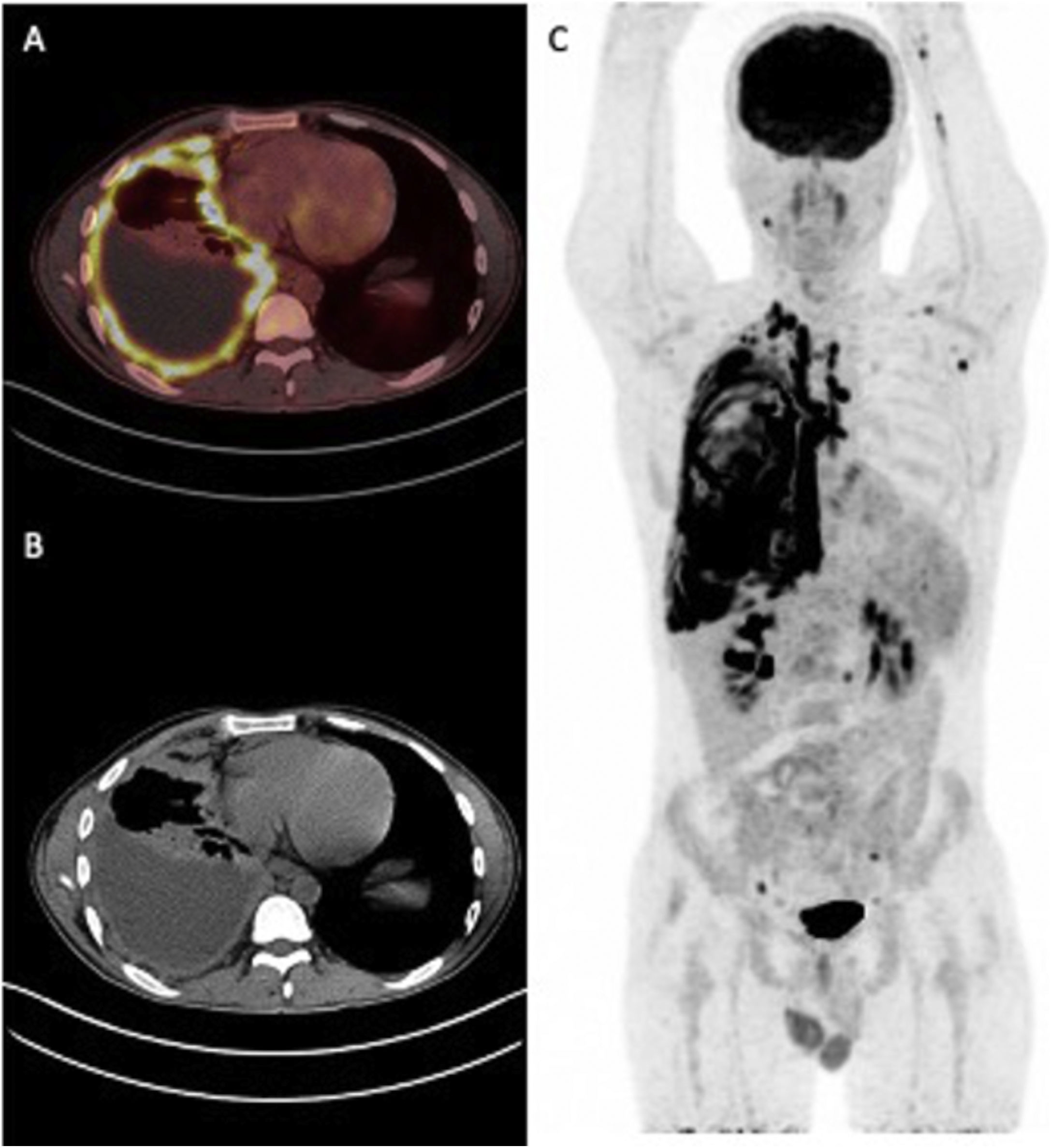
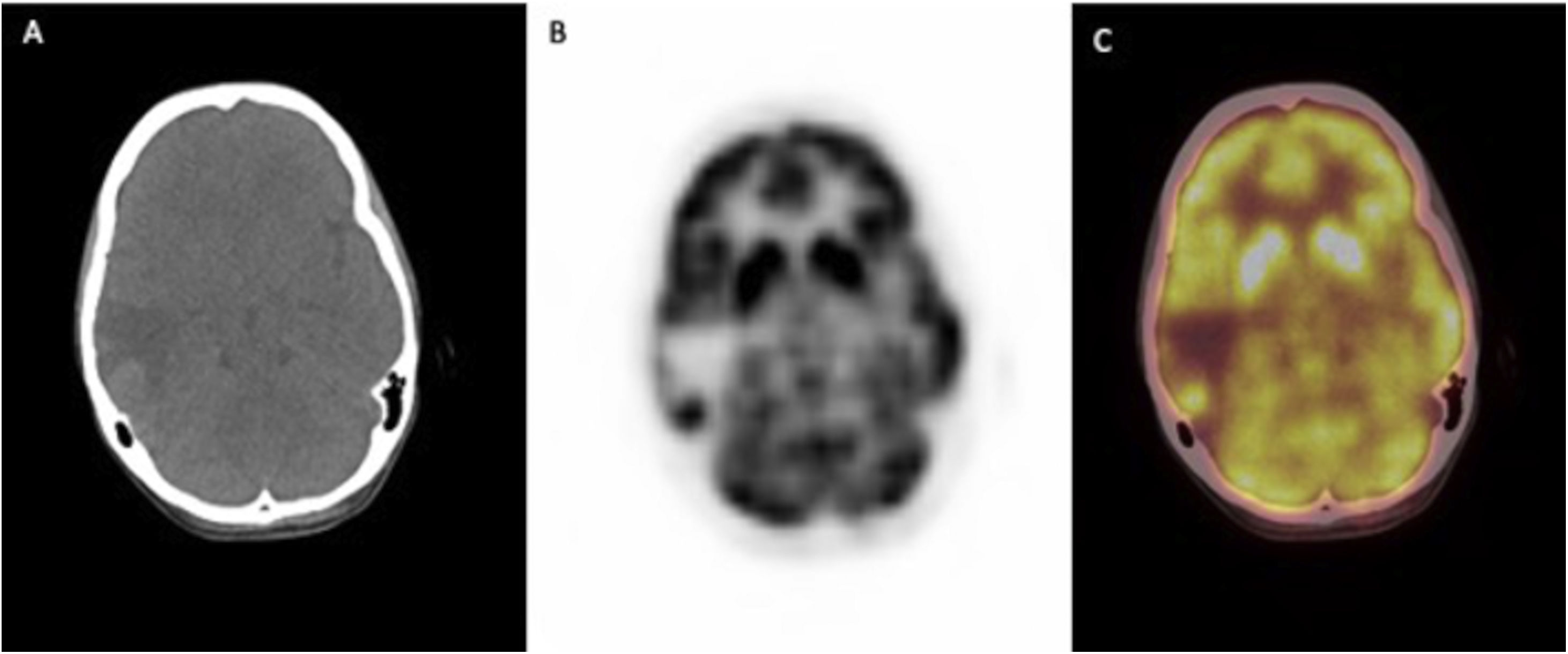
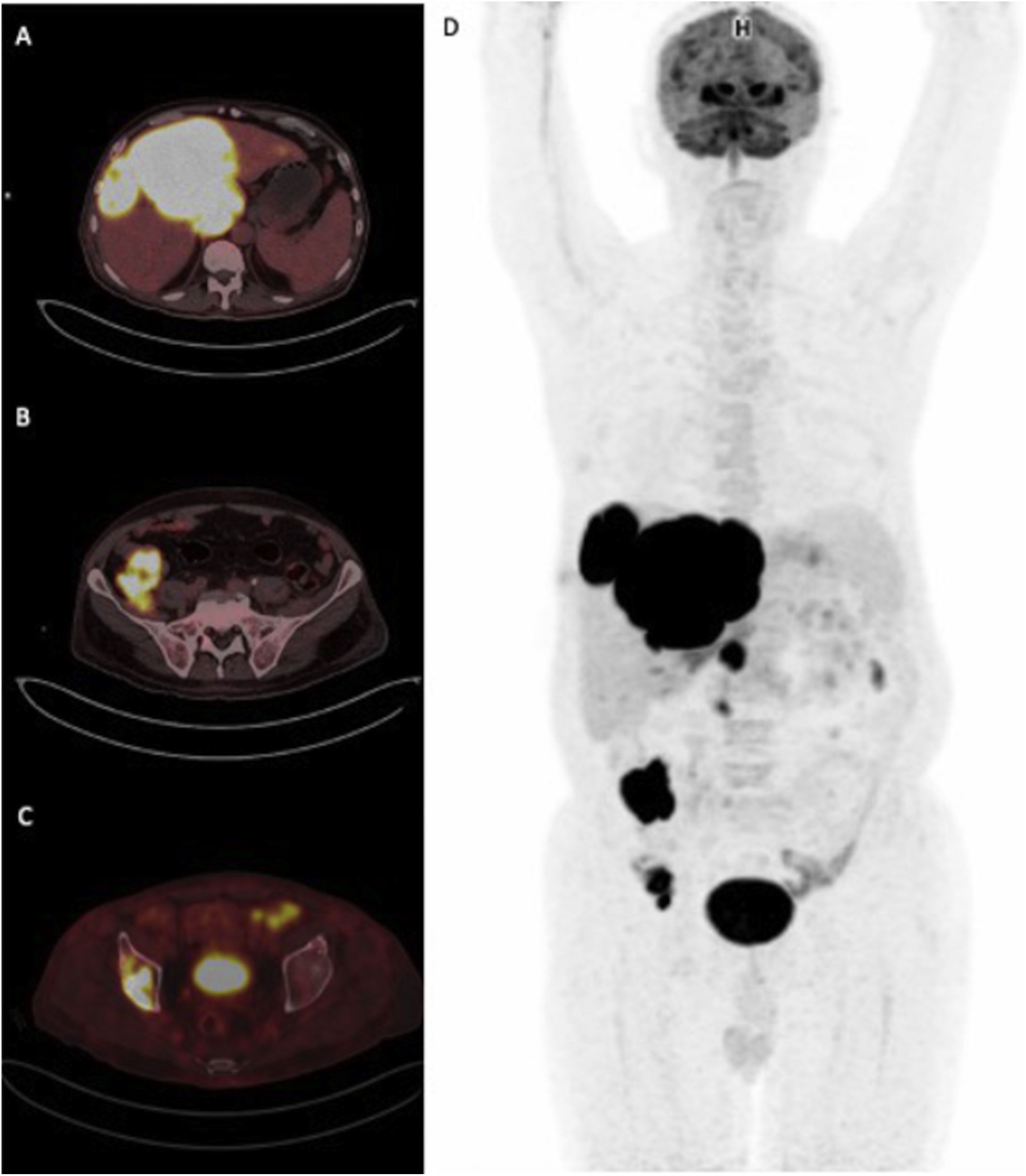
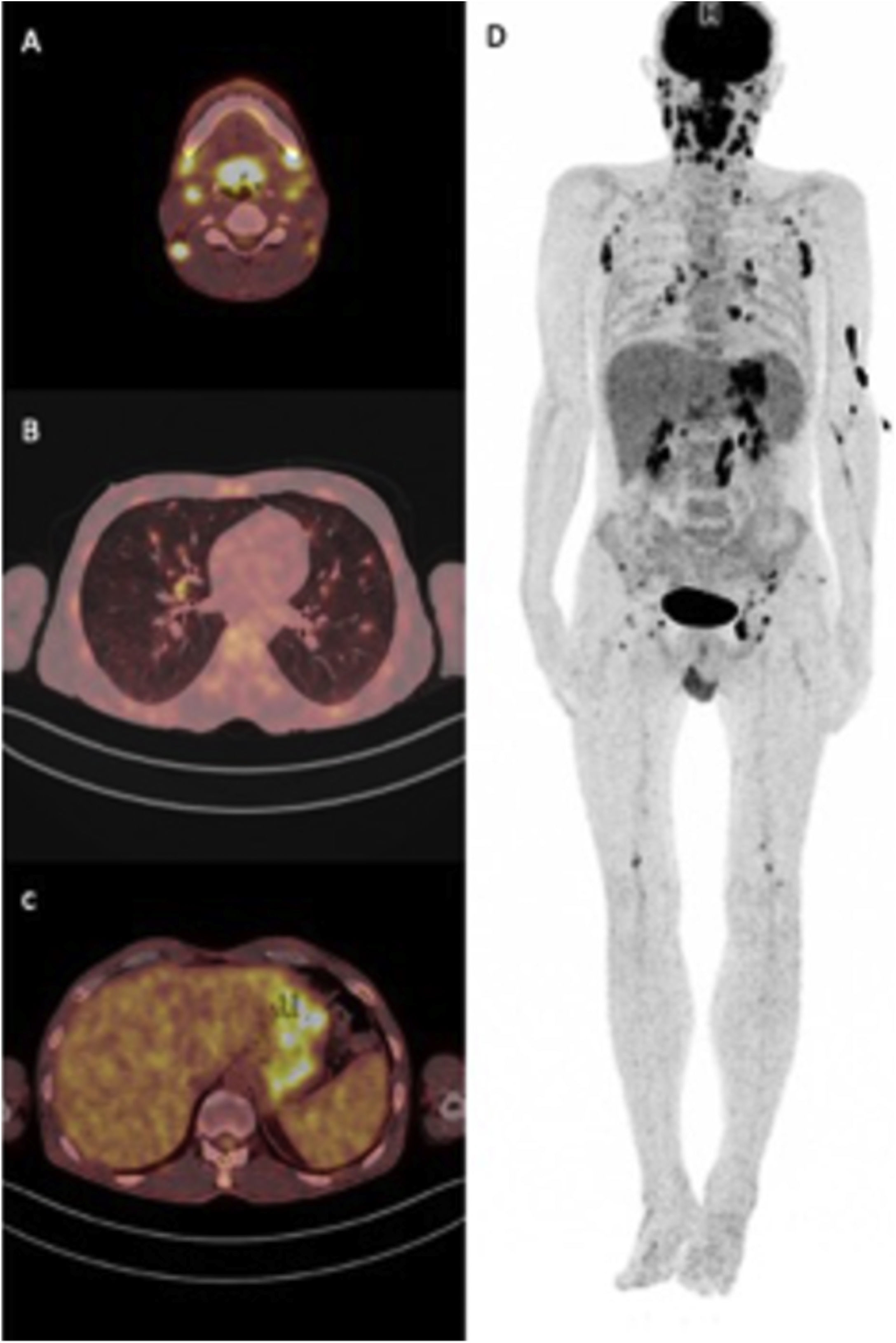
The human immunodeficiency virus [HIV] is a lentevirus, primarily infects certain cells of the immune system, thereby greatly weakens the body’s own defenses against diseases. This study was aimed to explore the value and significance of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the assessment of patients with HIV infection and to examine the presence of quantitative alterations in 18F-FDG uptake among patients with HIV-related infections or malignant diseases in HIV-positive patients.
Patients and methodsForty patients with HIV infection were scanned on PET/CT system. The data were registered according to immune status, antiretroviral therapy, and definitive diagnosis. All pathologic lesions and disease related areas were described, 18F-FDG uptake patterns were evaluated. Semiquantitative analysis of 18F-FDG uptake was performed and SUVmax were calculated.
