To investigate the relationship between maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of ovarian lesions and histopathology subtypes, and their involvement in the response and prognosis of patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma (EOC).
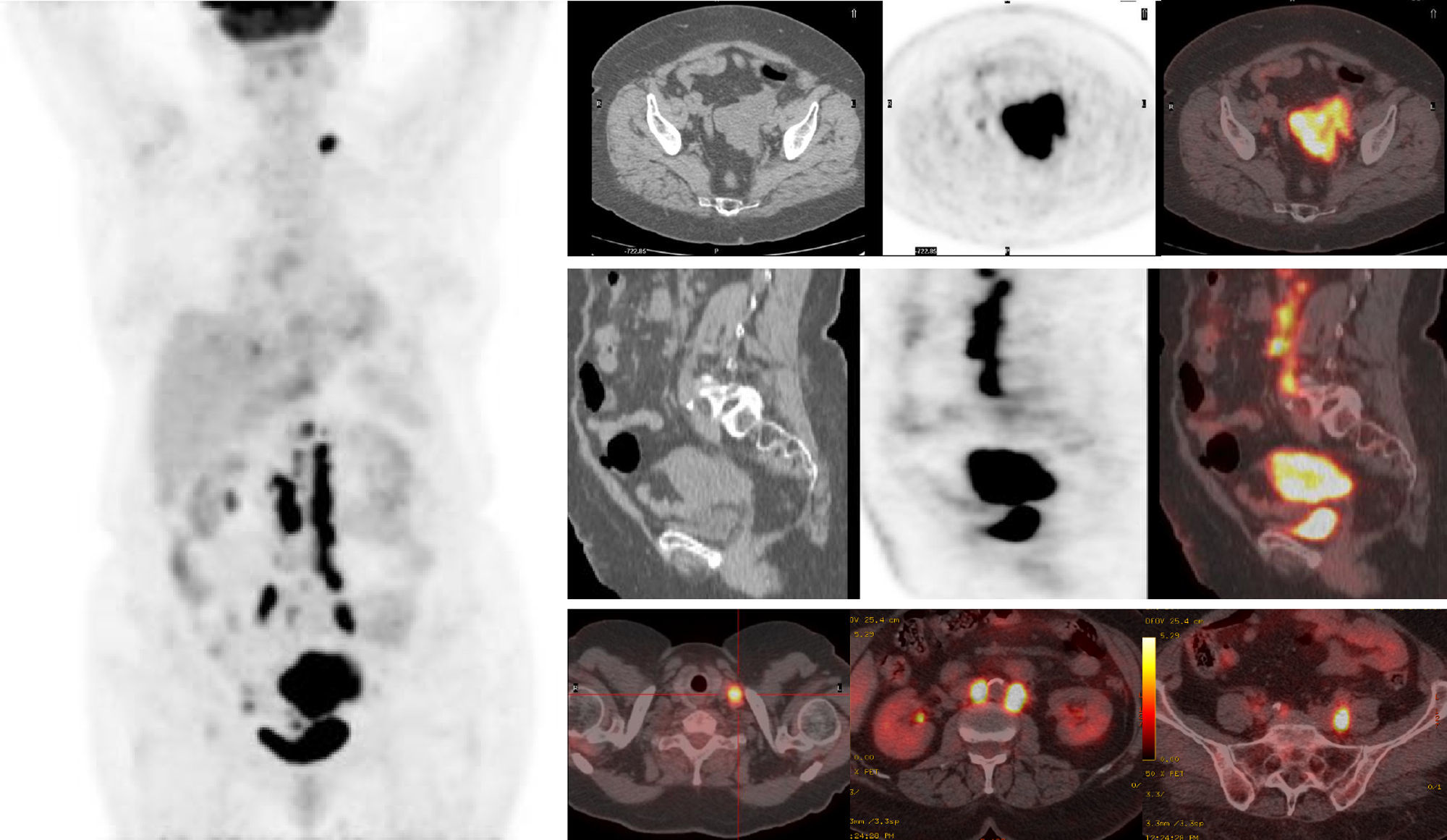
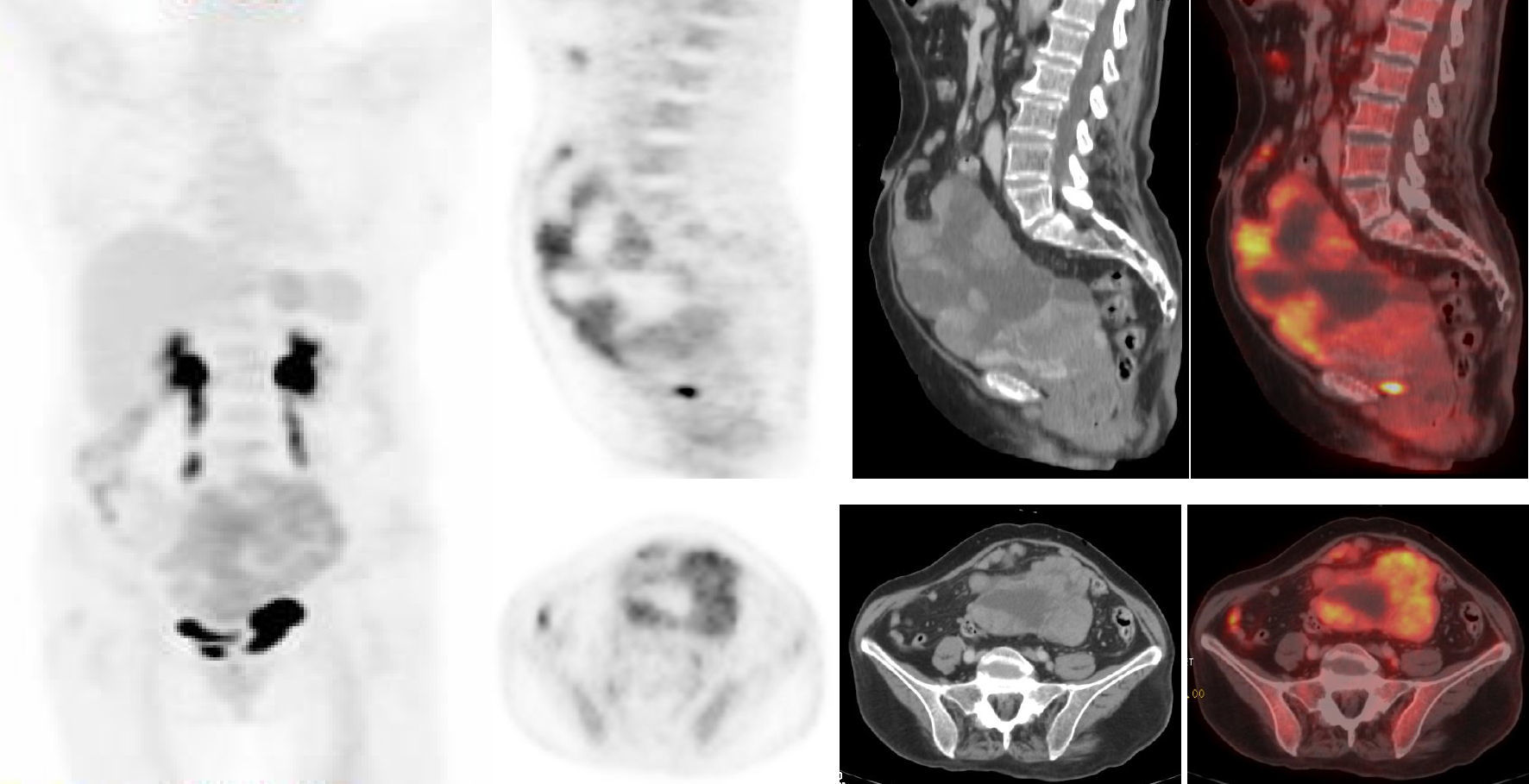
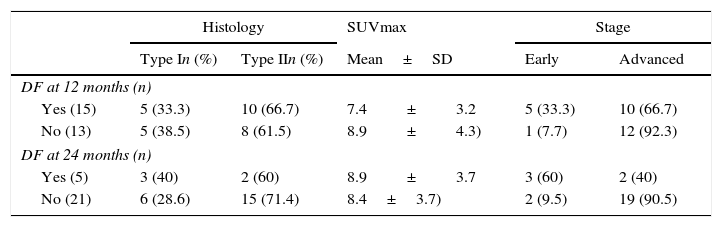
Material and methodsA retrospective analysis of 31 patients with EOC and 18F-FDG PET/CT before treatment, including an assessment of the SUVmax of ovarian lesion. Histopathological diagnosis and follow-up was performed.
A study was made on the relationship between the SUVmax and histological type (type I and II) and tumor stage, as well as the role of various parameters (SUVmax, histology, stage) on the patient outcomes (complete response [CR], overall survival [OS], disease-free survival [DFS], and disease-free [DF] status, at 12 and 24 months).
