To assess the clinical value of [18F]F-PSMA negative PET/CT, in patients diagnosed with prostate cancer treated with prostatectomy with elevated PSA less than 1 ng/mL, on the outcome of salvage radiotherapy.
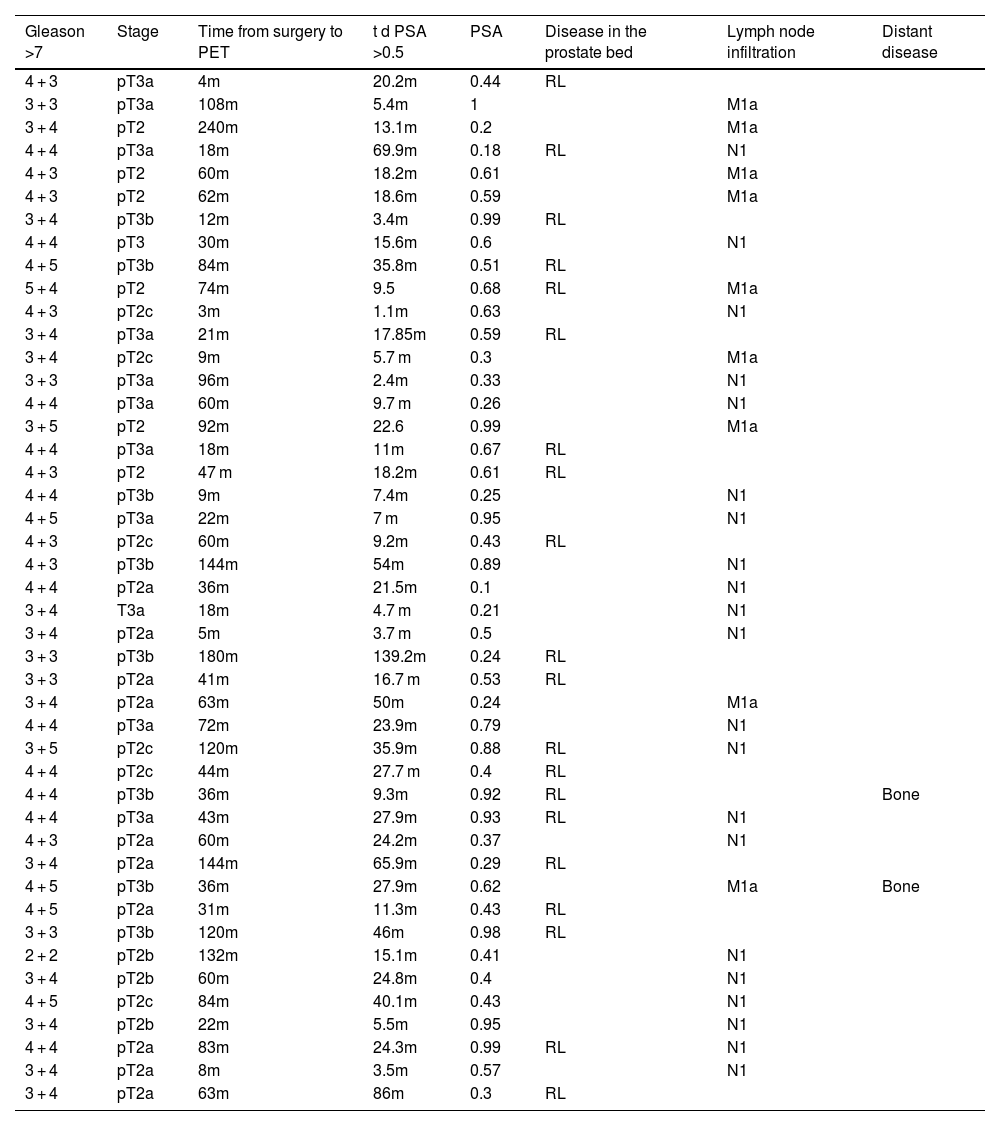
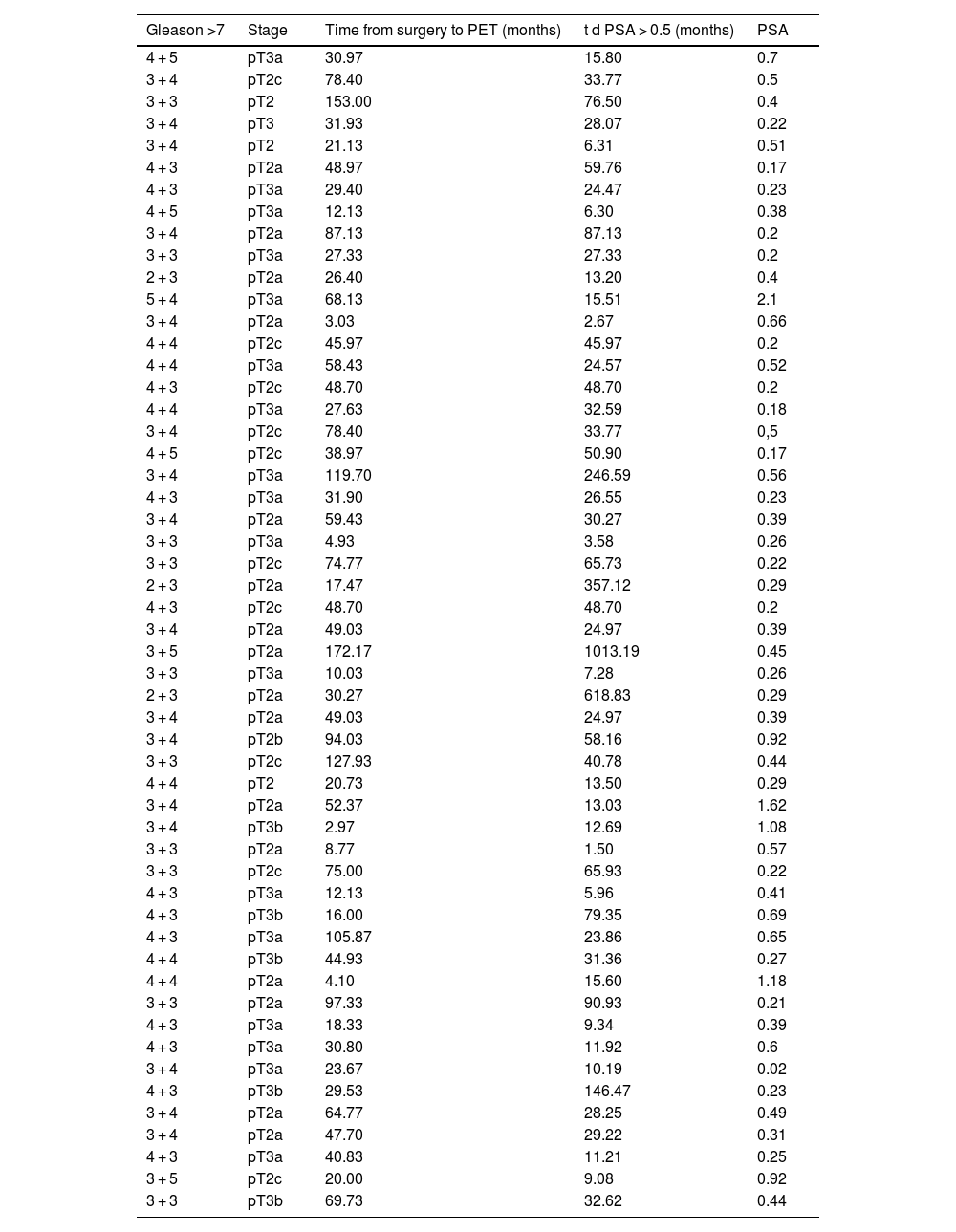
MethodWe prospectively included 98 patients diagnosed with prostate cancer treated with prostatectomy with biochemical recurrence [mean PSA 0.51 ng/mL (range 0.17–1.0 ng/mL)] who were referred for an [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT study.
