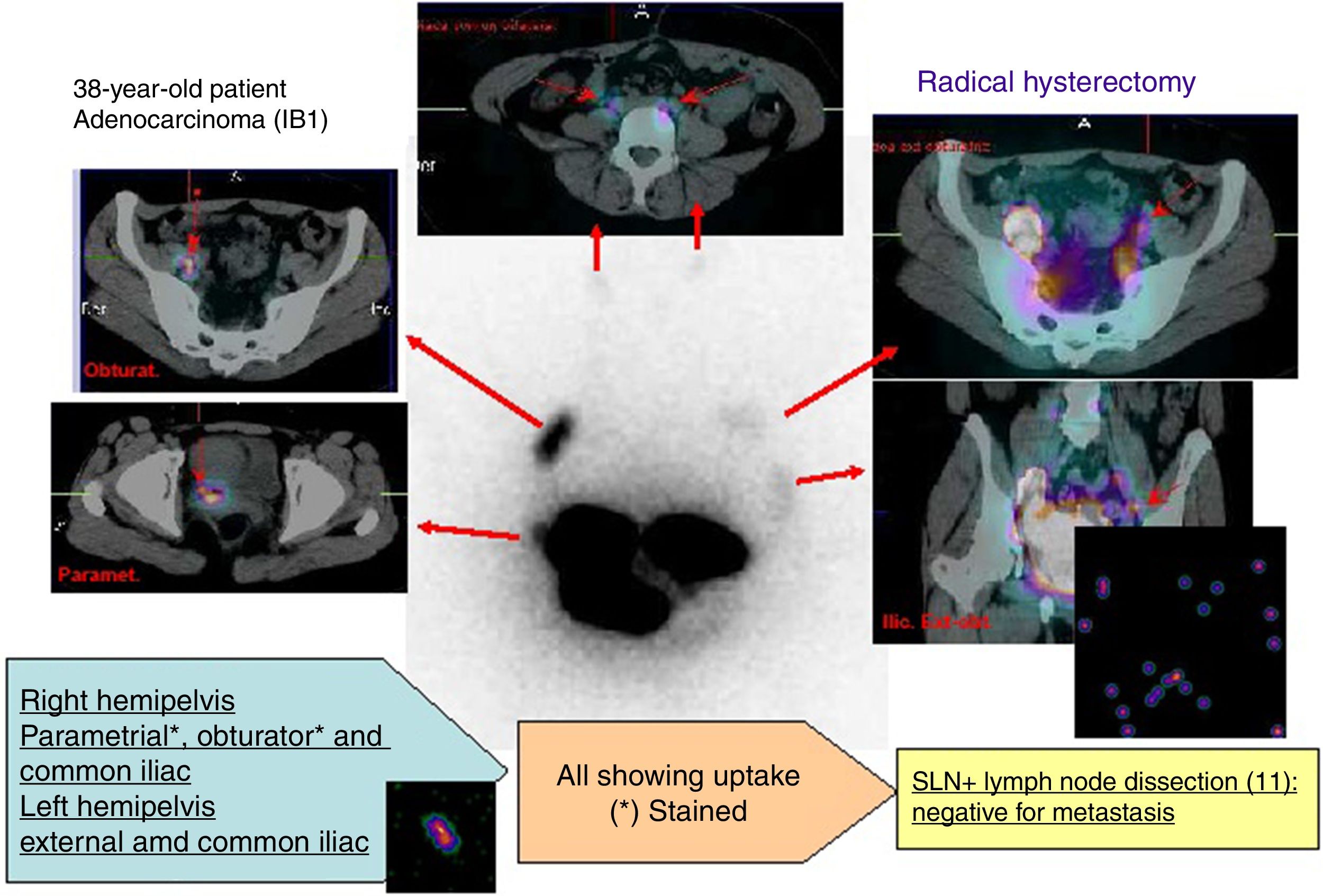
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) was created to reduce the morbidity associated with pelvic lymphadenectomy in the early stages of cervical cancer (CC), preserving its prognostic information. The goal is to assess the diagnostic validity of SLNB in CC in initial stages (IA1 with lymphovascular infiltration (LVI)+, IA2, IB1 and IIA1), thus avoiding unnecessary lymphadenectomies in many of the cases.
Material and methodFrom January 2012 to April 2017, 23 patients with initial stages of CC were included in a cross-sectional study to evaluate the effectiveness of the SLNB in CC with a mixed technique of cervical injection of 99mTc-nanocolloid of albumin and methylene blue, using combined planar lymphoscintigraphy with multimodality SPECT/CT image and subsequent removal of the sentinel node (SN) by laparoscopy.
