Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare and aggressive neuroendocrine tumor with limited evidence on the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. The aim of this study was to assess the impact of the 18F-FDG PET/CT in the management of MCC.
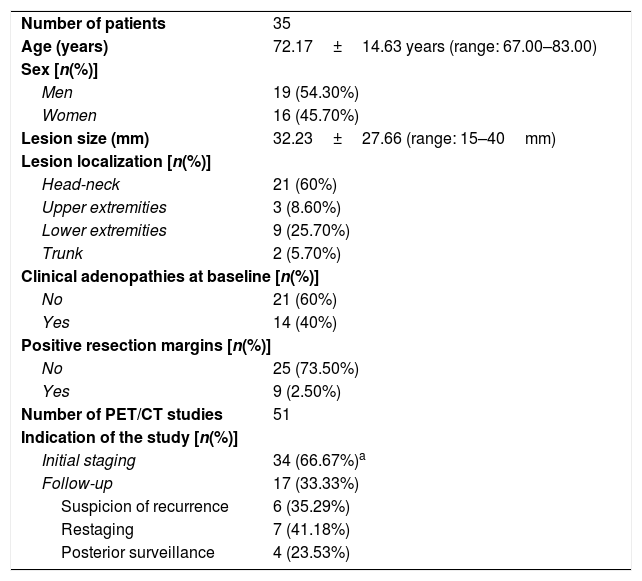
MethodsFifty-one studies of 18F-FDG PET/CT of 35 patients (19 men [54.30%]; 72.17±14.63 years) with histologic diagnosis of MCC were retrospectively evaluated. The change in tumor staging and the impact on the treatment were analysed.
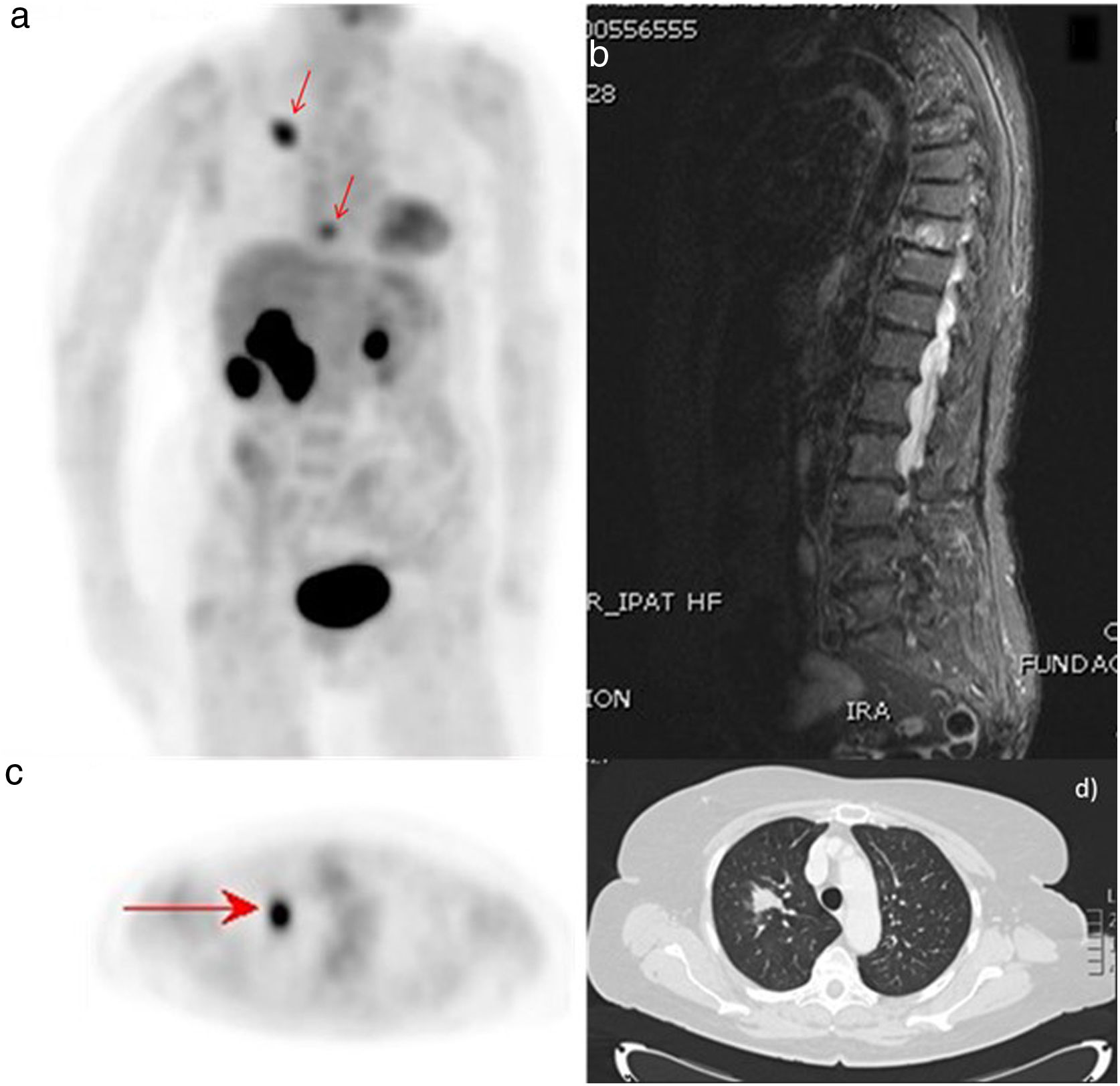
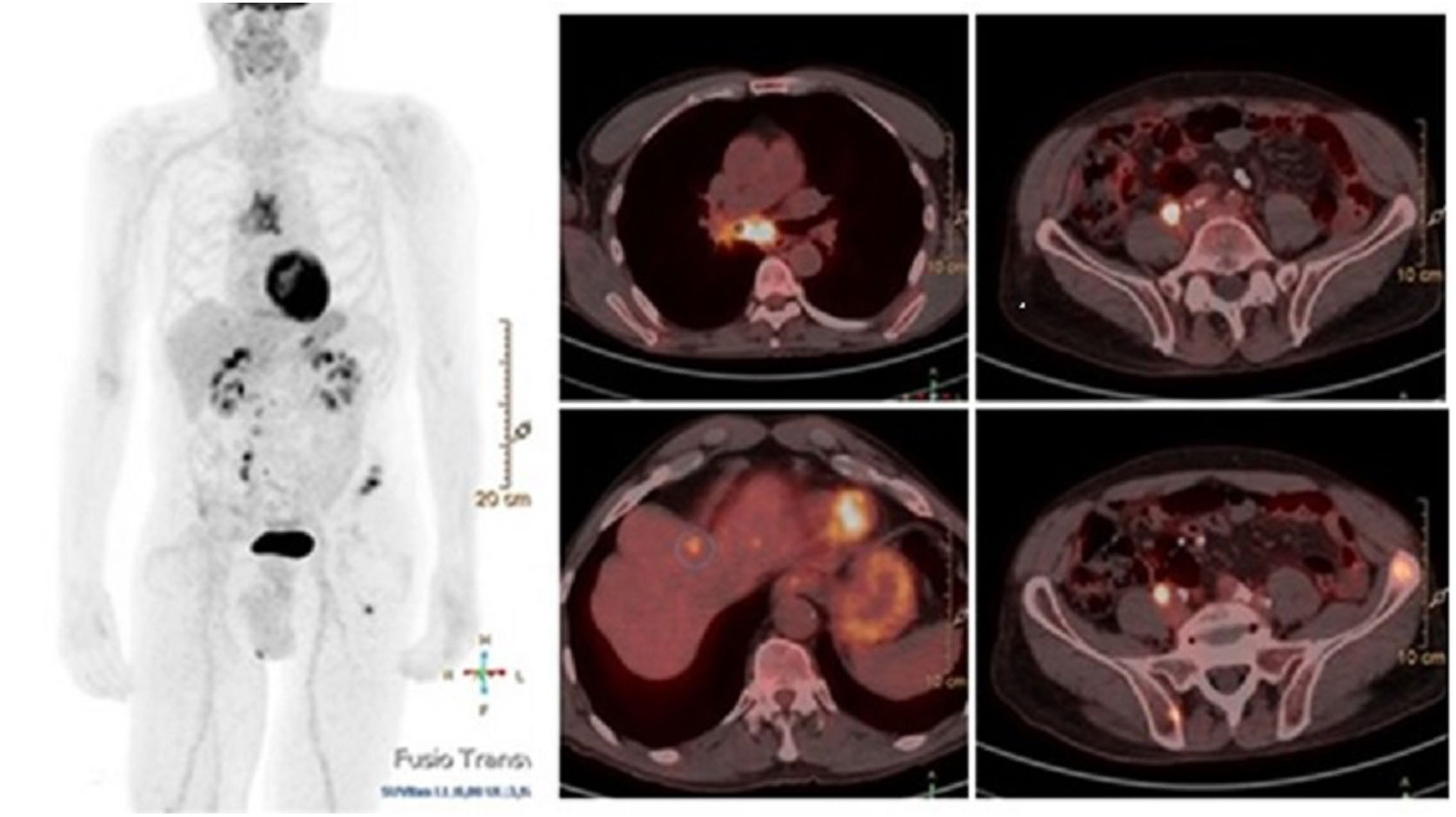
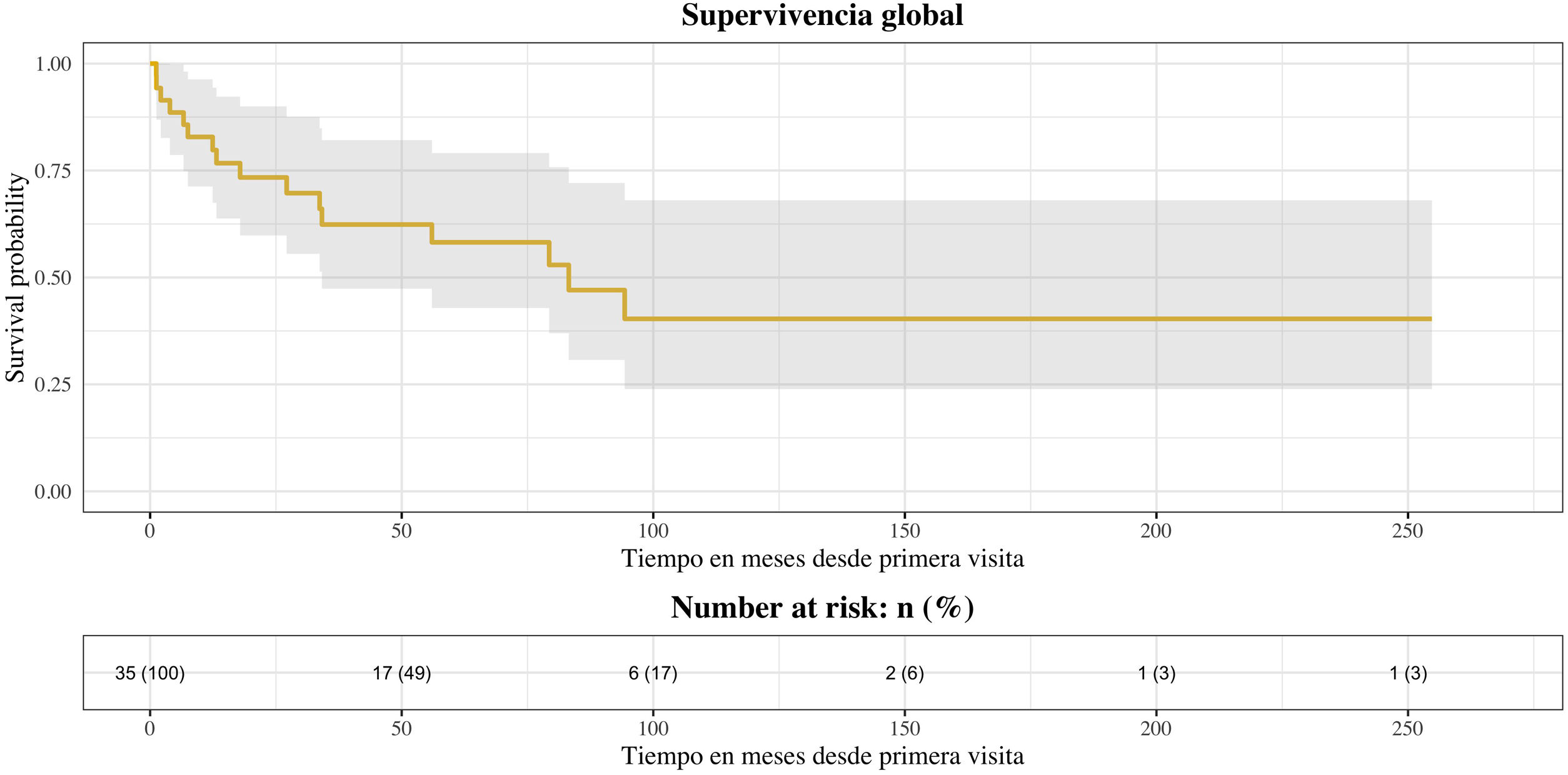
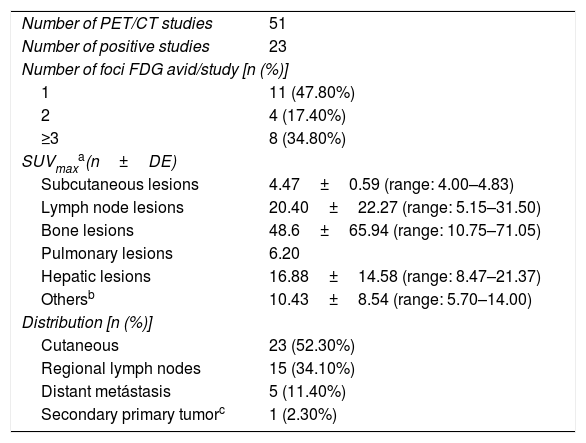
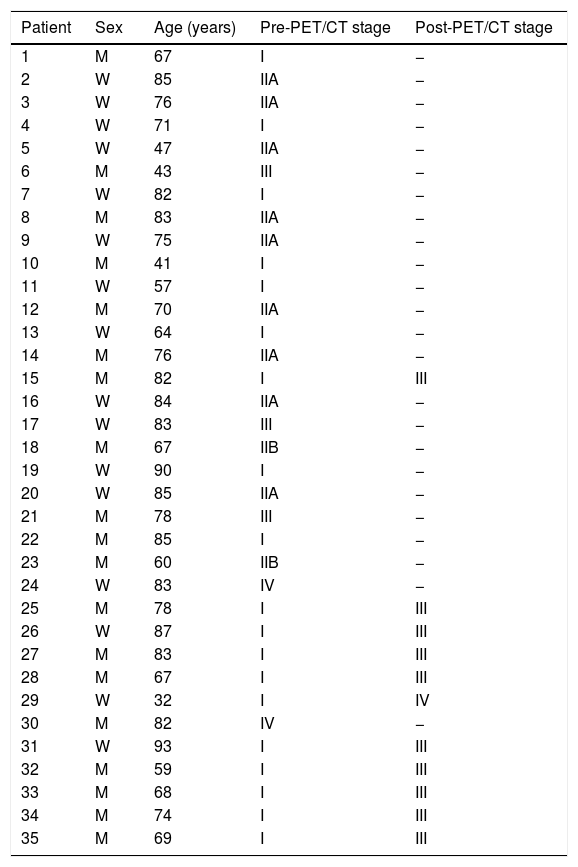
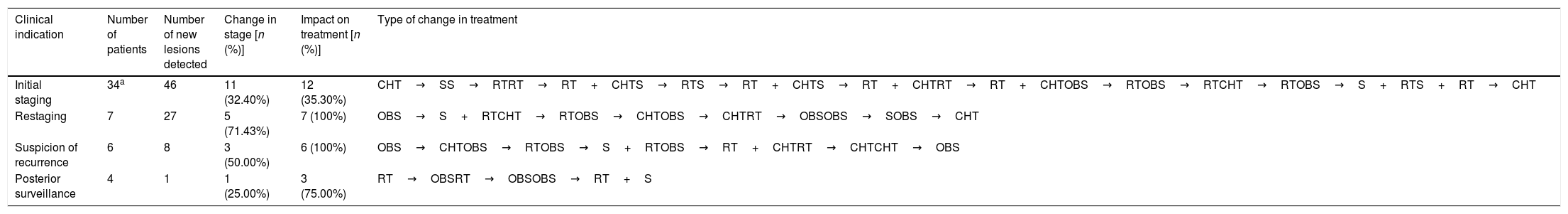
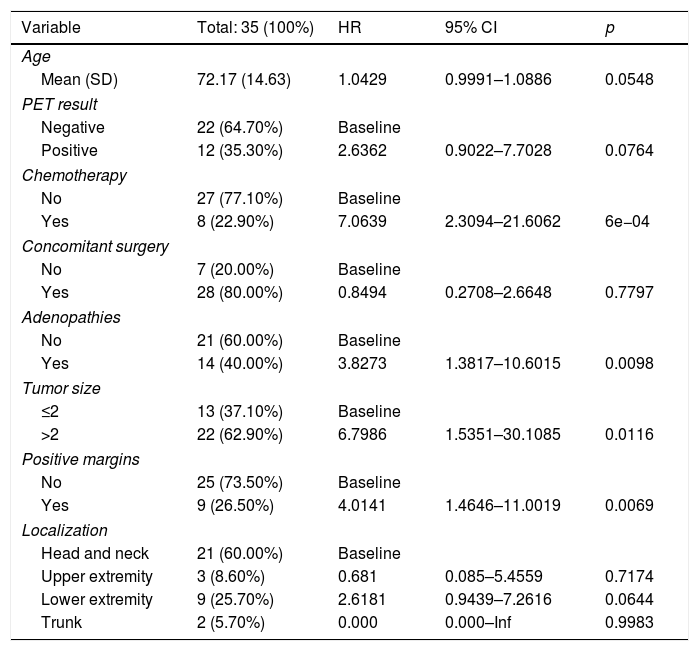