The [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT scan was negative in 53/98 patients (54.09%). Differences were analysed between those patients who were or were not candidates for pelvic salvage radiotherapy (PSRT) decided upon multidisciplinary committee and patient consent, with a minimum follow-up time for 1 year. Response to treatment was defined as a 50% reduction in PSA levels. Recurrence was ascertained upon clinical, analytical and imaging follow-up outcomes.
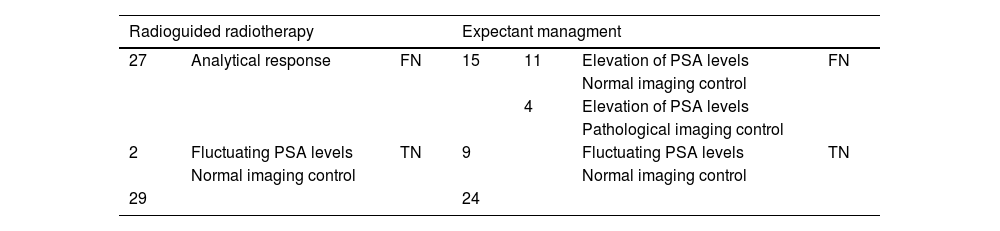
Results54.7% (29/53) of the patients with a negative [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT underwent PSRT.
Of these, 93.1% (27/29) patients demonstrated response to treatment (PSMA false negatives).
The remaining two patients showed fluctuating PSA levels without detecting disease on the [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT follow-up study.
