To evaluate the use of 4D PET/CT to quantify tumor respiratory motion compared to the «Slow»-CT (CTs) in the radiotherapy planning process.
Material and methodsA total of 25 patients with inoperable early stage non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were included in the study. Each patient was imaged with a CTs (4s/slice) and 4D PET/CT.
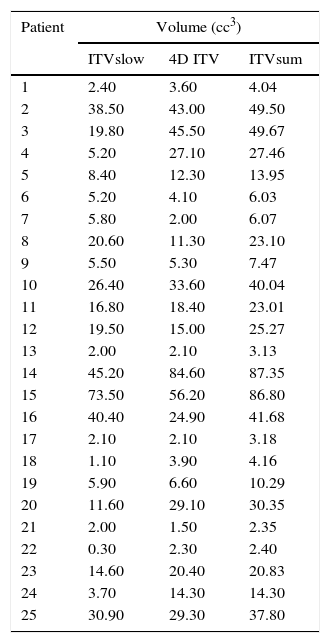
The adequacy of each technique for respiratory motion capture was evaluated using the volume definition for each of the following: Internal target volume (ITV) 4D and ITVslow in relation with the volume defined by the encompassing volume of 4D PET/CT and CTs (ITVtotal).
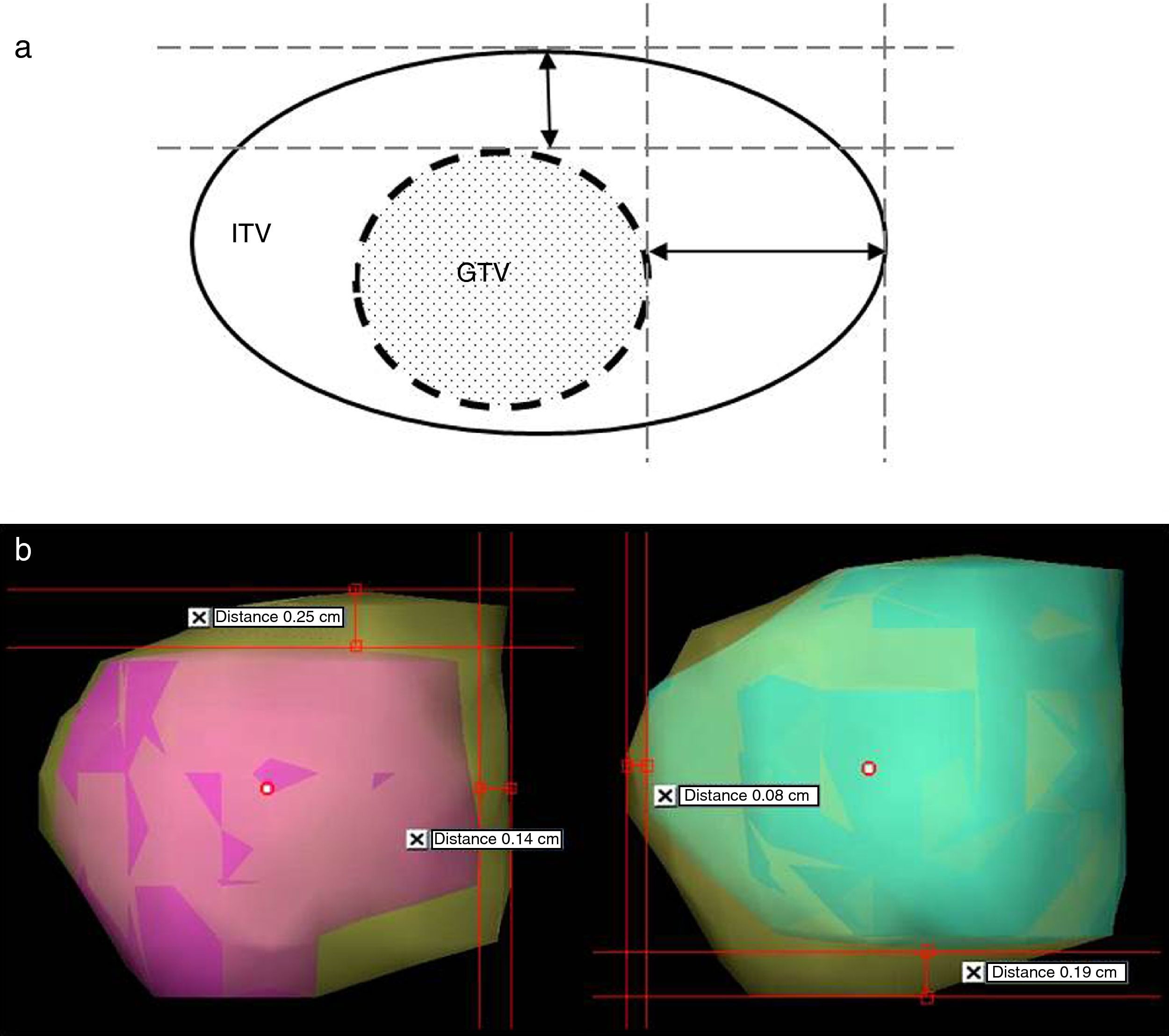
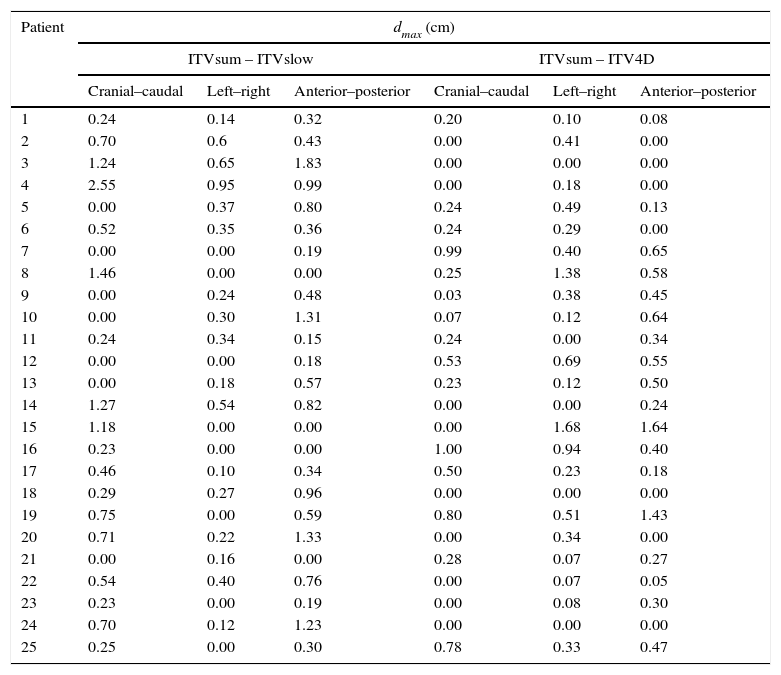
The maximum distance between the edges of the volume defined by each technique to that of the total volume was measured in orthogonal beam's eye view.
ResultsThe ITV4D showed less differences in relation with the ITVtotal in both the cranio-caudal and the antero-posterior axis compared to the ITVslow. The maximum differences were 0.36mm in 4D PET/CTand 0.57mm in CTs in the antero-posterior axis.