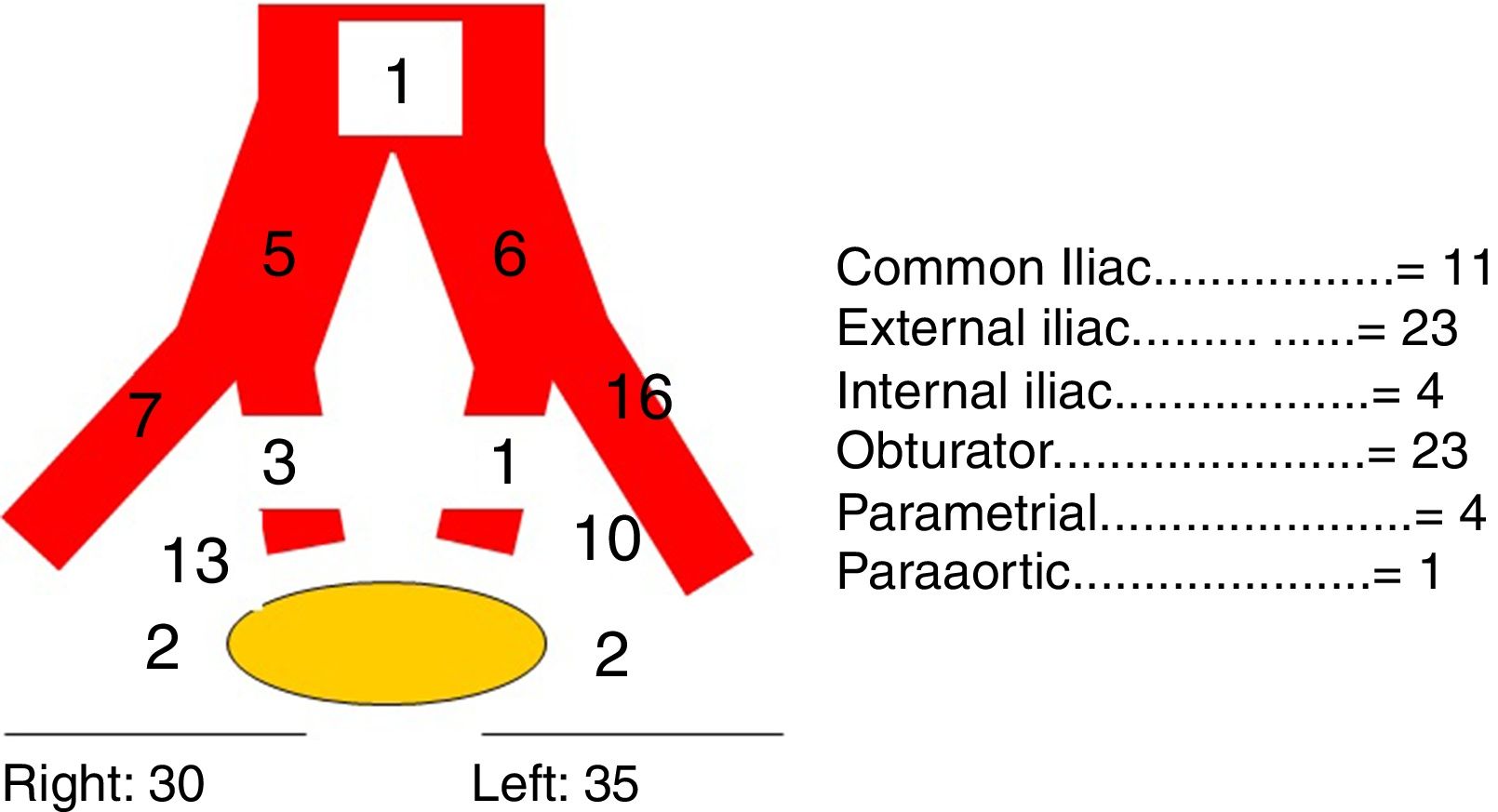
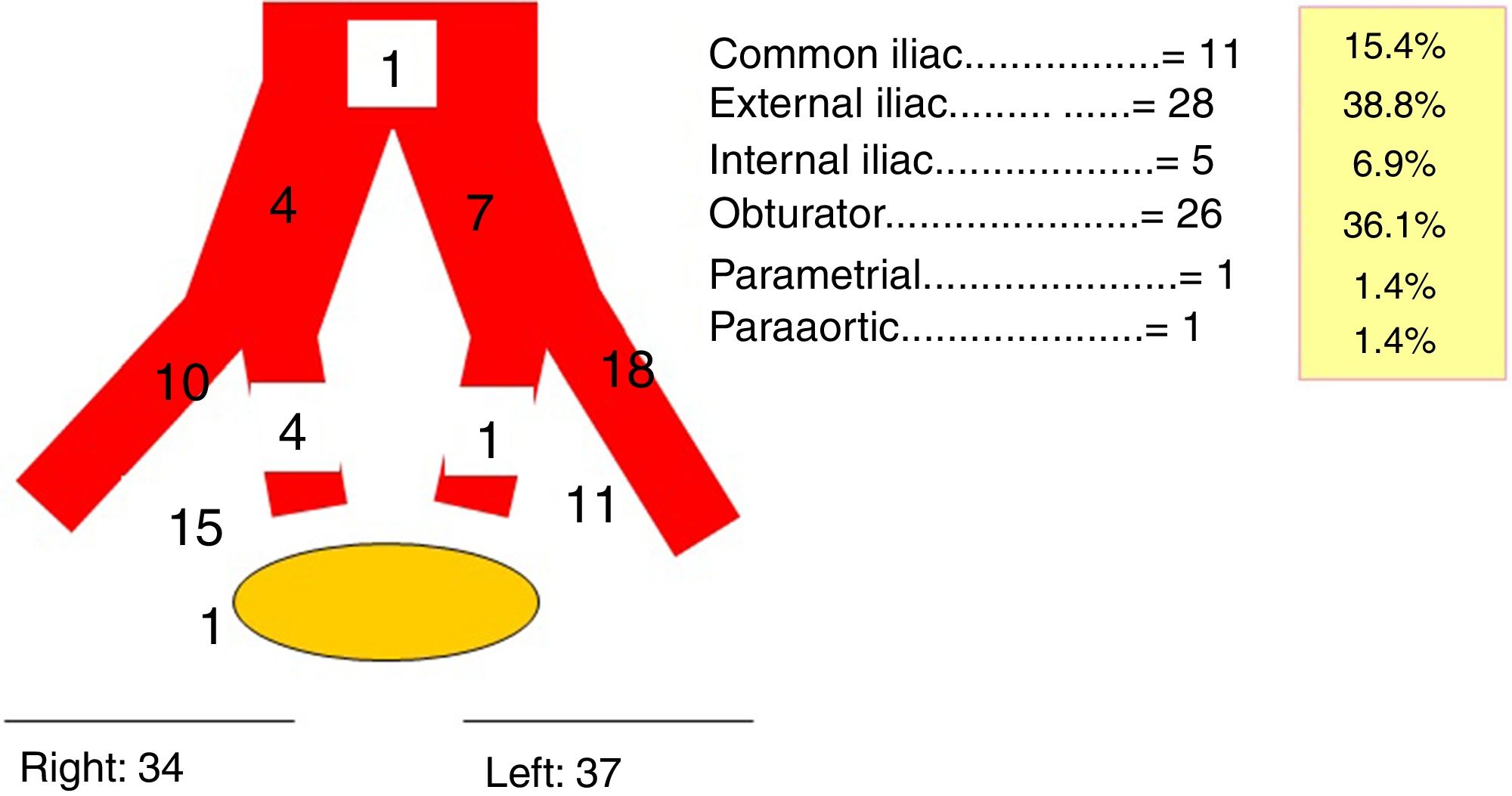
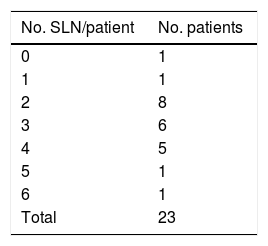
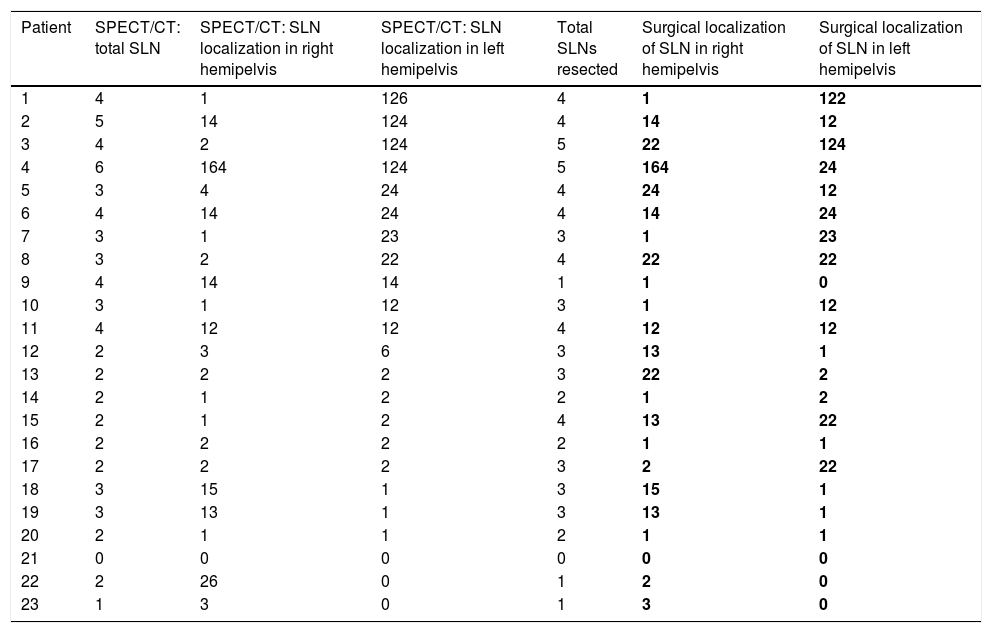
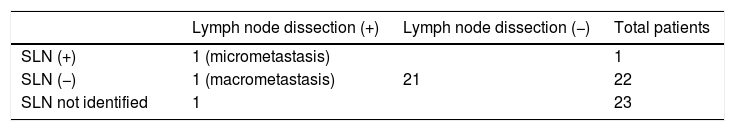
ResultsThe detection rate of SLNB with the mixed technique was 95.65%, with a negative predictive value (NPV) of 95.45% and sensitivity (S) of 100% in the case of bilateral drainage. The mean of excised SN was 3 (range 1–5). The bilateral detection rate in laparoscopy was 85.35%. The concordance between SPECT/CT and laparoscopy for the number and bilaterality of the SN using the Pearson coefficient was r=0.727 and r=0.833, respectively; p=0.01. We only found one SN with a deferred result of micrometastasis and one false negative was detected.
ConclusionsSLNB in CC using a mixed technique has a high detection and bilateral drainage rate, but S is still low if we include cases of unilateral drainage. A greater number of cases and the development of intraoperative ultrastaging could increase the S of the technique and to reduce the number of false negatives.