45.3% (24/53) of patients with negative [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT did not undergo PSRT.
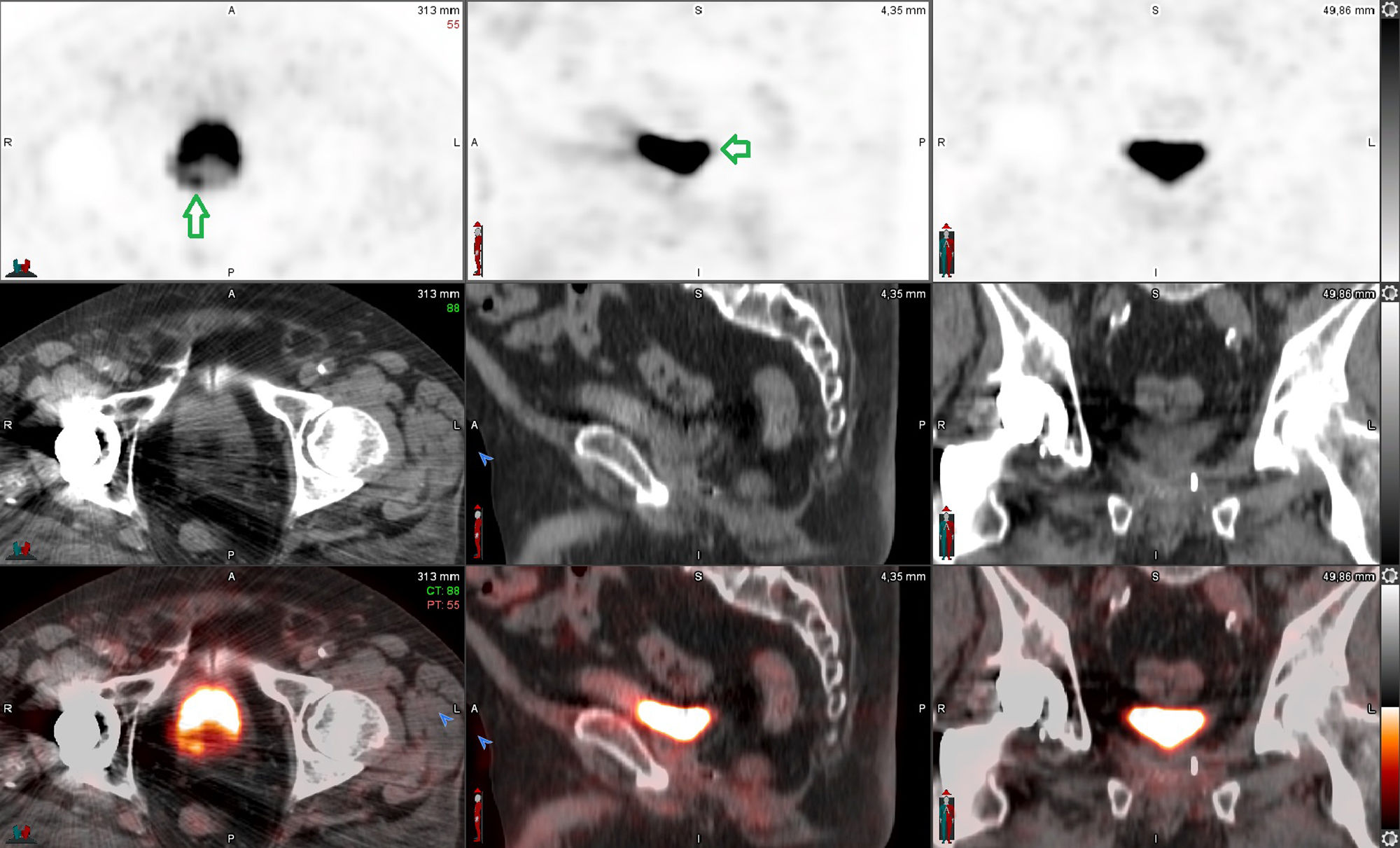
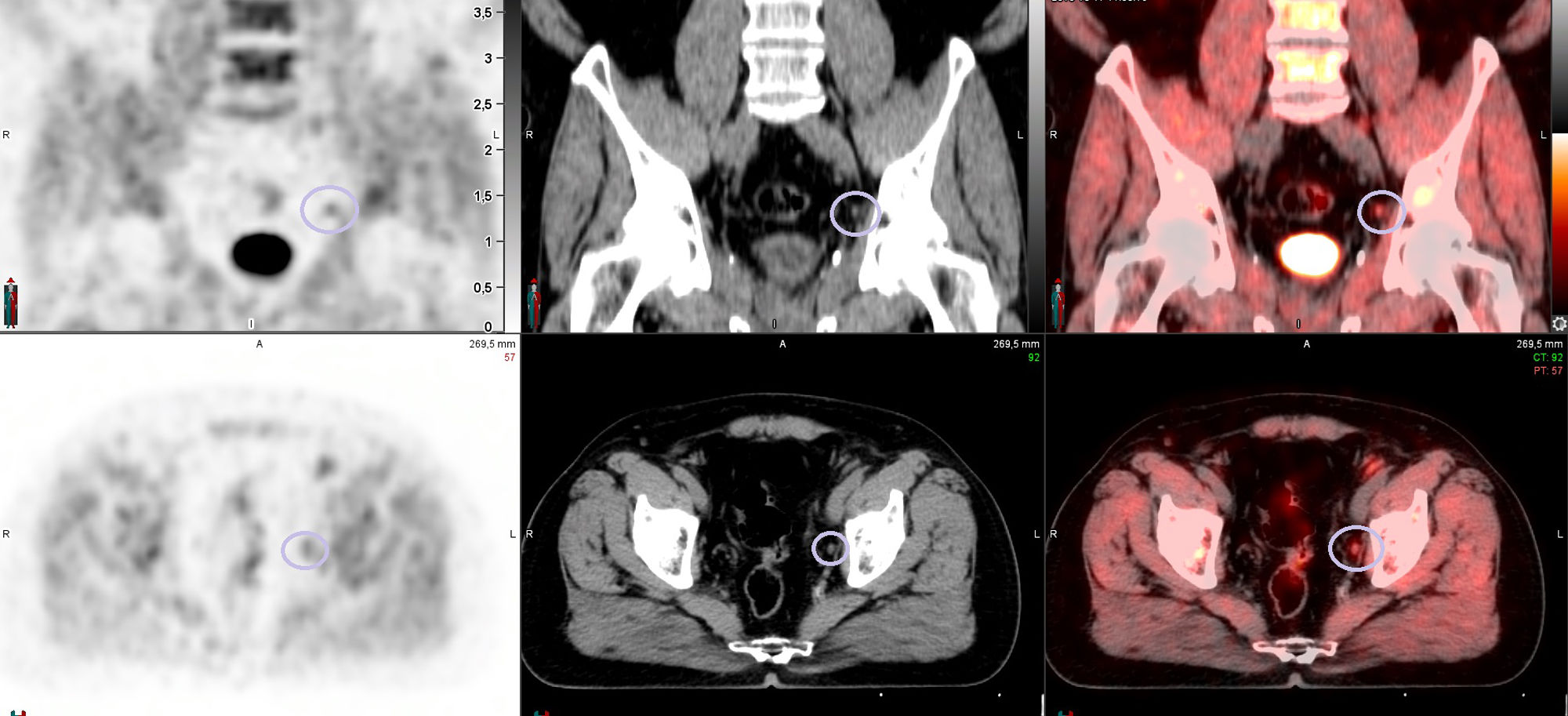
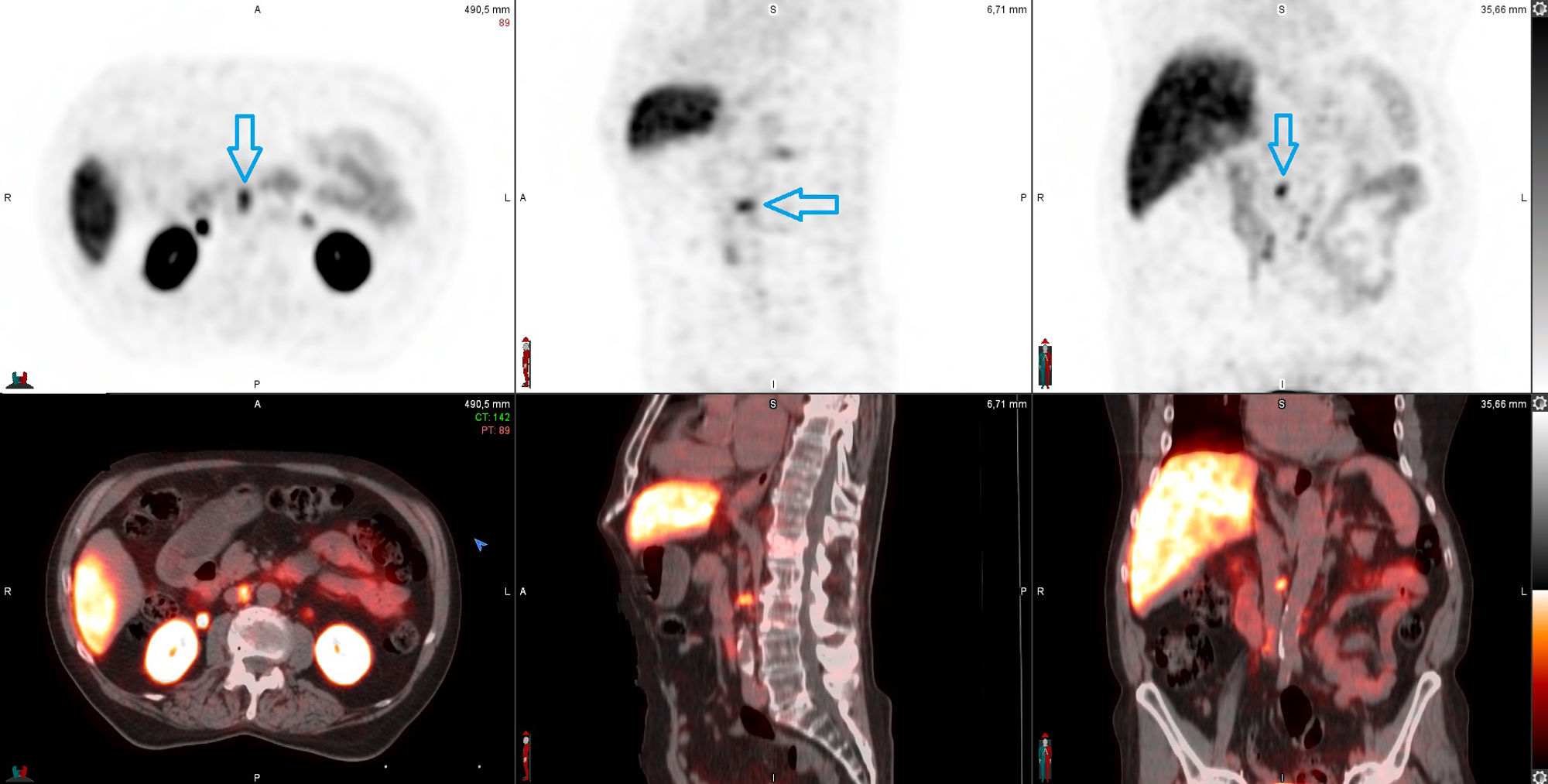
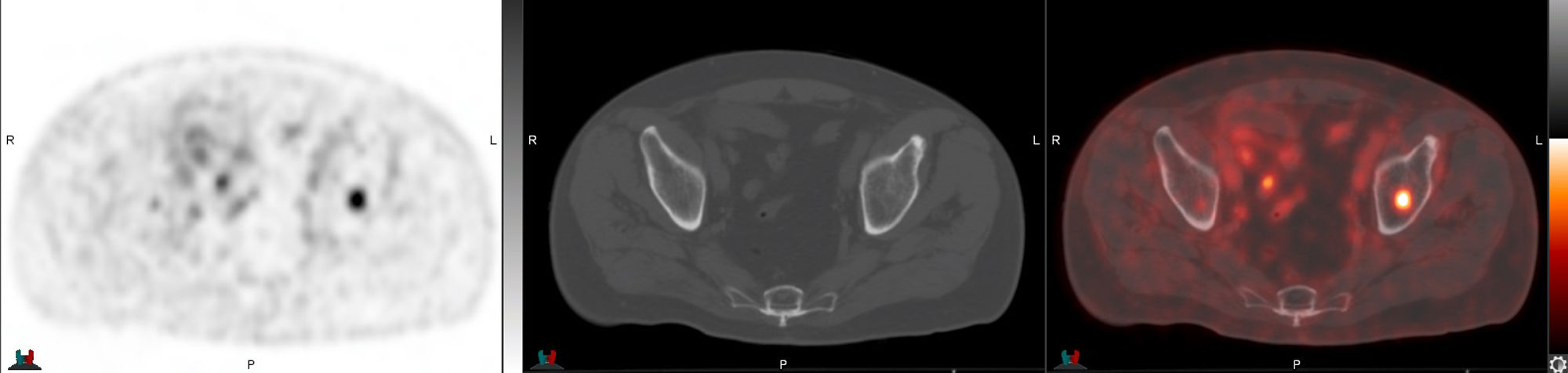
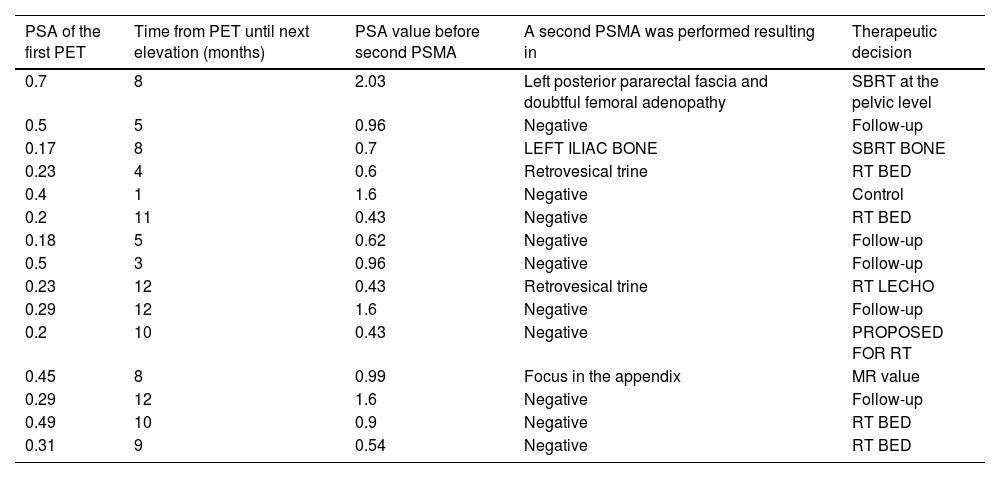
Of these, progressive PSA elevation was observed in 62.5% (15/24) (PSMA false negatives), localising recurrence on the [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT follow-up study in 4 patients.
The remaining 9 patients (37.5%) showed fluctuating PSA levels without detecting disease on the [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT follow-up study.
Our series confirmed 42 (42.85%) [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT false negatives cases.