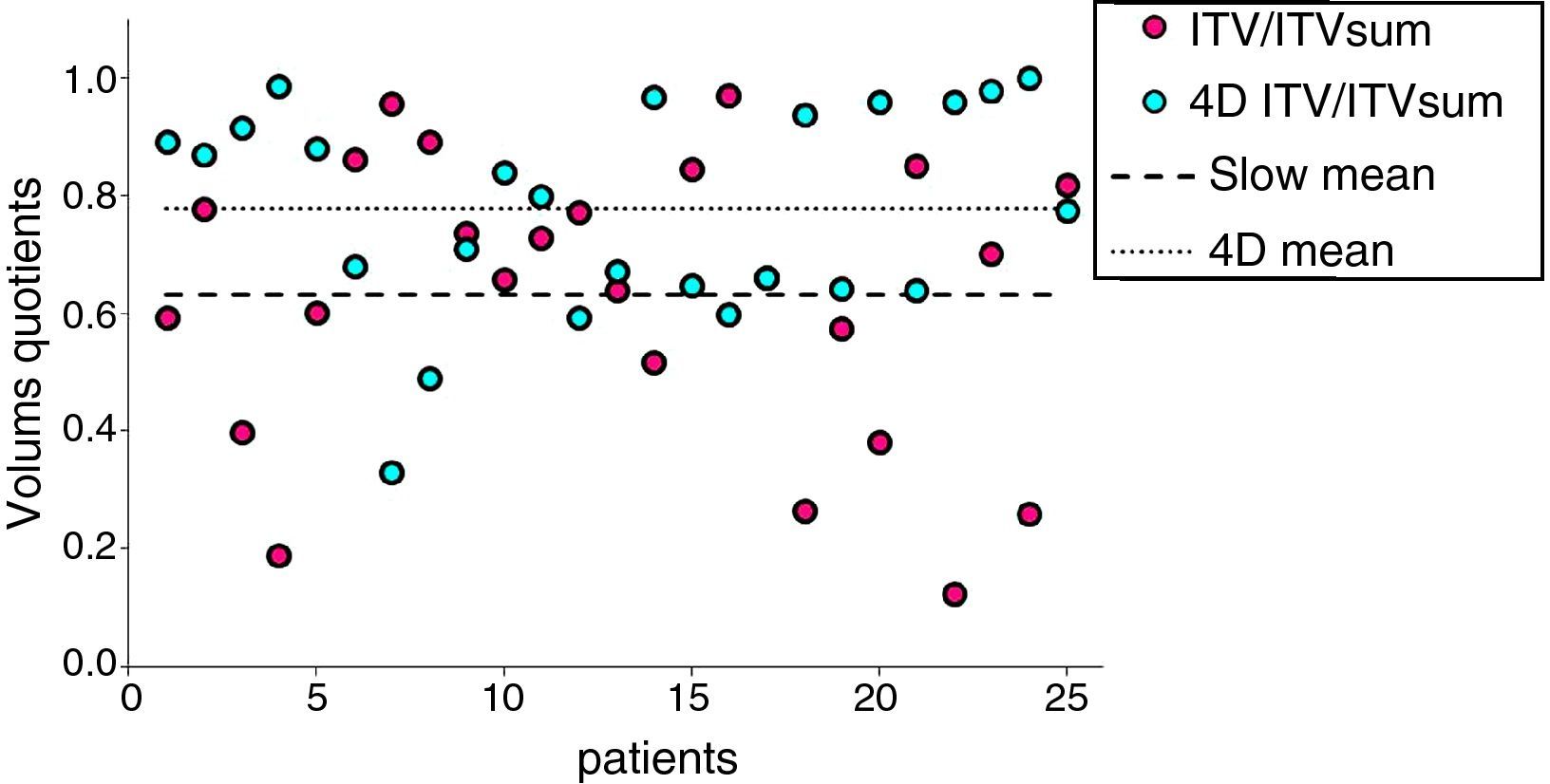
4D PET/CT resulted in the definition of more accurate (ITV4D/ITVtotal 0.78 vs. ITVs/ITVtotal 0.63), and larger ITVs (19.9cc vs. 16.3cc) than those obtained with CTs.
ConclusionPlanning with 4D PET/CT in comparison with CTs, allows incorporating tumor respiratory motion and improving planning radiotherapy of patients in early stages of lung cancer.
Evaluar el uso de la 4D PET/TC para capturar el movimiento respiratorio en comparación con la «slow»-TC (TCs), en el procedimiento de planificación de radioterapia.
Material y métodosSe ha incluido a 25 pacientes diagnosticados de estadio inicial de cáncer de pulmón de célula no pequeña (NSCLC) médicamente inoperable. A cada paciente se le realizó una TCs (4 s/corte) y una 4D PET/TC.
La idoneidad de cada técnica en la captura del movimiento respiratorio fue evaluada comparando el volumen definido por cada una de ellas: internal target volumen (ITV) 4D y el ITVslow, con relación a la suma de los volúmenes de la 4D PET/TC y la TCs (ITVsuma).
La máxima diferencia entre el volumen definido por cada técnica respecto al volumen suma fue evaluada en una proyección antero-posterior y otra lateral.
ResultadosLos volúmenes generados con 4D PET/TC consiguen una definición más precisa del ITV que los volúmenes obtenidos con TCs (ITV4D/ITVsuma 78% vs. ITVslow/ITVsuma 63%). En general, los volúmenes de la 4D PET/TC son de mayor tamaño (19,9 vs. 16,3 cc).
El ITV4D muestra menor diferencia con el ITVsuma en los ejes cráneo-caudal y antero-posterior respecto al ITVslow y capta el movimiento de forma más exacta. La máxima diferencia observada es de 0,36mm en la 4D PET/TC y de 0,57mm en la TCs en el eje antero-posterior.
ConclusionesLa planificación con 4D PET/TC en comparación con TCs permite cuantificar el movimiento respiratorio del tumor y mejorar la planificación de radioterapia en estadios iniciales de NSCLC.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)