La biopsia selectiva del ganglio centinela (BSGC) surgió para disminuir la morbilidad asociada a la linfadenectomía pélvica en estadios iniciales del cáncer cervical (CC), conservando la información pronóstica obtenida de ella. El objetivo es determinar la validez diagnóstica de la BSGC en CC en estadios iniciales (IA1 con infiltración linfovascular [ILV]+, IA2, IB1 y IIA1), evitando así linfadenectomías innecesarias en muchos de los casos.
Material y métodoDesde enero del 2012 hasta abril del 2017, 23 pacientes con estadios iniciales de CC fueron incluidas en un estudio transversal de evaluación de la eficacia de la BSGC usando la técnica mixta de inyección cervical de 99mTc-nanocoloide de albúmina y azul de metileno, empleando linfogammagrafía planar combinada con imagen multimodalidad SPECT/TC y posterior extirpación del GC mediante laparoscopia.
ResultadosLa tasa de detección de la BSGC con técnica mixta fue del 95,6%, siendo el valor predictivo negativo (VPN) del 95,4% y la sensibilidad (S) del 100% en caso de drenaje bilateral. La media de GC extirpados fue de 3 (rango 1-5). La tasa de detección bilateral en la laparoscopia fue del 85,3%. La concordancia entre SPECT/TC y laparoscopia para el número y bilateralidad del GC mediante el coeficiente de Pearson fue r=0,73 y r=0,83, respectivamente; p=0,01. Solo encontramos un GC con resultado diferido de micrometástasis y se detectó un falso negativo.
ConclusionesLa BSGC en CC mediante técnica mixta tiene una elevada tasa de detección y de drenaje bilateral, pero aún la S es baja si incluimos casos de drenaje unilateral. Un mayor número de casos y el desarrollo de la ultraestadificación intraoperatoria podrían aumentar la S de la técnica y reducir el número de falsos negativos.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)