To assess the diagnostic accuracy of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in detecting asymptomatic recurrences in patients with lymphoma. To define uptake patterns of recurrence indicative of recurrence.
Material and methodsThose patients with lymphoma who fulfilled the following inclusion criteria of clinical complete remission and negative PET/CT study were included retrospectively and longitudinally. Conventional surveillance of these patients was performed only by 18F-FDG PET/CT following a standardized procedure. Pathologic locations (supra- and infradiaphragmatic) and their character (single or multiple) were analyzed in order to determine reliable metabolic patterns of recurrence. The final diagnosis was established by histopathological analysis or clinical follow-up greater than 8 months.
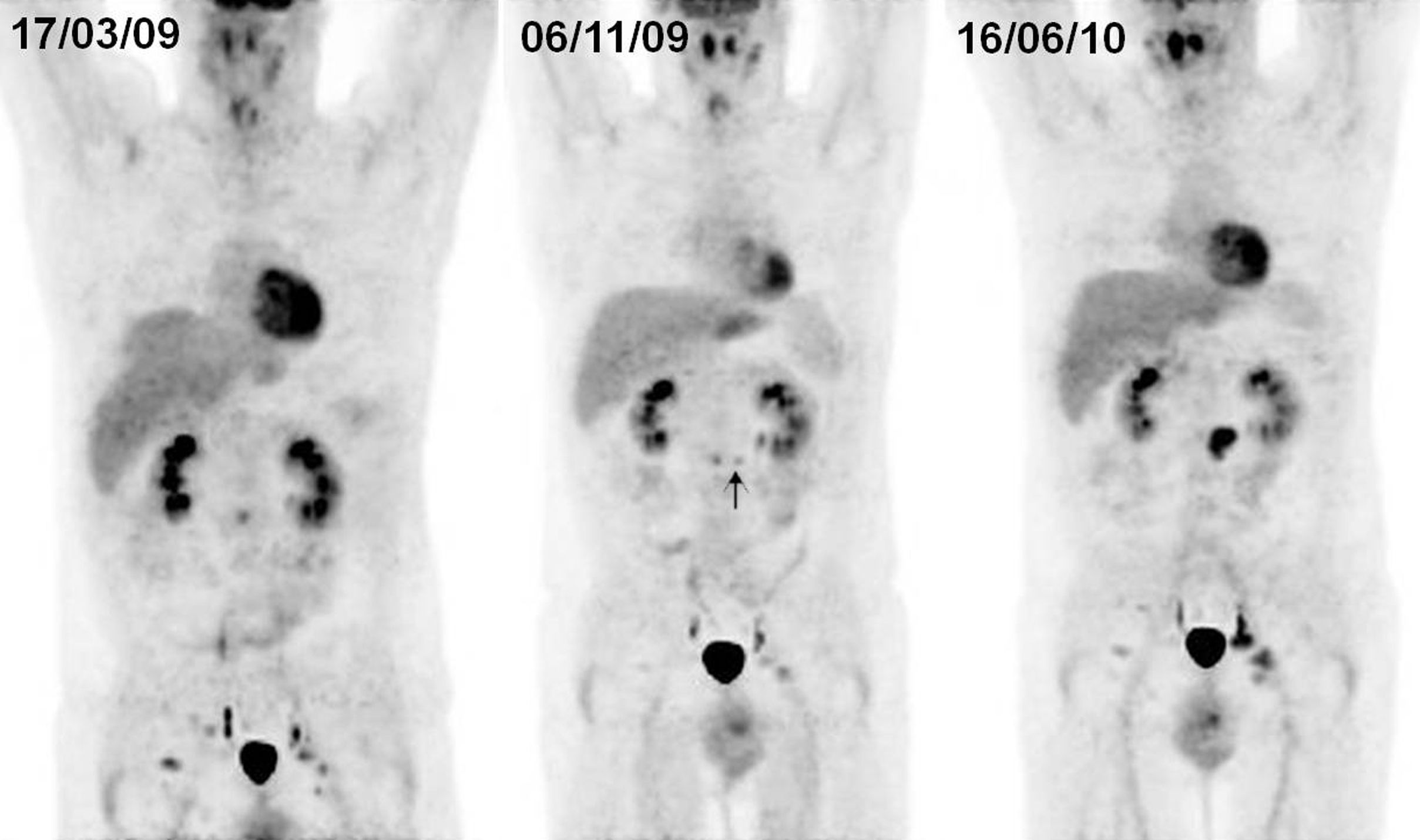
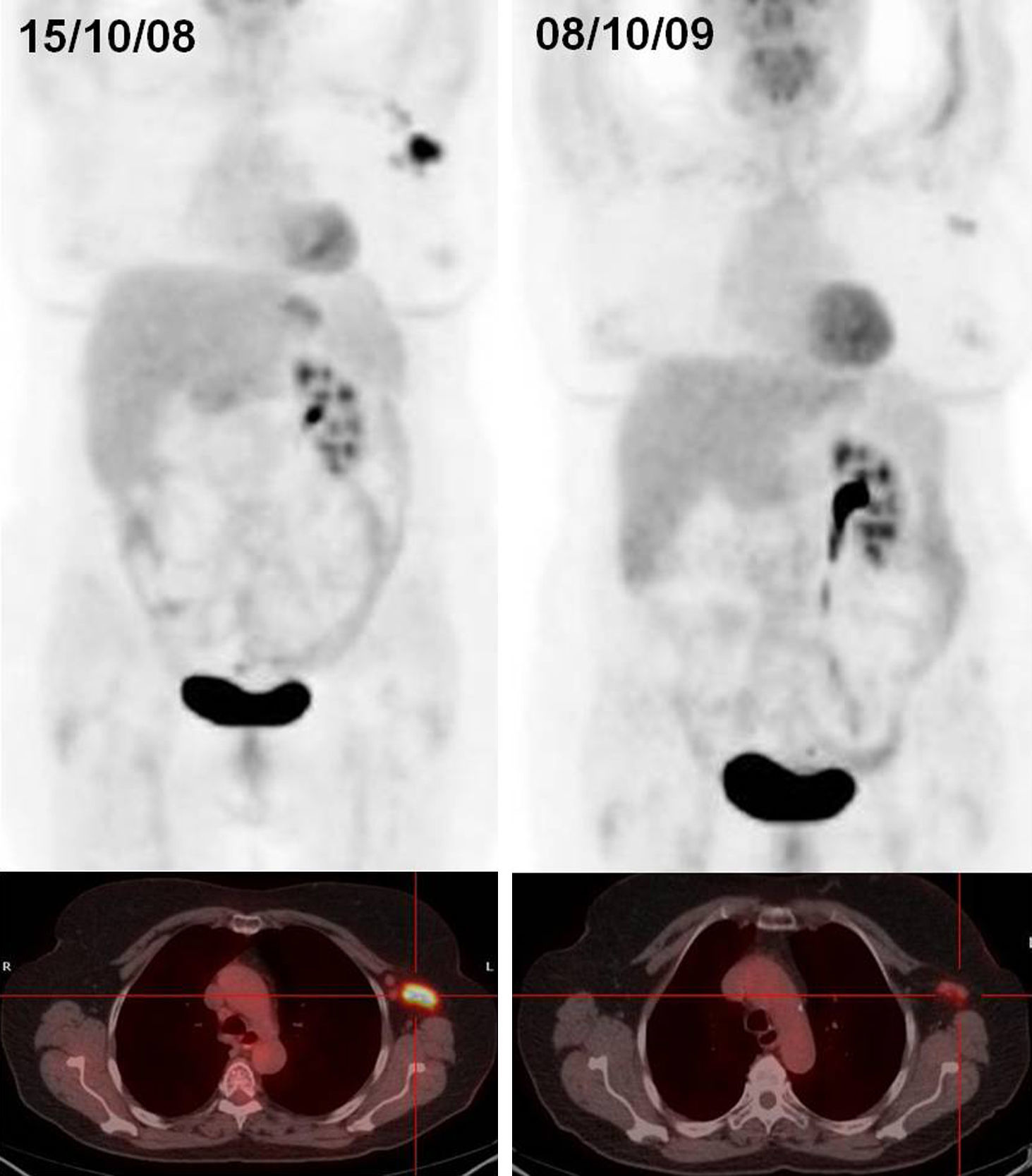
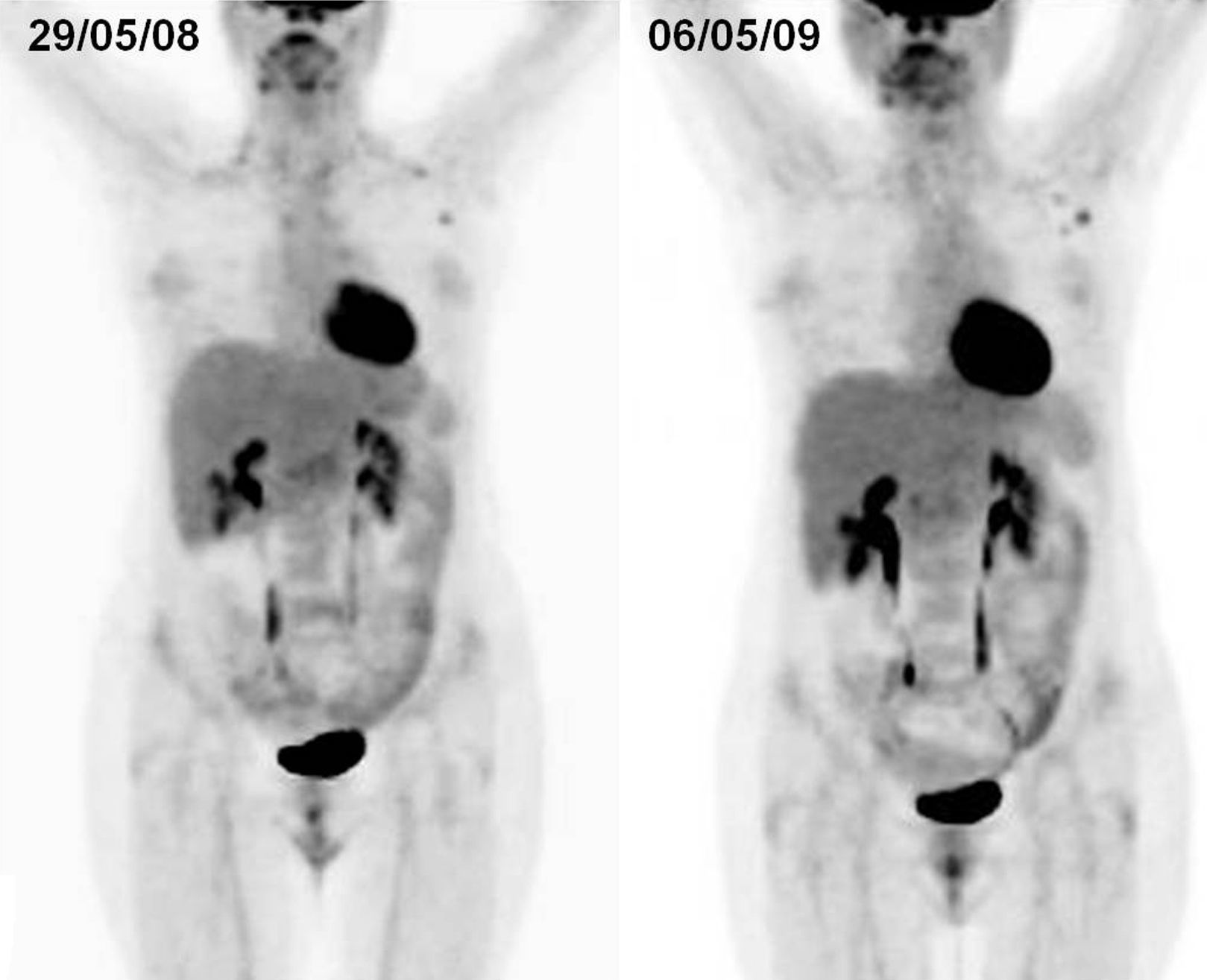
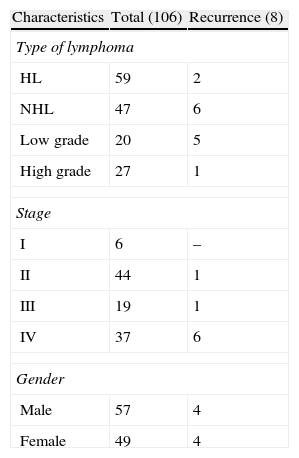