ConclusionPatients diagnosed with prostate cancer with post-prostatectomy biochemical recurrence and a negative [18F]F-PSMA -PET/CT study are likely to benefit from pelvic salvage radiotherapy, with response seen in 93.1% of our cases.
Evaluar el valor clínico de un PET/TC con [18F]F-PSMA negativo, en pacientes diagnosticados de cáncer de próstata tratados con prostatectomía con elevación del PSA inferior a 1 ng/mL, en los resultados de la radioterapia de rescate.
MétodoIncluimos prospectivamente 98 pacientes diagnosticados de cáncer de próstata tratados con prostatectomía que presentan recidiva bioquímica [PSA medio 0.51 ng/mL (0.17–1.0 ng/mL)] y han acudido para la realización de un [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC.
La [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC fue negativa en 53/98 pacientes (54.09%). Se analizaron las diferencias entre los que se consideraron o no candidatos a radioterapia de rescate pélvica (RTR), a decisión del comité y consentimiento del paciente, con seguimiento durante al menos 1 año. La respuesta al tratamiento se definió como reducción del PSA del 50%. La recurrencia se determinó en base al seguimiento clínico, analítico y de imagen.
ResultadosEl 54.7% (29/53) de los pacientes con [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC negativo se sometieron a RTR.
De ellos el 93.1% (27/29) demostraron respuesta al tratamiento (falsos negativos del PSMA).
De los otros dos: mostraron cifras oscilantes del PSA sin detectarse enfermedad en las exploraciones [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC de seguimiento.
El 45.3% (24/53) de los pacientes con [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC negativo no se sometieron a RTR.
De ellos se objetivó una elevación progresiva del PSA en el 62.5% (15/24) (falsos negativos del PSMA), localizando la recidiva con seguimiento por [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC en 4 pacientes.
Los 9 pacientes restantes (37.5%), mostraron niveles de PSA fluctuantes sin que la [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC mostrara enfermedad.
Se han confirmado 42 falsos negativos del [18F]F-PSMA -PET/TC (42.85%).
ConclusiónLos pacientes diagnosticados de cáncer de próstata con recidiva bioquímica post-prostatectomía con estudio [18F]F-PSMA PET/TC negativo tienen posibilidades de beneficiarse de la radioterapia de rescate pélvica, con respuesta en el 93.1%.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)