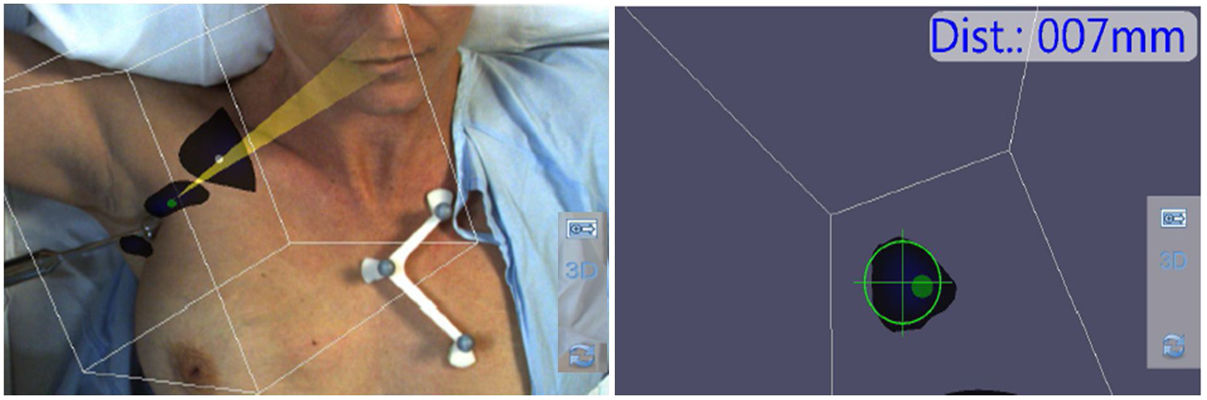
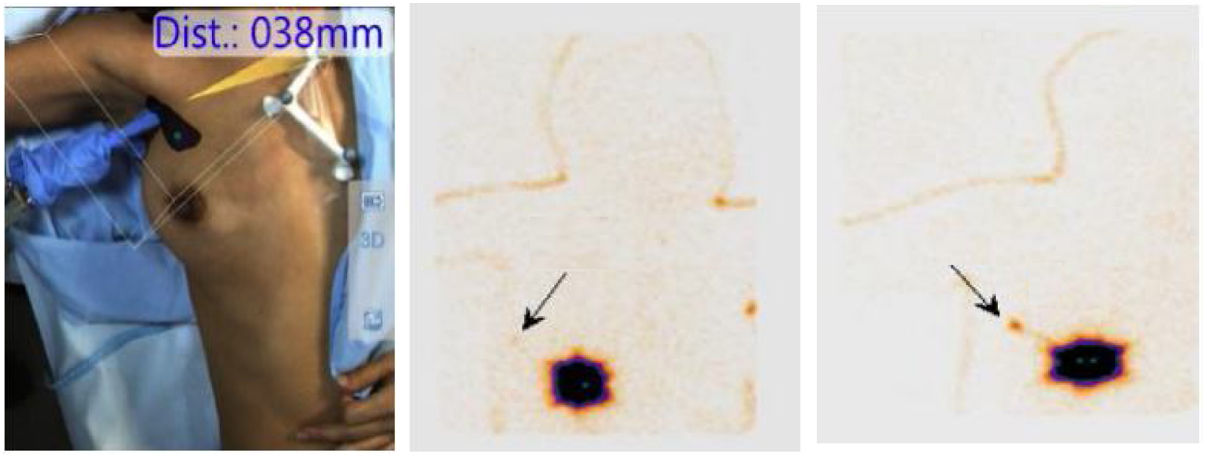
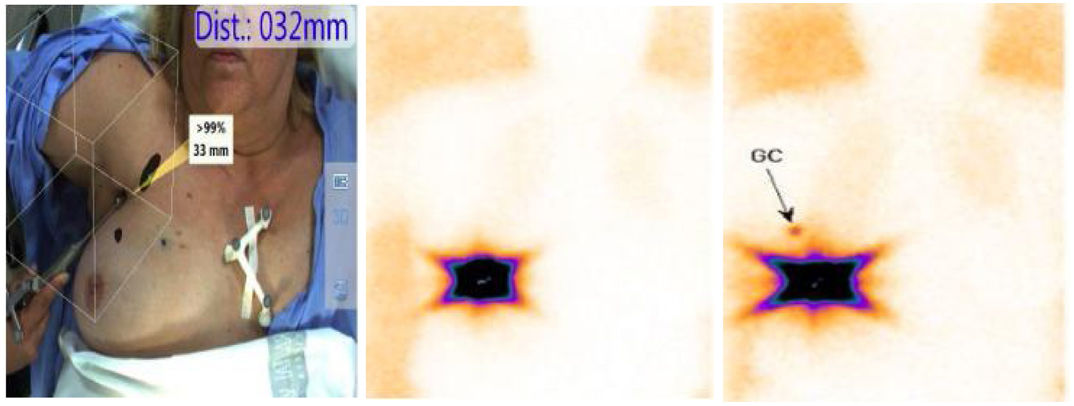
Freehand SPECT can be a useful imaging technique for preoperative planning of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) as it allows localization of the sentinel node by 3D and real-time tomographic imaging and determines its depth after a few minutes of scanning.
The aim of the study was to evaluate the correlation between the number of detected SNs between freehand SPECT images and lymphoscintigraphy (LS).