ResultsThere were 23 PET/CT positive studies (45.10%) and 28 (54.90%) negative. Thirty four (66.7%) studies were performed for assessment of stage at initial presentation and 17 (33.3%) were performed during the follow up: 6 (35.29%) for suspected recurrence; 7 (41.18%) for restaging; 4 (23.53%) as a part of ongoing surveillance. On the basis of PET/CT results, there was a change in disease stage (SC) in 20 studies (39.20%) and impact in the management (MI) in 28 (54.90%): 11 (32.40%) SC and 12 (35.30%) MI in the initial staging; 5 (71.43%) SC and 7 (100%) MI in the restaging; 3 (50%) SC and 6 (100%) MI in suspected recurrence; 1 (25%) SC and 3 (75%) MI in the surveillance. 18F-FDG PET/CT incidentally detected one additional histologically confirmed cancer. The presence of nodal involvement in the beginning (0.0098; HR 3.82; 95% CI: 1.38–10.6), chemotherapy treatment (6e−04; HR 7.06; 95% CI: 2.30–21.60), size of primary tumor >2cm (6e−04; HR 7.06; 95% CI: 2.30–21.60) and positive resection margin (0.00069; HR 4.01; 95% CI: 1.46–11.00) were statistically significant prognostic factors for overall survival. There was a trend towards significance for worse overall survival with initial positive 18F-FDG PET/CT but the trend did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusion18F-FDG PET/CT altered the stage in 2 out of 5 studies and changed the treatment in more than half of the studies performed. The study confirms the important impact of 18F-FDG PET/CT on the management of MCC patients.
El carcinoma de células de Merkel (CCM) es un raro y agresivo tumor neuroendocrino en el que existe poca evidencia del papel de la 18F-FDG PET/TC. El objetivo del estudio es evaluar el impacto de 18F-FDG PET/TC en el manejo de estos pacientes.