ResultsTwenty-eight patients [70%] were diagnosed with HIV-related infection or malignant diseases. The sensitivity of PET/CT was shown to be 100% and the specificity 92% for concomitant diseases requiring additional treatment to antiretroviral therapy. The SUVmax and CD4 counts were not statistically different between HIV-related reactive lymphadenopathy, HIV-related malignancy, and HIV-related infections.
ConclusionsThe pattern of distribution of nodal/extranodal uptake on 18F-FDG PET/CT may facilitate distinction between HIV-related generalized lymphadenopathies, HIV-related opportunistic infections, and malignancies. In this context, 18F-FDG PET/CT should be preferred for routine use in the management of patients infected with HIV.
El virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana [VIH] es un lentevirus, que infecta principalmente ciertas células del sistema inmunitario, por lo que debilita las defensas propias frente a las enfermedades. El objetivo de este estudio fue analizar el valor y significado de la PET/TC con 18F-FDG en la evaluación de pacientes con infección por VIH y determinar la presencia de diferencias cuantitativas de captación de 18F-FDG entre pacientes con infecciones relacionadas con el VIH o neoplasia maligna en pacientes VIH positivos.
MétodosSe estudiaron cuarenta pacientes con infección por VIH mediante PET/TC con 18F-FDG. Se registró el estado inmunitario, el tratamiento antirretroviral y el diagnóstico definitivo de cada paciente. Se describieron todas las lesiones patológicas y áreas relacionadas con la enfermedad, se evaluaron los patrones de captación de 18F-FDG. Se realizó un análisis semicuantitativo de la captación de 18F-FDG mediante el calculó SUVmax.
ResultadoVeintiocho pacientes [70%] fueron diagnosticados con infección relacionada con el VIH o neoplasia maligna. La sensibilidad de la PET/TC con 18F-FDG fue del 100% y la especificidad del 92% para las enfermedades concomitantes que requerían tratamiento adicional a la terapia antirretroviral. El SUVmax y el recuento de CD4 no fueron estadísticamente diferentes entre la linfadenopatía reactiva relacionada con el VIH, la neoplasia maligna relacionada con el VIH y las infecciones relacionadas con el VIH.
ConclusionEl patrón de distribución de la captación ganglionar/extraganglionar en la PET/TC con 18F-FDG puede facilitar la distinción entre las adenopatías generalizadas relacionadas con el VIH, las infecciones oportunistas relacionadas con el VIH y las neoplasias malignas. En este contexto, se debe realizar el estudio PET/TC con 18F-FDG de forma rutinaria en el manejo de pacientes infectados por el VIH.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)