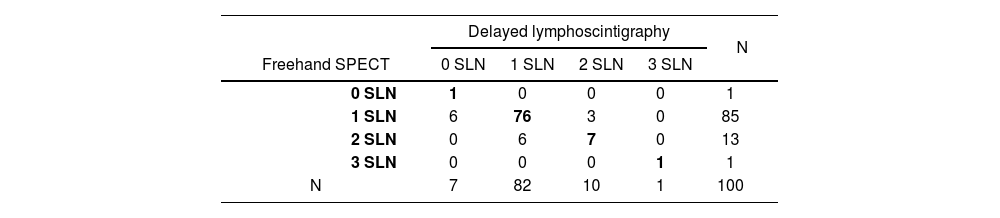
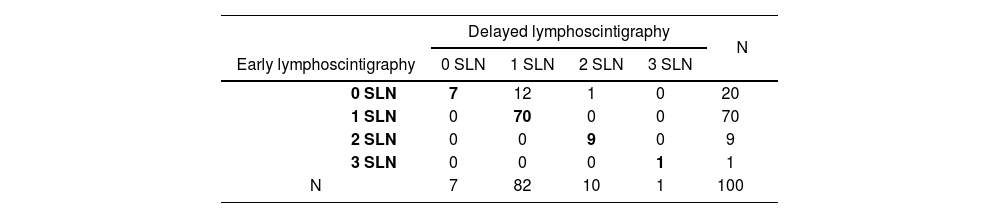
Materials and methods100 patients with a diagnosis of invasive breast cancer and no clinical evidence of lymph node involvement prospectively underwent SLNB. The preoperative study included freehand SPECT imaging at 15min after injection and LS imaging at 25 and 60−90min after injection (early and late). The observed agreement was analyzed and a concordance study was performed between the number of SNs detected with freehand SPECT and LS.
