To evaluate the usefulness of 11C-methionine PET/CT (MET) in the localization of the parathyroid adenomas and to compare the results with those obtained with the conventional technique in double-phase 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy (MIBI). We evaluated the optimal timing to acquire MET images.
Material and methodsA prospective study that included 14 patients (mean age: 65.5±9.7 years) with primary hyperparathyroidism (PH) who underwent surgery was performed. Mean serum iPTH was 215.8±108pg/mL and serum calcium 10.8±0.9mg/dL. MIBI (planar and SPECT) was obtained 10 min and 2–3h after injection of 740MBq (20mCi) of 99mTc-sestamibi. MET was obtained 10 min and 40 min after injection of 740MBq (20mCi) of 11C-methionine. MIBI and MET images were visually evaluated and compared. A score for 10 min and 40 min MET images from 0 (no abnormal uptake) to 3 (intense uptake) was assigned.
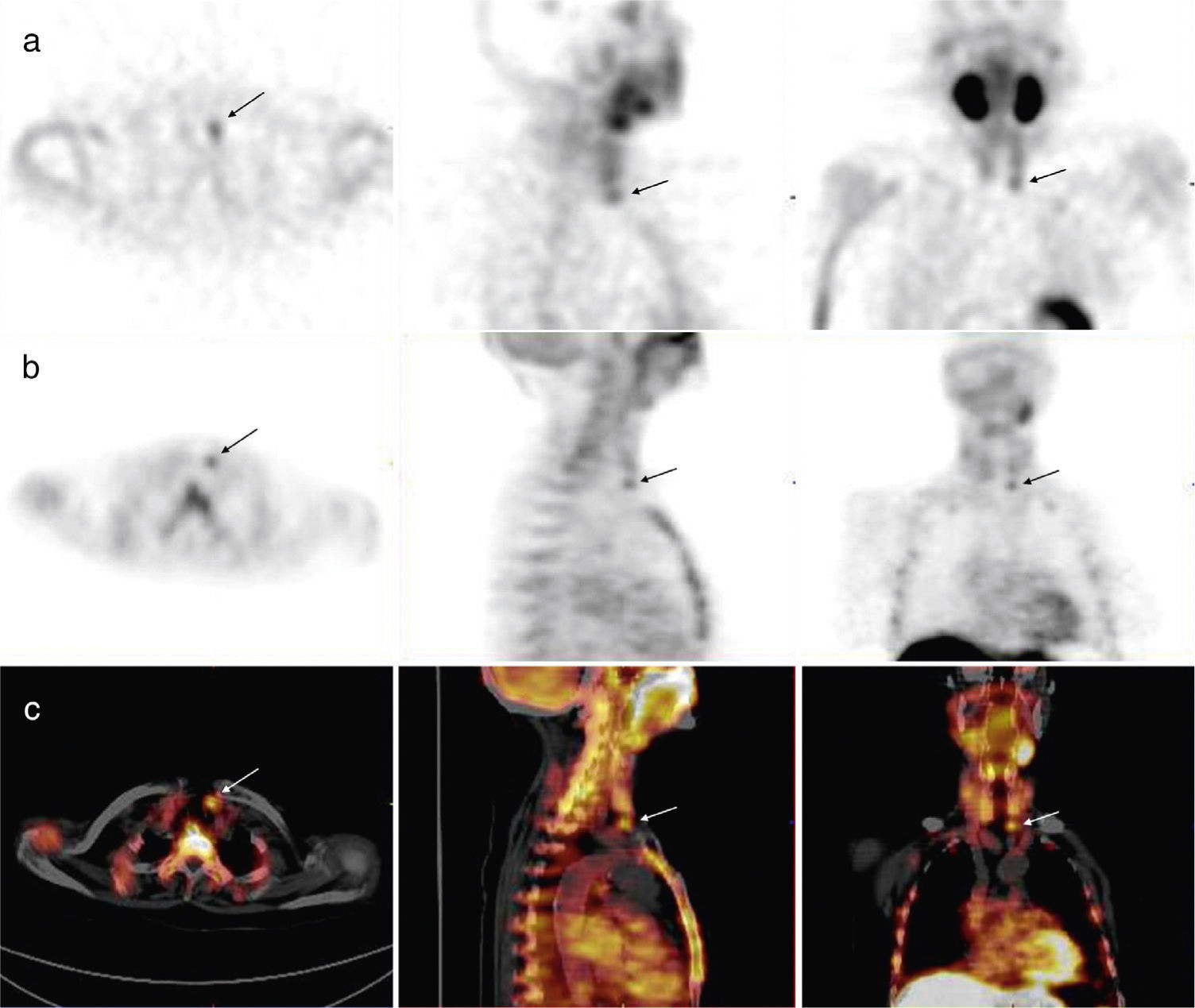
ResultsMIBI and MET were positive and concordant in 11/14 patients and in 10 of them the parathyroid adenoma was correctly localized. In 3/14 MIBI was positive and MET negative (MIBI correctly localized the parathyroid adenoma in 2 of them). According to the timing of MET imaging acquisition, the 10 min and 40 min acquisition showed the same score in 10 patients, it was higher at 10 min acquisition in 3 and in 1 the parathyroid adenoma was only detected at 40 min acquisition.
ConclusionMIBI remains the technique of choice for the localization of parathyroid adenomas in patients with PH. MET may play a complementary role in selected patients. Delayed acquisition should be included in the MET protocol when the early acquisition is negative.
Evaluar la utilidad de la 11C-metionina PET/TC (MET) en la localización de adenoma de paratiroides comparado con la técnica convencional en doble fase con 99mTc-sestamibi (MIBI). Evaluar el tiempo adecuado para la adquisición de imágenes MET.
Material y métodosEste estudio prospectivo incluyó 14 pacientes (edad: 65,5±9,7 años) con hiperparatiroidismo primario (HPTP) sometidos a cirugía. La iPTH fue de 215,8±108pg/mL y el calcio sérico 10,8±0,9mg/dL. El MIBI (planar, SPECT) fue realizado a los 10 min y 2–3 horas tras la inyección de 740MBq (20mCi) de MIBI. La MET fue realizada 10 min y 40 min tras la inyección de 740MBq (20mCi) de MET. Las imágenes fueron evaluadas visualmente y comparadas. Las imágenes con MET a 10 min y 40 min fueron valoradas según el grado de captación (0[no captación] a 3[intensa]).
ResultadosMIBI y MET fueron positivos y concordantes en 11/14 pacientes, en 10 de ellos el adenoma de paratiroides fue correctamente localizado. En 3/14 el MIBI fue positivo y la MET negativa (el MIBI localizó correctamente 2). Con respecto al tiempo de adquisición imágenes MET a los 10 min y 40 min se observó la misma puntuación en 10 pacientes, fue mayor a los 10 min en 3 y en unpaciente sólo fue positivo a los 40 min.
ConclusionesEl MIBI continúa siendo la técnica de elección para la localización del adenoma de paratiroides en pacientes con HPTP. La MET podría tener un papel complementario en pacientes seleccionados. La adquisición tardía de la MET debería ser incluida cuando la imagen precoz sea negativa.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)