Material y métodoEvaluamos retrospectivamente 51 estudios 18F-FDG PET/TC de 35 pacientes (19 hombres [54,30%], de 72,17±14,63años) con histología de CCM. Se analiza el cambio en el estadio (CE) y el impacto en el tratamiento (IT).
ResultadosHubo 23 estudios PET/TC positivos (45,10%) y 28 (54,90%) negativos. Treinta y cuatro (66,7%) estudios se realizaron para estadificación inicial y 17 (33,3%) se hicieron en el seguimiento: 6 (35,29%) por sospecha de recurrencia, 7 (41,18%) para reestadificación y 4 (23,53%) como parte de la vigilancia posterior. En base a los resultados PET/TC hubo CE en 20 estudios (39,20%) e IT en 28 (54,90%): en la estadificación inicial CE en 11 (32,40%) e IT en 12 (35,30%); en la reestadificación CE en 5 (71,43%) e IT en 7 (100%); en la sospecha de recurrencia CE en 3 (50%) e IT en 6 (100%); en la vigilancia posterior CE en 1 (25%) e IT en 3 (75%). La PET/TC incidentalmente detectó un cáncer adicional confirmado histológicamente. La presencia de adenopatías clínicas al inicio (0,0098; HR 3,82; IC 95%: 1,38-10,6), el haber recibido tratamiento quimioterápico (6e−04; HR 7,06; IC 95%: 2,30-21,60), un tamaño tumoral ≥2cm (0,0116; HR 6,79; IC 95%: 1,53-30,10) y la presencia de márgenes positivos (0,00069; HR 4,01; IC 95%: 1,46-11,00) fueron factores pronósticos estadísticamente significativos para la supervivencia global. Se observa una tendencia a peor supervivencia global con una PET/TC positiva al inicio pero sin alcanzar la significación estadística.
ConclusionesLa 18F-FDG PET/TC alteró el estadio en 2 de cada 5 estudios y cambió el tratamiento en más de la mitad de los estudios realizados. El estudio confirma el importante impacto de la 18F-FDG PET/TC en el manejo de los estos pacientes.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)