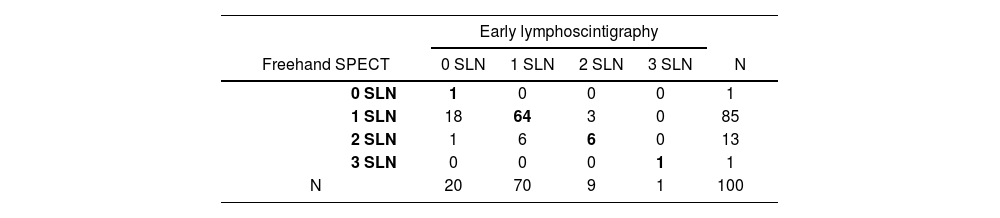
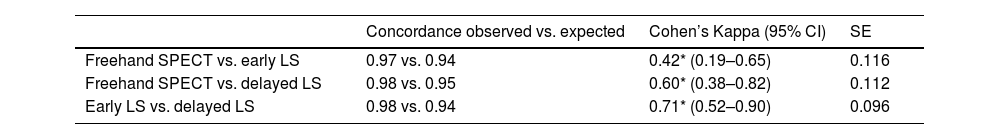
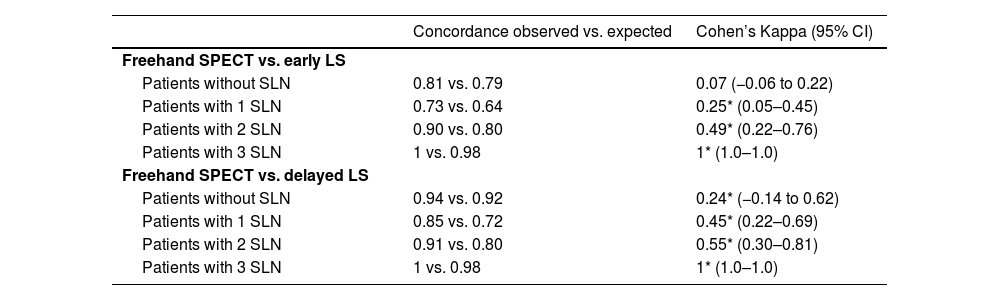
ResultsThe observed agreement in the detection of SNs between freehand SPECT and early LS was 72%; between freehand SPECT and late LS was 85%; and between early and late LS was 87%. In the concordance study, there was moderate concordance between freehand SPECT and early LS (kappa coefficient: 0.42); moderate-high concordance between freehand SPECT and late LS (kappa coefficient: 0.60); and moderate-high concordance between early and late LS (kappa coefficient: 0.70), with no significant differences between them (p-value=0.16).
ConclusionFreehand SPECT showed a moderate-high concordance with conventional imaging studies and could be a valid alternative for the presurgical study of SLNB in breast cancer.
La SPECT portátil puede ser una técnica de imagen útil para la planificación preoperatoria de la biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BSGC) ya que permite la localización del ganglio centinela mediante imágenes tomográficas en 3D y en tiempo real y determina su profundidad, después de unos minutos de exploración.
El objetivo del estudio fue evaluar la correlación entre el número de GC detectados entre las imágenes de la SPECT portátil y la linfogammagrafía (LG).
Materiales y métodos100 pacientes con diagnóstico de cáncer de mama infiltrante y sin evidencia clínica de afectación ganglionar, se sometieron prospectivamente a una BSGC. El estudio preoperatorio incluyó imágenes de SPECT portátil a los 15 minutos tras la inyección y de LG a los 25 y 60–90 minutos (precoz y tardía). Se analizó el acuerdo observado y se realizó un estudio de concordancia entre el número de GC detectados con SPECT portátil y LG.
ResultadosEl acuerdo observado en la detección de GC entre SPECT portátil y LG precoz fue del 72%; entre SPECT portátil y LG tardía del 85%; y entre la LG precoz y la tardía de un 87%. En el estudio de concordancia se registró una concordancia moderada entre la SPECT portátil y la LG precoz (coeficiente kappa: 0,42); una concordancia moderada-alta entre la SPECT portátil y la LG tardía (coeficiente kappa: 0,60); y una concordancia de moderada-alta entre la LG precoz y la tardía (coeficiente kappa: 0,70), sin diferencias significativas entre ellos (valor p=0,16).
ConclusiónLa SPECT portátil presentó una concordancia moderada-alta con los estudios de imagen convencional y podría ser una alternativa válida para el estudio prequirúrgico de la BSGC en el cáncer de mama.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)