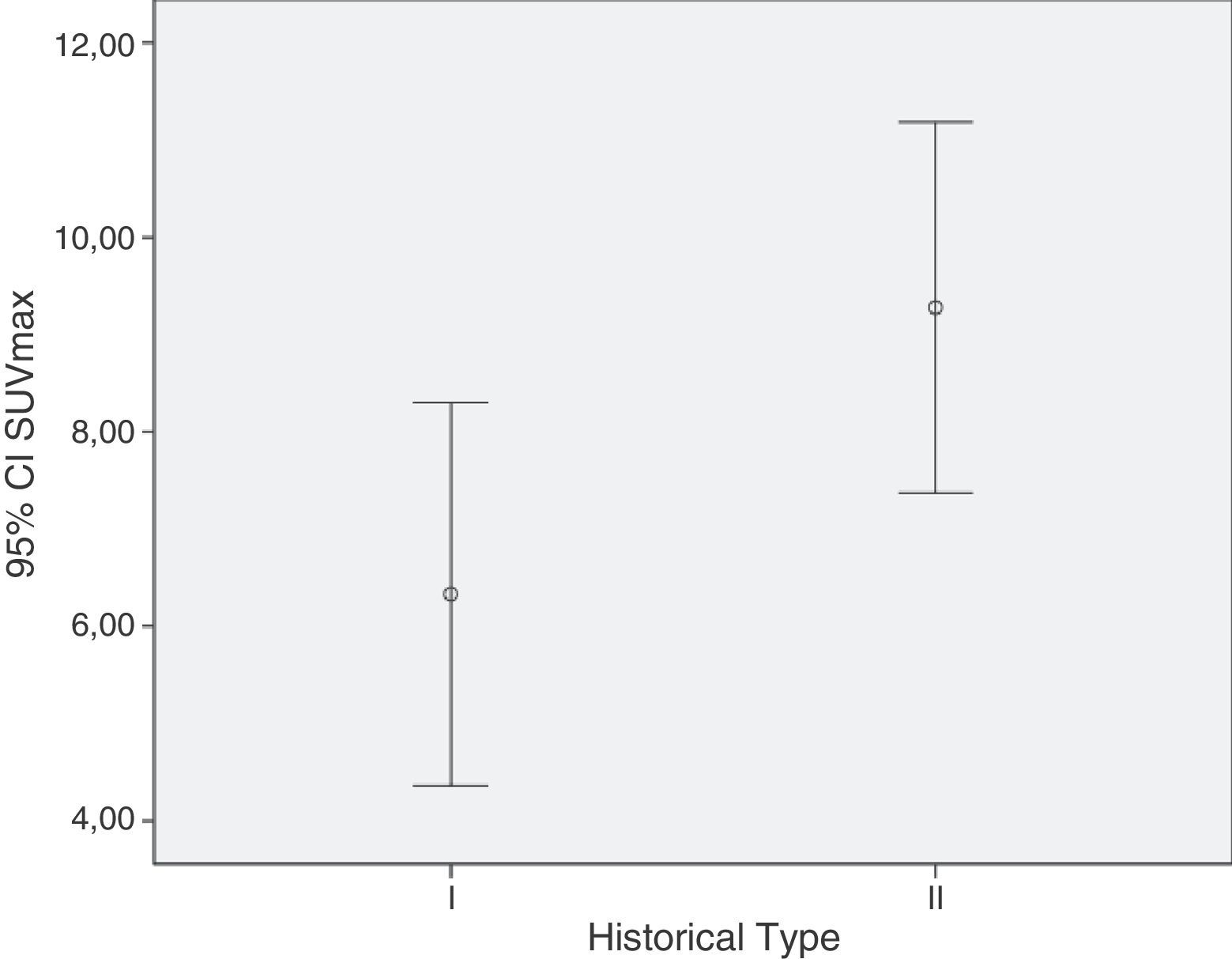
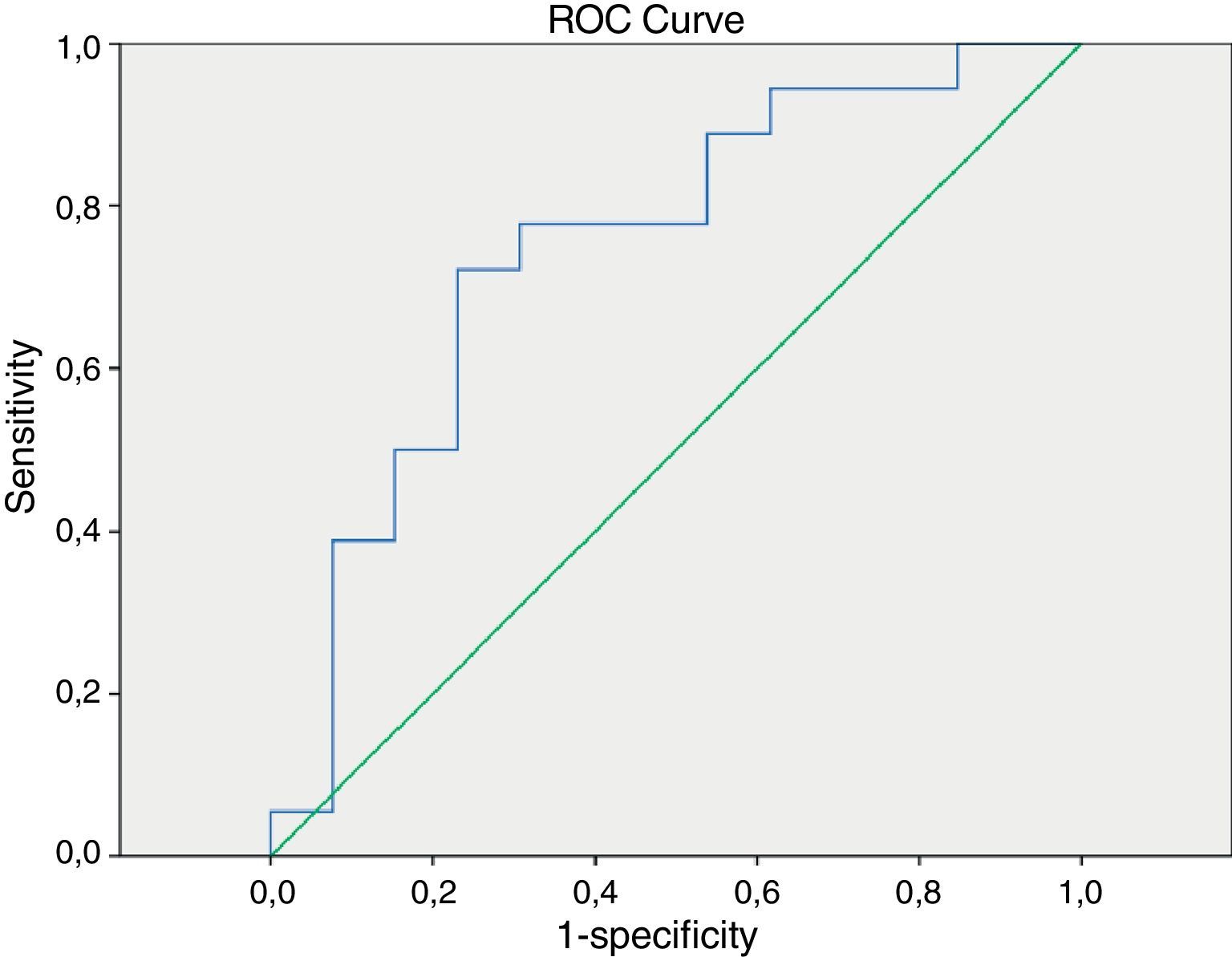
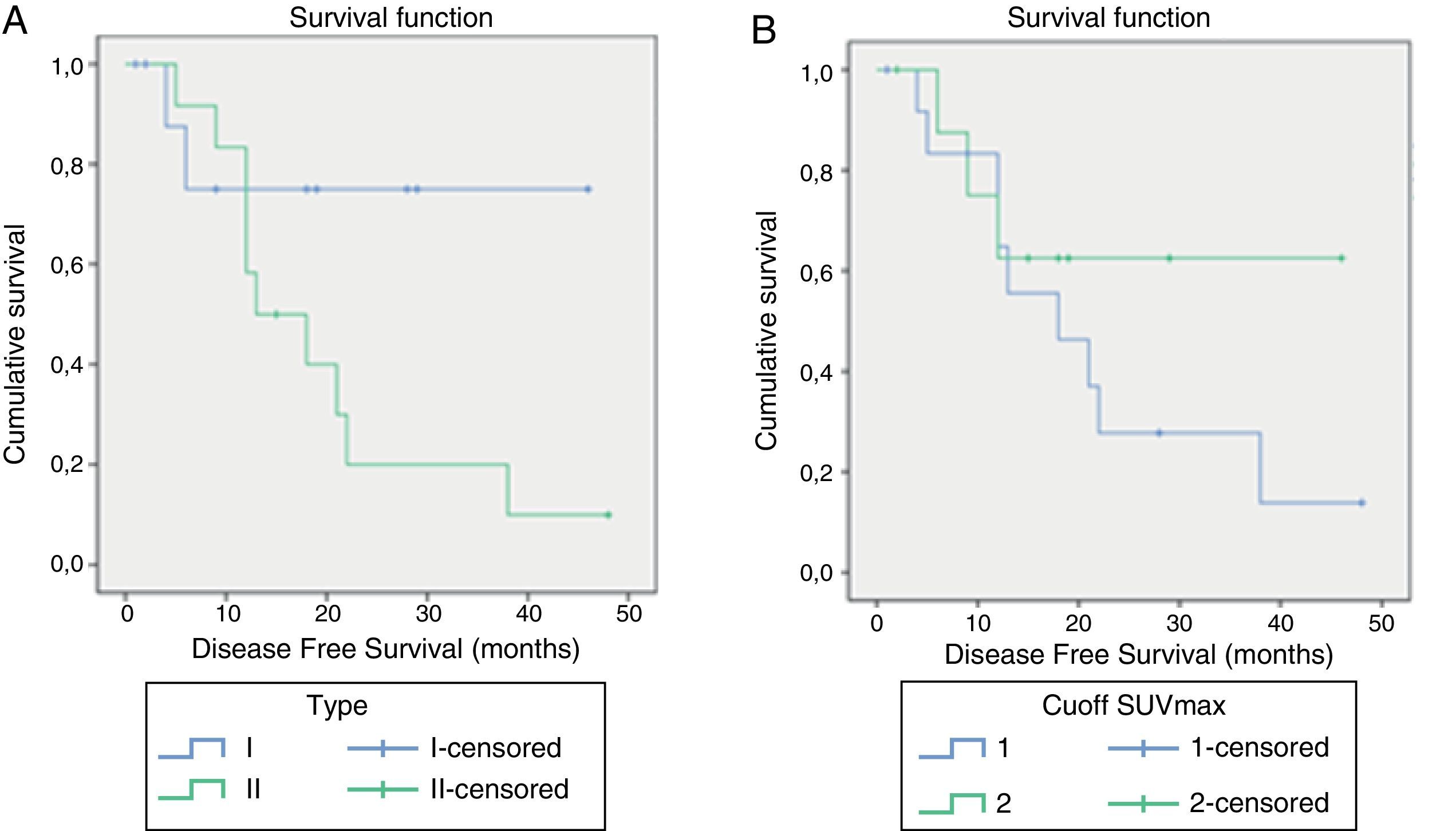
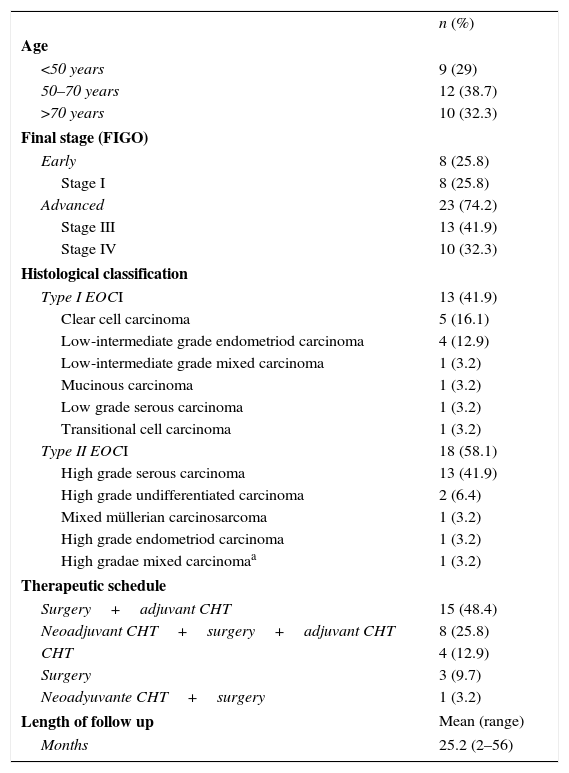
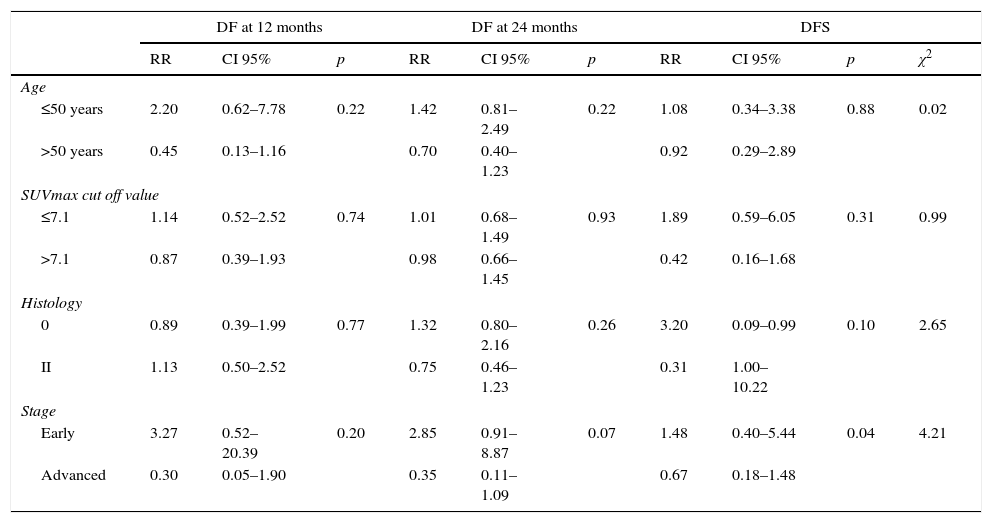
ResultsThe medium SUVmax in type I lesions was lower than in type II (6.3 and 9.3, respectively; p=0.03). A 7.1 cut-off was set for SUVmax in order to identify type II EOC (sensitivity: 77.8%, specificity: 69.2%; AUC=0.748; p=0.02). No significant relationship was found between tumor stage and SUVmax.
CR was more common in early stages; relative risk (RR) of 1.64; p=0.003, as well as in type I tumors and a lower SUVmax.