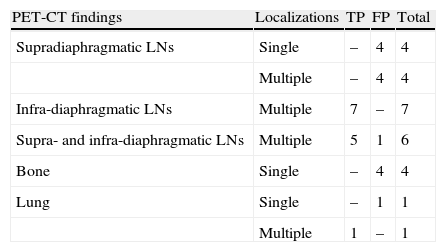
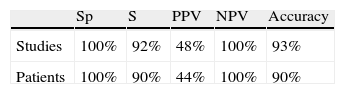
ResultsA total of 199 explorations belonging to 106 patients with lymphoma were included. Of these patients, 59 had Hodgkin's lymphoma and 47 non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. There was suspicion of relapse from the metabolic point of view in 27 of the PET/CT scans. Of these, 14 (10 patients) were false positive (FP), and 13 (8 patients) true positive. The remaining studies were true negative, no false negatives being detected. The pattern most frequently related to recurrence was infradiaphragmatic lymph node involvement while most of the FP had isolated supradiaphragmatic involvement. Sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and diagnostic accuracy of PET/CT parameters for the study were 100%, 92%, 48%, 100% and 93%, respectively.
Conclusion18F-FDG-PET/CT is a sensitive technique in the detection of asymptomatic recurrences in patients with lymphoma during their follow-up. Multiple character and infradiaphragmatic locations were the patterns that best correlated to the diagnosis of recurrence.