Tumor stage was decisive in DFS (p=0.04), LE24m (0.07) and OS (p=0.08). Longer DFS and a higher percentage of DF 24m were observed in type I tumors (RR: 1.32; p=0.26).
ConclusionsSUVmax was related to EOC histology, so could predict the response and prognosis of these patients. No association was found between glycolytic activity of the primary tumor with the response and prognosis.
Investigar la relación del valor máximo estandarizado de captación (SUVmáx) de la lesión ovárica con el subtipo histopatológico (I/II) y su implicación en la respuesta al tratamiento y en el pronóstico de las pacientes con carcinoma epitelial de ovario (CEO).
Material y métodosAnálisis retrospectivo de 31 pacientes con CEO y 18F-FDG PET/TC previo al tratamiento, determinándose el SUVmáx de la lesión ovárica y realizándose diagnóstico histopatológico del tumor y seguimiento clínico-radiológico.
Se estudió la relación del SUVmáx con el tipo histológico (tipos I y II) y el estadio tumoral, así como la implicación de este y otros parámetros (histología, estadio) en la evolución de las pacientes (respuesta completa [RC], supervivencia global [SG], supervivencia libre de enfermedad [SLE], estado libre de enfermedad a los 12 meses [LE12m] y a los 24 meses [LE24m]).
ResultadosEl SUVmáx medio en lesiones tipo I fue menor que en las tipo II (6,3 y 9,3, respectivamente; p=0,03). Se obtuvo un valor de corte de SUVmáx de 7,1 en la identificación del CEO tipo II (sensibilidad: 77,8%; especificidad: 69,2%; AUC=0,748; p=0,02). No se halló relación significativa entre SUVmáx y estadio tumoral.
Alcanzar RC fue más frecuente en estadios precoces; riesgo relativo (RR) de 1,64; p=0,003, en tumores tipo I y en los de menor SUVmáx.
El estadio tumoral fue determinante en la SLE (p=0,04), en el LE24m (p=0,07) y en la SG (p=0,08). Observamos SLE más prolongadas y mayor porcentaje de pacientes LE24m en tumores tipo I (RR: 1,32; p=0,26).
ConclusionesEl SUVmáx se relacionó con el tipo histológico del CEO. No se encontró relación entre la actividad glucolítica del tumor primario con la respuesta y el pronóstico.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)