Determinar la rentabilidad diagnóstica de la PET-TAC con 18F-FDG en la detección de recidivas asintomáticas en pacientes con linfoma. Definir patrones de captación indicativos de recidiva.
Material y métodosSe incluyeron de forma retrospectiva y longitudinal pacientes afectos de linfoma con los siguientes criterios de inclusión: remisión completa clínica con estudio PET-TAC negativo. Se realizó seguimiento convencional de estos pacientes únicamente mediante PET-TAC con 18F-FDG según técnica estándar. Se analizaron las localizaciones patológicas (supra e infradiafragmáticas) y su carácter (único o múltiple) con vistas a determinar patrones metabólicos fidedignos de recidiva. El diagnóstico final se estableció por análisis histopatológico o seguimiento clínico-radiológico superior a 8 meses.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 199 exploraciones pertenecientes a 106 pacientes, 59 afectos de linfoma de Hodgkin y 47 de linfoma no Hodgkin. Veintisiete estudios fueron indicativos de recidiva desde el punto de vista metabólico. De ellos 14 fueron falsos positivos (FP), 10 pacientes y 13 verdaderos positivos, 8 pacientes. El resto de los estudios fueron verdaderos negativos y no se detectaron falsos negativos. El patrón más frecuentemente relacionado con recidiva fue la afectación adenopática infradiafragmática mientras que la mayoría de los FP poseían afectación supradiafragmática aislada. Los parámetros de sensibilidad, especificidad, VPP, VPN y exactitud diagnóstica por exploración fueron de: 100%, 92%, 48%, 100% y 93% respectivamente.
ConclusiónLa PET-TAC con 18F-FDG es una técnica sensible en la detección de recidivas asintomáticas de pacientes con linfoma durante el seguimiento. El carácter múltiple y las localizaciones infradiafragmáticas fueron los parámetros mejor correlacionados con el diagnóstico de recidiva.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)